Open source tools offer transparency, customization, and community-driven support, allowing users to modify and distribute the software freely. Proprietary tools provide dedicated customer service, consistent updates, and specialized features tailored to specific business needs but often come with licensing fees and restricted access to the source code. Choosing between these options depends on priorities like cost, flexibility, security, and long-term scalability.
Table of Comparison
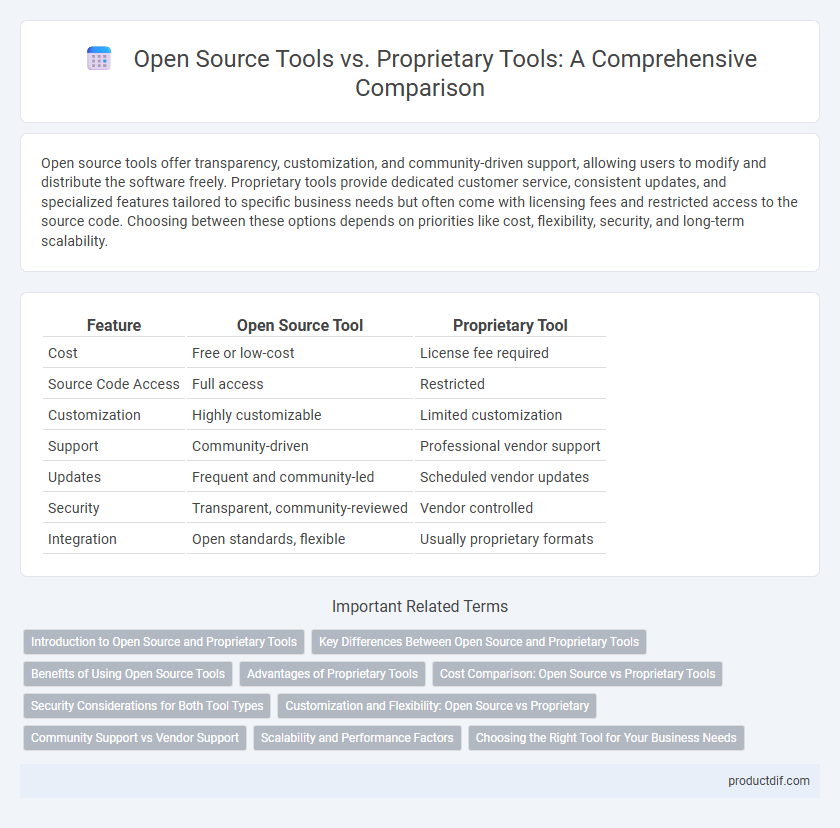
| Feature | Open Source Tool | Proprietary Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free or low-cost | License fee required |
| Source Code Access | Full access | Restricted |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Limited customization |
| Support | Community-driven | Professional vendor support |
| Updates | Frequent and community-led | Scheduled vendor updates |
| Security | Transparent, community-reviewed | Vendor controlled |
| Integration | Open standards, flexible | Usually proprietary formats |
Introduction to Open Source and Proprietary Tools
Open source tools provide access to their source code, enabling users to modify, distribute, and customize software freely, which fosters collaboration and innovation. Proprietary tools, in contrast, are developed and maintained by companies that restrict access to the source code, offering controlled features and customer support through licensing agreements. Understanding the fundamental differences in access, flexibility, and cost structure helps organizations choose the appropriate tool for their specific needs.
Key Differences Between Open Source and Proprietary Tools
Open source tools provide users with access to the source code, enabling customization, transparency, and community-driven development. Proprietary tools are developed and maintained by specific companies, offering dedicated support, regular updates, and restricted access to the underlying code. Key differences include licensing models, cost structures, flexibility, and security controls, influencing adoption decisions in various business environments.
Benefits of Using Open Source Tools
Open source tools provide greater flexibility and customization options, enabling developers to modify and adapt the software to specific project needs without licensing restrictions. They foster collaboration and innovation through community-driven development, ensuring continuous updates, bug fixes, and security improvements. Reduced costs and transparency further enhance their appeal by eliminating expensive licensing fees and allowing users to inspect the source code for vulnerabilities.
Advantages of Proprietary Tools
Proprietary tools offer robust customer support and regular updates, ensuring seamless integration and enhanced security for enterprise environments. These tools often provide specialized features tailored to industry standards, delivering higher reliability and performance compared to open source alternatives. Access to dedicated development teams enables faster issue resolution and customized solutions, maximizing business efficiency and reducing downtime.
Cost Comparison: Open Source vs Proprietary Tools
Open source tools often reduce upfront costs by eliminating licensing fees, making them more accessible for startups and small businesses. Proprietary tools generally involve higher expenses due to licensing, subscription, and ongoing support fees, which can strain budgets over time. Total cost of ownership for open source tools can increase with custom development and maintenance, whereas proprietary tools may offer integrated support that offsets those costs.
Security Considerations for Both Tool Types
Open source tools often benefit from transparent code reviews that enable rapid identification and patching of security vulnerabilities by the global developer community, enhancing trust and reliability. Proprietary tools rely on internal security audits and controlled access, which may limit exposure to external threats but can delay vulnerability detection and patch deployment. Evaluating security considerations between open source and proprietary tools requires assessing factors like code transparency, update frequency, vendor reputation, and community responsiveness.
Customization and Flexibility: Open Source vs Proprietary
Open source tools offer extensive customization and flexibility due to their accessible source code, allowing developers to modify and tailor the software to specific needs. Proprietary tools typically have limited customization options, as their source code is closed and modifications depend on vendor updates or permissions. This distinction makes open source solutions more adaptable in dynamic environments, while proprietary tools often provide standardized features with less variability.
Community Support vs Vendor Support
Open source tools benefit from vibrant communities that offer extensive peer-to-peer support, continuous updates, and collaborative problem-solving, ensuring rapid innovation and flexibility. Proprietary tools provide vendor-backed support that delivers structured, official troubleshooting, service-level agreements, and consistent updates tailored to business requirements. Community-driven forums and documentation enhance open source adaptability, while vendor support ensures reliability and accountability for proprietary solutions.
Scalability and Performance Factors
Open source tools offer scalable solutions with customizable performance optimizations, allowing organizations to tailor system resources and workflows to specific needs without licensing constraints. Proprietary tools often provide out-of-the-box high performance supported by dedicated development teams but may face limitations in scalability due to fixed architecture and licensing models. Evaluating scalability in terms of horizontal scaling capabilities and performance factors like latency, throughput, and resource efficiency is critical when choosing between open source and proprietary tools.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Business Needs
Selecting between open source tools and proprietary tools depends on your business's need for customization, scalability, and support. Open source tools offer flexibility, community-driven innovation, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for businesses with technical expertise and evolving requirements. Proprietary tools provide dedicated customer support, regular updates, and enhanced security features, suited for organizations prioritizing reliability and vendor accountability.
Open Source Tool vs Proprietary Tool Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com