Cybersecurity risk in medical devices primarily involves unauthorized access or attacks that compromise device functionality and patient safety, while data privacy risk centers on the unauthorized collection, use, or disclosure of sensitive patient information. Effective risk management must balance protecting device integrity against threats like malware and hacking, with safeguarding the confidentiality and compliance requirements of patient data. Both risks demand robust encryption, regular security updates, and strict access controls to ensure comprehensive protection within healthcare environments.
Table of Comparison
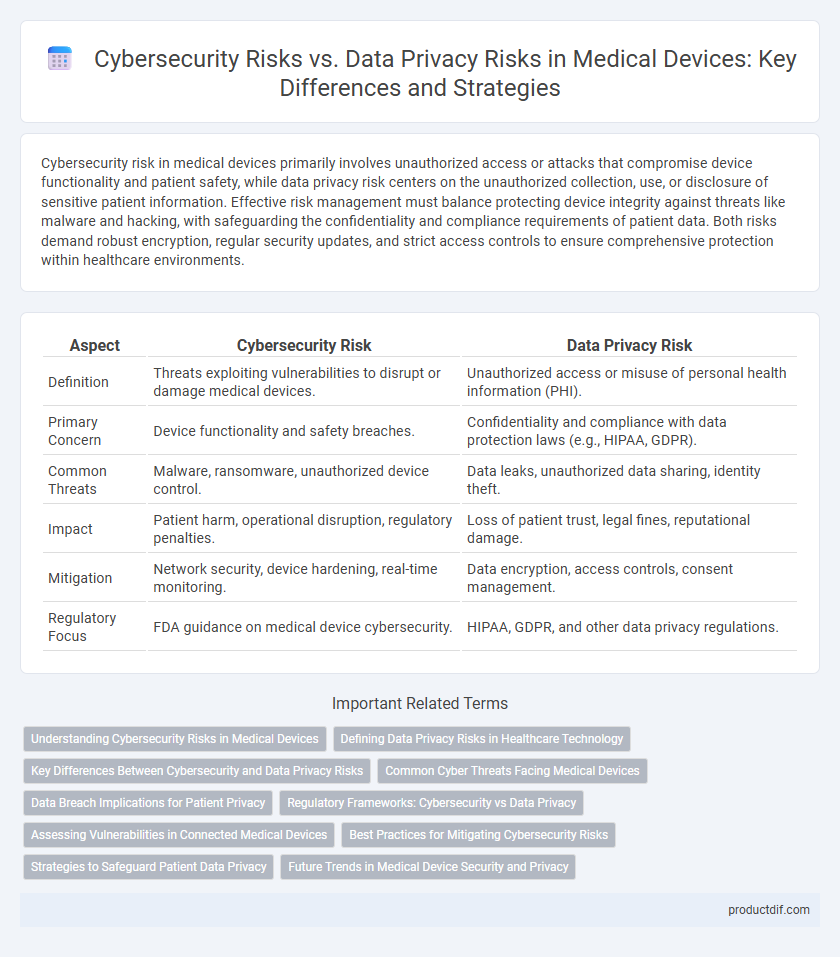
| Aspect | Cybersecurity Risk | Data Privacy Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Threats exploiting vulnerabilities to disrupt or damage medical devices. | Unauthorized access or misuse of personal health information (PHI). |
| Primary Concern | Device functionality and safety breaches. | Confidentiality and compliance with data protection laws (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR). |
| Common Threats | Malware, ransomware, unauthorized device control. | Data leaks, unauthorized data sharing, identity theft. |
| Impact | Patient harm, operational disruption, regulatory penalties. | Loss of patient trust, legal fines, reputational damage. |
| Mitigation | Network security, device hardening, real-time monitoring. | Data encryption, access controls, consent management. |
| Regulatory Focus | FDA guidance on medical device cybersecurity. | HIPAA, GDPR, and other data privacy regulations. |
Understanding Cybersecurity Risks in Medical Devices
Cybersecurity risks in medical devices involve threats such as unauthorized access, malware attacks, and system vulnerabilities that can compromise device functionality and patient safety. These risks differ from data privacy concerns, which primarily focus on protecting sensitive patient information from breaches and unauthorized disclosure. Addressing cybersecurity risks requires robust security protocols, continuous monitoring, and timely software updates to prevent exploitation that could disrupt device operation and endanger patient health.
