Postmarket surveillance involves continuous monitoring of a medical device's safety and effectiveness after it has been released to the market, ensuring timely identification of risks and performance issues. Premarket notification, commonly known as 510(k) submission, is the process of demonstrating that a new device is substantially equivalent to an existing legally marketed device before commercialization. Effective integration of both processes enhances regulatory compliance, patient safety, and product improvement throughout the device lifecycle.
Table of Comparison
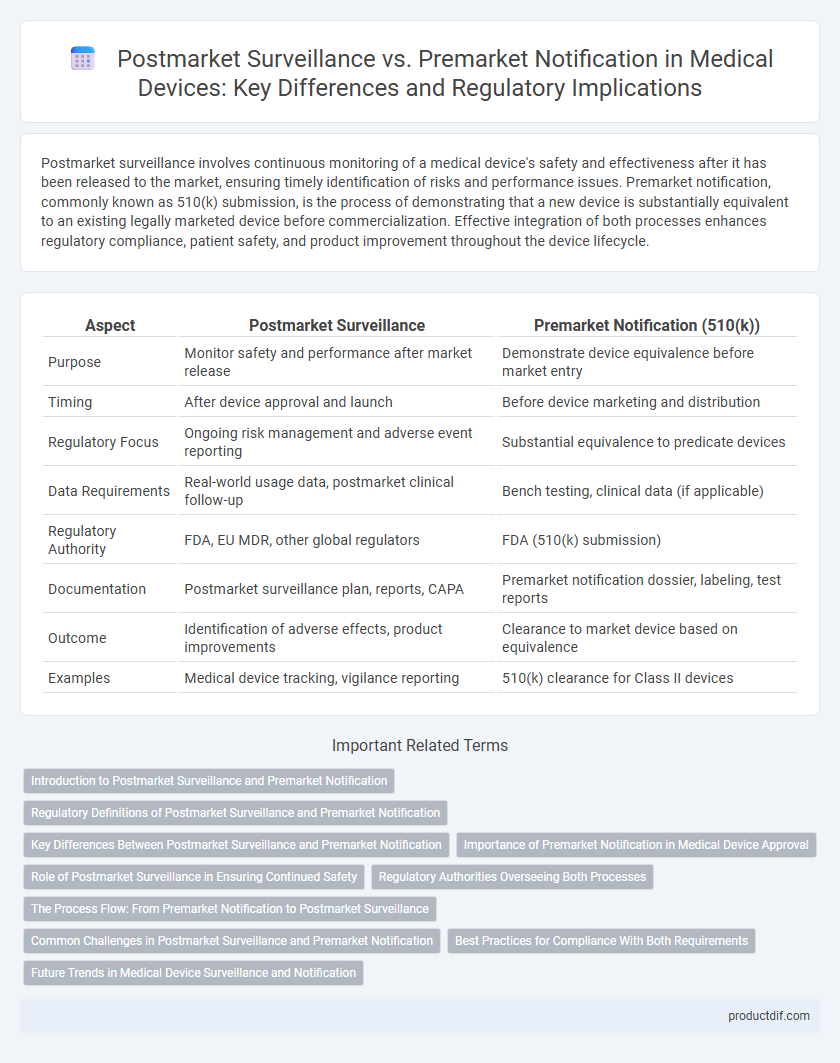
| Aspect | Postmarket Surveillance | Premarket Notification (510(k)) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Monitor safety and performance after market release | Demonstrate device equivalence before market entry |
| Timing | After device approval and launch | Before device marketing and distribution |
| Regulatory Focus | Ongoing risk management and adverse event reporting | Substantial equivalence to predicate devices |
| Data Requirements | Real-world usage data, postmarket clinical follow-up | Bench testing, clinical data (if applicable) |
| Regulatory Authority | FDA, EU MDR, other global regulators | FDA (510(k) submission) |
| Documentation | Postmarket surveillance plan, reports, CAPA | Premarket notification dossier, labeling, test reports |
| Outcome | Identification of adverse effects, product improvements | Clearance to market device based on equivalence |
| Examples | Medical device tracking, vigilance reporting | 510(k) clearance for Class II devices |
Introduction to Postmarket Surveillance and Premarket Notification
Postmarket surveillance involves the continuous monitoring of medical devices after they have been approved and released to the market, ensuring ongoing safety and effectiveness through real-world data collection. Premarket notification, also known as 510(k), requires manufacturers to demonstrate that their device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed device before commercialization. Both processes are critical for regulatory compliance with the FDA, balancing initial safety assessments with long-term device performance monitoring.
