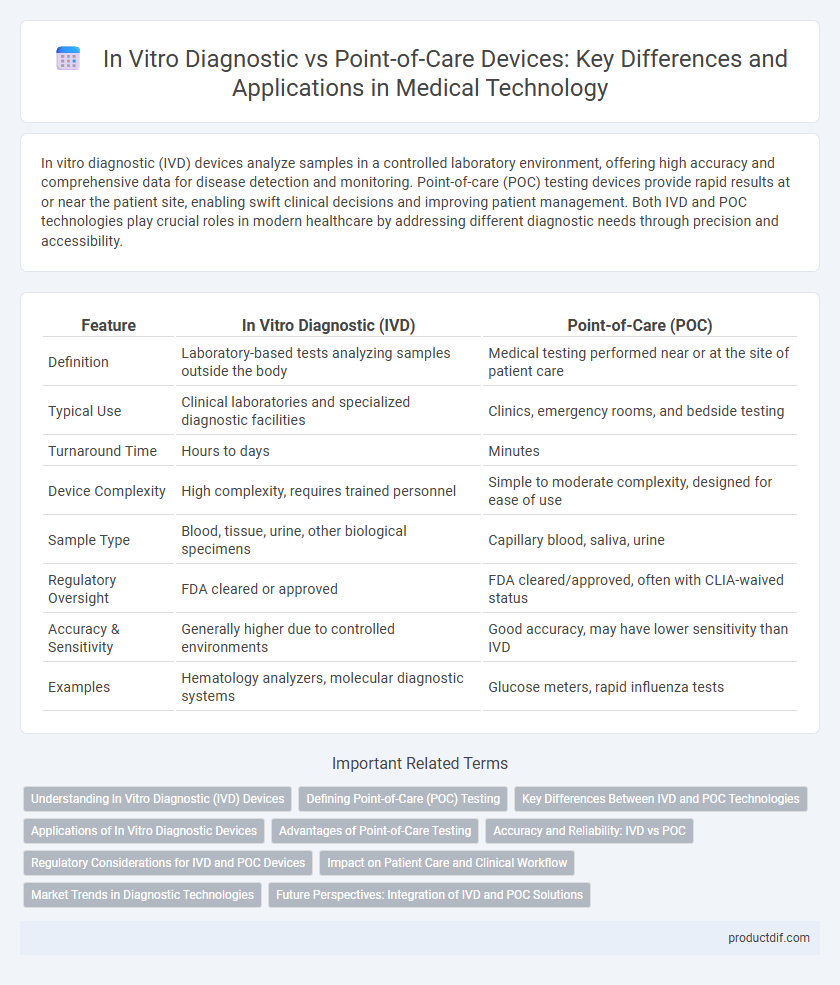
In vitro diagnostic (IVD) devices analyze samples in a controlled laboratory environment, offering high accuracy and comprehensive data for disease detection and monitoring. Point-of-care (POC) testing devices provide rapid results at or near the patient site, enabling swift clinical decisions and improving patient management. Both IVD and POC technologies play crucial roles in modern healthcare by addressing different diagnostic needs through precision and accessibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) | Point-of-Care (POC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Laboratory-based tests analyzing samples outside the body | Medical testing performed near or at the site of patient care |
| Typical Use | Clinical laboratories and specialized diagnostic facilities | Clinics, emergency rooms, and bedside testing |
| Turnaround Time | Hours to days | Minutes |
| Device Complexity | High complexity, requires trained personnel | Simple to moderate complexity, designed for ease of use |
| Sample Type | Blood, tissue, urine, other biological specimens | Capillary blood, saliva, urine |
| Regulatory Oversight | FDA cleared or approved | FDA cleared/approved, often with CLIA-waived status |
| Accuracy & Sensitivity | Generally higher due to controlled environments | Good accuracy, may have lower sensitivity than IVD |
| Examples | Hematology analyzers, molecular diagnostic systems | Glucose meters, rapid influenza tests |
Understanding In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) Devices
In vitro diagnostic (IVD) devices analyze specimens such as blood, urine, or tissue outside the human body to detect diseases, conditions, or infections with high accuracy. These devices provide critical laboratory-based results enabling clinicians to make informed decisions regarding patient diagnosis and treatment. Advanced IVD technologies encompass immunoassays, molecular diagnostics, and clinical chemistry analyzers, emphasizing precision and comprehensive data for comprehensive healthcare management.