Defining Data Privacy Risks in Healthcare Technology
Data privacy risks in healthcare technology involve unauthorized access, collection, or sharing of sensitive patient information, leading to potential breaches of confidentiality. These risks encompass improper handling of electronic health records (EHRs), inadequate consent management, and vulnerabilities in data transmission processes. Ensuring compliance with HIPAA and GDPR regulations is critical to mitigating these risks and protecting patient trust.
Key Differences Between Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Risks
Cybersecurity risks in medical devices primarily involve threats to device functionality and patient safety caused by unauthorized access or malicious attacks targeting system integrity. Data privacy risks focus on unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of personal health information (PHI) stored or transmitted by medical devices, potentially compromising patient confidentiality. Unlike cybersecurity risks that target the operational aspects and physical harm, data privacy risks mainly affect regulatory compliance and patient trust due to exposure of sensitive personal data.
Common Cyber Threats Facing Medical Devices
Medical devices commonly face cyber threats such as ransomware, unauthorized access, and malware attacks that compromise device functionality and patient safety. These cybersecurity risks often lead to data privacy breaches, exposing sensitive health information and violating regulations like HIPAA. Robust encryption, regular software updates, and stringent access controls are essential to mitigate these intertwined risks.
Data Breach Implications for Patient Privacy
Data breaches in medical devices expose sensitive patient health information, leading to potential identity theft and unauthorized access to personal medical histories. Cybersecurity vulnerabilities can result in compromised device functionality, but data privacy risks directly threaten patient confidentiality and trust in healthcare systems. Ensuring robust encryption and strict access controls is crucial to mitigate the implications of data breaches on patient privacy.
Regulatory Frameworks: Cybersecurity vs Data Privacy
Regulatory frameworks for medical devices address cybersecurity risk by enforcing standards such as the FDA's guidance on cybersecurity management and the IEC 62443 series, which focus on protecting device functionality and preventing unauthorized access. Data privacy risk is governed by regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), emphasizing patient data confidentiality and data handling practices. While cybersecurity regulations prioritize device integrity and threat mitigation, data privacy frameworks concentrate on safeguarding personal health information and ensuring compliance with consent and data processing requirements.
Assessing Vulnerabilities in Connected Medical Devices
Assessing vulnerabilities in connected medical devices requires a comprehensive evaluation of cybersecurity risks, including unauthorized access, malware attacks, and data breaches that compromise device functionality and patient safety. Data privacy risk involves the potential exposure of sensitive personal health information, emphasizing encryption, access controls, and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. Effective risk assessment integrates penetration testing and real-time monitoring to identify weaknesses in both system security and data protection mechanisms.
Best Practices for Mitigating Cybersecurity Risks
Implementing multi-layered security protocols, including encryption, access controls, and regular software updates, significantly reduces cybersecurity risks in medical devices. Conducting thorough risk assessments and continuous monitoring helps identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Adhering to industry standards like ISO 27001 and FDA guidelines ensures robust protection against cyber threats while maintaining data integrity and patient safety.
Strategies to Safeguard Patient Data Privacy
Implementing robust encryption protocols and access controls significantly reduces cybersecurity risks that could expose sensitive patient information in medical devices. Regular software updates and vulnerability assessments help identify and mitigate potential breaches compromising data privacy. Integrating advanced authentication methods and strict compliance with healthcare data regulations ensures the protection of patient data against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Future Trends in Medical Device Security and Privacy
Emerging trends in medical device security emphasize advanced encryption techniques and AI-driven threat detection to mitigate escalating cybersecurity risks. Concurrently, data privacy frameworks are evolving to address stricter regulatory compliance and patient consent management in real-time data sharing environments. Integration of blockchain technology is anticipated to enhance both security and privacy by ensuring immutable audit trails and transparent data access controls.
Cybersecurity risk vs Data privacy risk Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com