Cutting tools are designed to shape or remove material from a workpiece through processes like slicing, grinding, or drilling, enabling precise alterations to size or form. Measuring tools, on the other hand, are used to assess dimensions, angles, and tolerances, ensuring components meet specified standards for accuracy and consistency. While cutting tools transform material, measuring tools provide critical feedback to guide and verify the cutting process.
Table of Comparison
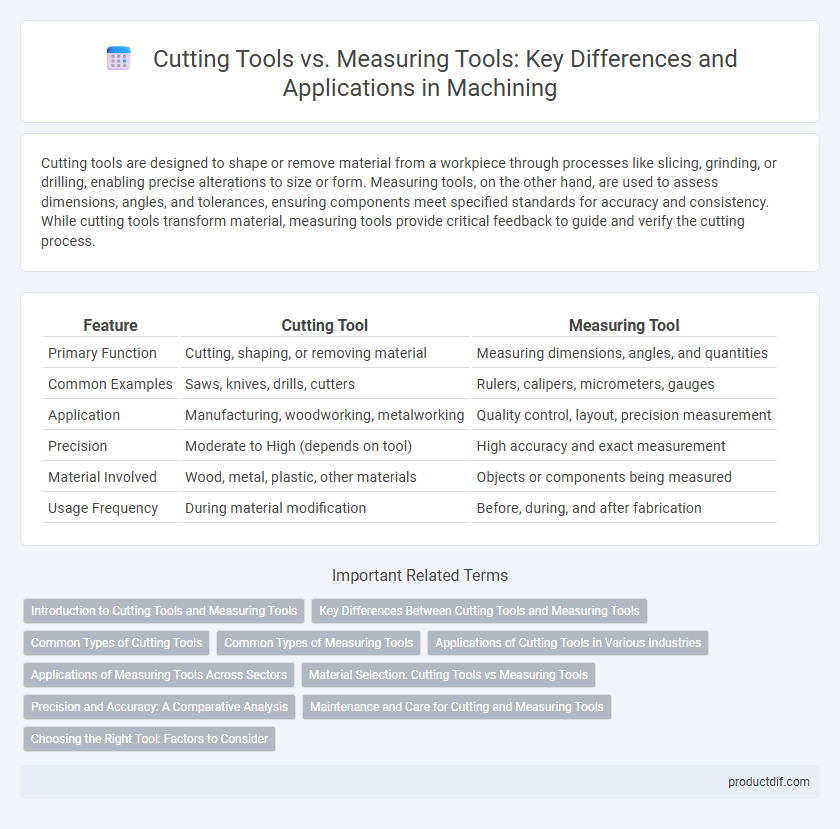
| Feature | Cutting Tool | Measuring Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Cutting, shaping, or removing material | Measuring dimensions, angles, and quantities |
| Common Examples | Saws, knives, drills, cutters | Rulers, calipers, micrometers, gauges |
| Application | Manufacturing, woodworking, metalworking | Quality control, layout, precision measurement |
| Precision | Moderate to High (depends on tool) | High accuracy and exact measurement |
| Material Involved | Wood, metal, plastic, other materials | Objects or components being measured |
| Usage Frequency | During material modification | Before, during, and after fabrication |
Introduction to Cutting Tools and Measuring Tools
Cutting tools are designed to remove material from a workpiece through processes like shearing, grinding, or drilling, essential for shaping and manufacturing components. Measuring tools, on the other hand, provide precise dimensional data to ensure accuracy and quality control in engineering and production environments. Both tool categories are crucial for achieving precision and efficiency in industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Cutting Tools and Measuring Tools
Cutting tools are designed to shape or remove material from a workpiece by applying force through sharp edges, such as drills, saws, and milling cutters, while measuring tools function to accurately determine dimensions, angles, and tolerances, examples including calipers, micrometers, and gauges. The primary difference lies in their purpose: cutting tools modify physical objects, whereas measuring tools assess the properties of those objects without altering them. Precision in cutting tools depends on blade sharpness and material hardness, whereas measuring tools rely on calibration and resolution to ensure accuracy.
Common Types of Cutting Tools
Common types of cutting tools include drills, milling cutters, lathes, and saw blades, each designed for specific material removal processes in manufacturing. These tools feature sharp edges or abrasive surfaces to shear through metals, plastics, and wood efficiently, enhancing precision and productivity. Unlike measuring tools, which assess dimensions and tolerances, cutting tools actively alter the workpiece shape, playing a crucial role in shaping and finishing components.
Common Types of Measuring Tools
Common types of measuring tools include calipers, micrometers, rulers, and tape measures, each designed for precise measurement of dimensions in various applications. Calipers and micrometers are essential for high-accuracy measurements of thickness, length, and diameter in machining and manufacturing. Rulers and tape measures provide quick, versatile measurements for general use in construction and woodworking.
Applications of Cutting Tools in Various Industries
Cutting tools are essential in manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and construction industries for shaping materials through processes like milling, turning, and drilling. Their applications include precision machining of metals, plastics, and composites, enabling the production of complex components and structural parts. Advancements in cutting tool materials and coatings enhance durability and efficiency, contributing to higher productivity and product quality.
Applications of Measuring Tools Across Sectors
Measuring tools play a critical role across industries such as manufacturing, construction, and healthcare by ensuring precision and quality control in processes and final products. In sectors like automotive and aerospace, devices like calipers and micrometers guarantee component accuracy, directly affecting safety and performance. In healthcare, tools like digital calipers and measuring tapes assist in diagnostics and treatment planning, highlighting their indispensable application beyond traditional engineering fields.
Material Selection: Cutting Tools vs Measuring Tools
Cutting tools are typically made from high-speed steel, carbide, or ceramics to maintain hardness and wear resistance during material removal processes. Measuring tools prioritize materials like stainless steel, hardened alloys, or plastics to ensure durability, corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability for precise measurements. Material selection directly impacts the performance and longevity of cutting tools in machining and measuring accuracy in inspection tasks.
Precision and Accuracy: A Comparative Analysis
Cutting tools require high precision to ensure material removal matches design specifications, often relying on sharpness and rigidity for accurate cuts. Measuring tools emphasize accuracy by providing exact dimensional data, utilizing calibrated scales or digital sensors to minimize errors. Both tool types depend on precision and accuracy, but cutting tools prioritize consistent performance during operation, whereas measuring tools focus on reliable data acquisition.
Maintenance and Care for Cutting and Measuring Tools
Proper maintenance of cutting tools involves regular sharpening, cleaning to remove debris, and applying protective coatings to prevent rust and wear, ensuring precise and efficient performance. Measuring tools require careful calibration, gentle handling to avoid damage, and storage in protective cases to maintain accuracy and longevity. Both tool types benefit from routine inspections and adherence to manufacturer maintenance guidelines to uphold functionality and extend service life.
Choosing the Right Tool: Factors to Consider
Selecting between cutting tools and measuring tools depends on the specific task requirements, material type, and precision levels needed. Cutting tools must have appropriate hardness and edge geometry to handle different materials effectively, while measuring tools require high accuracy and calibration standards to ensure reliable measurements. Understanding the tool's purpose, compatibility with the workpiece, and operational environment is crucial for optimal performance and result quality.
Cutting tool vs Measuring tool Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com