Regulatory Definitions of Postmarket Surveillance and Premarket Notification
Postmarket surveillance refers to the ongoing monitoring of a medical device's safety and performance after it has been approved and released to the market, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards over its lifecycle. Premarket notification, often known as 510(k) in the U.S., is a regulatory submission demonstrating that a device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device before it can be marketed. Regulatory definitions emphasize that postmarket surveillance focuses on real-world device data collection, while premarket notification centers on pre-approval evidence for market authorization.
Key Differences Between Postmarket Surveillance and Premarket Notification
Postmarket surveillance involves the continuous monitoring of medical devices after they have been approved and released to the market, focusing on real-world performance, safety, and adverse event reporting. Premarket notification, also known as 510(k), requires manufacturers to demonstrate that their device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed device before it can be marketed. Key differences include the timing of regulatory activities, with premarket notification occurring before market entry and postmarket surveillance operating during the product's lifecycle to ensure ongoing compliance and safety.
Importance of Premarket Notification in Medical Device Approval
Premarket notification (510(k)) plays a crucial role in medical device approval by demonstrating that a new device is substantially equivalent to an already legally marketed device, ensuring safety and effectiveness before market entry. This regulatory step reduces risks by requiring manufacturers to provide detailed evidence of device design, intended use, and performance. Postmarket surveillance complements this by monitoring real-world device performance, but the foundational assurance of safety relies heavily on a thorough and compliant premarket notification process.
Role of Postmarket Surveillance in Ensuring Continued Safety
Postmarket surveillance plays a crucial role in ensuring the continued safety of medical devices by monitoring real-world performance and identifying potential risks after market approval. Unlike premarket notification, which focuses on initial device safety and efficacy evaluation, postmarket surveillance collects and analyzes data from clinical use, adverse event reports, and user feedback to detect safety issues that may not have been evident in premarket testing. This ongoing oversight allows manufacturers and regulatory bodies to implement corrective actions, update device labeling, and enhance patient safety throughout the device lifecycle.
Regulatory Authorities Overseeing Both Processes
Regulatory authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversee both postmarket surveillance and premarket notification to ensure medical device safety and efficacy. Premarket notification, often referred to as 510(k), requires manufacturers to demonstrate that the device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed device before market entry. Postmarket surveillance involves ongoing monitoring and reporting of device performance and adverse events to detect potential risks after commercialization.
The Process Flow: From Premarket Notification to Postmarket Surveillance
Premarket notification (510(k)) requires manufacturers to demonstrate that a medical device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed device before market entry, involving data submission and FDA review. Postmarket surveillance begins after device approval, focusing on continuous safety monitoring through adverse event reporting and periodic safety updates. This process flow ensures both initial regulatory clearance and ongoing risk management to maintain device efficacy and patient safety.
Common Challenges in Postmarket Surveillance and Premarket Notification
Postmarket surveillance faces challenges such as collecting accurate real-world evidence and managing adverse event reporting, which complicate ongoing safety evaluations of medical devices. Premarket notification struggles with demonstrating substantial equivalence to predicate devices while meeting rigorous regulatory documentation requirements. Both processes require robust data management systems and clear communication channels to ensure compliance and protect patient safety effectively.
Best Practices for Compliance With Both Requirements
Postmarket surveillance and premarket notification are critical components for medical device regulatory compliance, ensuring product safety and effectiveness throughout the device lifecycle. Best practices include maintaining thorough documentation, implementing robust risk management systems, and establishing proactive communication channels with regulatory authorities to promptly address any issues. Integrating real-world data collection and adhering to FDA guidelines for 510(k) submissions enhance the ability to meet both postmarket and premarket obligations efficiently.
Future Trends in Medical Device Surveillance and Notification
Postmarket surveillance increasingly integrates real-world data analytics and artificial intelligence to detect device performance issues more rapidly and accurately than traditional methods. Premarket notification processes are evolving to include digital submission platforms and predictive modeling to expedite regulatory review while ensuring safety and efficacy. Future trends emphasize continuous, data-driven monitoring and adaptive regulatory frameworks to enhance patient safety and device innovation.
Postmarket surveillance vs Premarket notification Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com