Defining Point-of-Care (POC) Testing
Point-of-Care (POC) testing refers to diagnostic testing conducted near or at the site of patient care, enabling immediate clinical decision-making. Unlike traditional in vitro diagnostic (IVD) tests performed in centralized laboratories, POC devices deliver rapid results using portable analyzers or test kits. This proximity to the patient reduces turnaround time and enhances treatment efficiency in various clinical settings.
Key Differences Between IVD and POC Technologies
In vitro Diagnostic (IVD) technologies are laboratory-based tests that analyze samples such as blood or tissue to provide precise diagnostic results, often requiring specialized equipment and trained personnel. Point-of-Care (POC) technologies deliver rapid diagnostic results near the patient site, enabling immediate clinical decision-making with portable, user-friendly devices. Key differences include the testing environment, turnaround time, and complexity, where IVD offers high accuracy in controlled settings, while POC prioritizes speed and convenience for on-the-spot diagnosis.
Applications of In Vitro Diagnostic Devices
In vitro diagnostic (IVD) devices are primarily used in clinical laboratories for analyzing biological samples such as blood, urine, and tissue to detect diseases, monitor health conditions, and guide treatment decisions. These devices enable high-throughput testing with precise quantitative results, making them essential for large-scale screening, disease surveillance, and epidemiological studies. IVD applications also include infectious disease detection, genetic testing, and biochemical analysis, supporting personalized medicine and improved patient outcomes.
Advantages of Point-of-Care Testing
Point-of-care testing (POCT) offers rapid diagnostic results directly at the site of patient care, significantly reducing turnaround times compared to traditional in vitro diagnostic (IVD) laboratory testing. POCT enhances clinical decision-making by enabling immediate treatment adjustments, improving patient outcomes, and minimizing the need for multiple healthcare visits. Its portability and ease of use facilitate testing in diverse settings such as emergency rooms, clinics, and remote locations, promoting accessibility and convenience.
Accuracy and Reliability: IVD vs POC
In vitro diagnostic (IVD) devices generally provide higher accuracy and reliability due to controlled laboratory environments and advanced testing methodologies. Point-of-care (POC) devices, while offering rapid results and convenience at the patient's side, may exhibit variable accuracy influenced by operator skill and environmental factors. The choice between IVD and POC depends on the clinical need for precision versus immediacy in diagnostic outcomes.
Regulatory Considerations for IVD and POC Devices
In vitro diagnostic (IVD) devices and point-of-care (POC) devices face distinct regulatory requirements governed by agencies such as the FDA and EMA, emphasizing safety, efficacy, and accuracy. IVD devices typically require comprehensive premarket approval involving analytical and clinical validation due to their laboratory-based use, whereas POC devices undergo streamlined regulatory pathways focusing on rapid diagnostics in decentralized settings. Compliance with standards like ISO 13485 and adherence to labeling, post-market surveillance, and risk management protocols remain critical for both categories to ensure patient safety and device reliability.
Impact on Patient Care and Clinical Workflow
In vitro diagnostic (IVD) devices enable comprehensive laboratory analysis with high accuracy, supporting detailed patient data for informed clinical decisions, but often involve longer turnaround times. Point-of-care (POC) testing provides rapid results at or near the patient site, significantly enhancing clinical workflow efficiency and enabling immediate treatment adjustments. The integration of POC testing into care pathways reduces hospital stays and improves patient outcomes by facilitating quicker diagnosis and intervention.
Market Trends in Diagnostic Technologies
The market for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) devices continues to grow rapidly, driven by advancements in molecular diagnostics, automation, and high-throughput technologies. Point-of-care (POC) testing is gaining significant traction due to its convenience, faster turnaround times, and increasing adoption in decentralized healthcare settings. Key market trends include the integration of artificial intelligence, connectivity solutions, and portable biosensors to enhance diagnostic accuracy and support real-time decision-making.
Future Perspectives: Integration of IVD and POC Solutions
Future perspectives in medical diagnostics emphasize the integration of In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) and Point-of-Care (POC) solutions to enhance accuracy, speed, and accessibility of diagnostic testing. Combining advanced IVD technologies with decentralized POC devices accelerates clinical decision-making, supports personalized medicine, and optimizes patient outcomes. Innovations in microfluidics, biosensors, and digital connectivity facilitate seamless data exchange and real-time monitoring, driving the next generation of precision diagnostics.
In vitro Diagnostic vs Point-of-Care Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com