Design freeze marks the point where all design specifications for a medical device are finalized and no further changes are allowed, ensuring consistency and regulatory compliance. Design transfer involves converting the finalized design into manufacturing instructions, facilitating the seamless production of the medical device while maintaining quality standards. This transition is critical to avoid errors, minimize risks, and achieve efficient scale-up from development to commercial manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
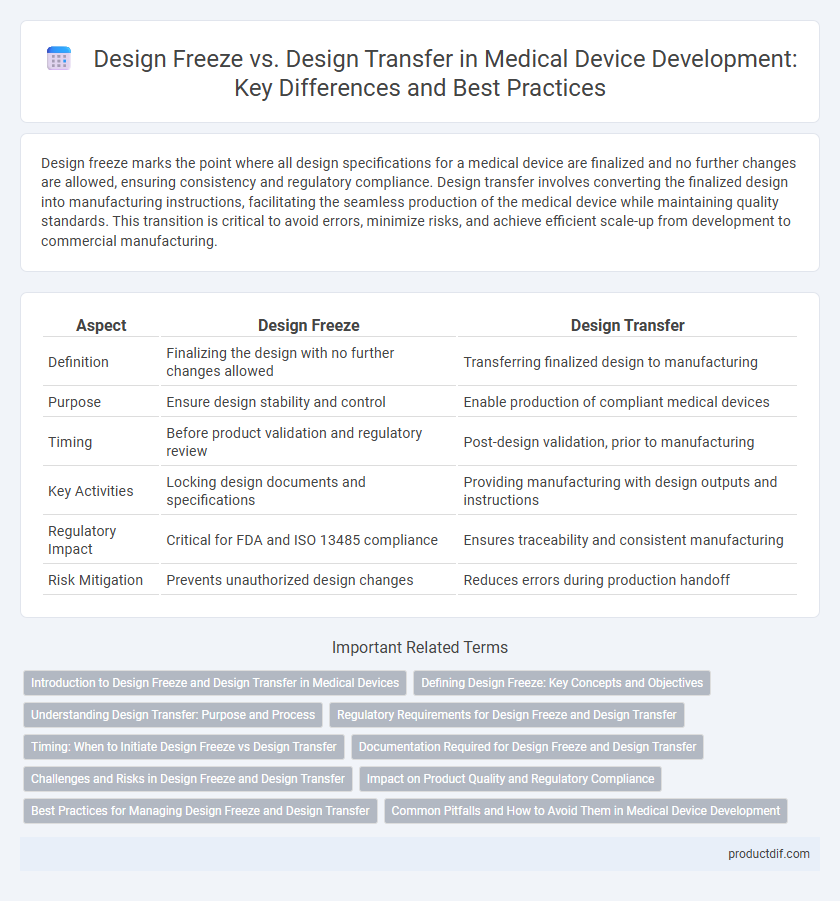
| Aspect | Design Freeze | Design Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Finalizing the design with no further changes allowed | Transferring finalized design to manufacturing |
| Purpose | Ensure design stability and control | Enable production of compliant medical devices |
| Timing | Before product validation and regulatory review | Post-design validation, prior to manufacturing |
| Key Activities | Locking design documents and specifications | Providing manufacturing with design outputs and instructions |
| Regulatory Impact | Critical for FDA and ISO 13485 compliance | Ensures traceability and consistent manufacturing |
| Risk Mitigation | Prevents unauthorized design changes | Reduces errors during production handoff |
Introduction to Design Freeze and Design Transfer in Medical Devices
Design Freeze in medical devices marks the stage where the product design is fully finalized and no further changes are allowed to ensure consistency and regulatory compliance. Design Transfer involves the systematic handover of design specifications and documentation from the development team to manufacturing for production. Both phases are critical to maintaining quality control and meeting FDA and ISO standards in medical device production.
Defining Design Freeze: Key Concepts and Objectives
Design freeze marks the finalization of a medical device's design, ensuring all specifications and requirements are locked and approved before production begins. This critical stage prevents further changes, minimizing risks and maintaining regulatory compliance in device development. Establishing design freeze solidifies the design baseline, enabling efficient transition to design transfer for manufacturing.
Understanding Design Transfer: Purpose and Process
Design transfer is the critical phase where the finalized medical device design is accurately translated into production specifications, ensuring manufacturability and compliance with regulatory standards. This process involves detailed documentation, validation of manufacturing methods, and cross-functional collaboration to mitigate risks and maintain quality. Successful design transfer bridges the gap between development and manufacturing, safeguarding product integrity and patient safety.
Regulatory Requirements for Design Freeze and Design Transfer
Regulatory requirements for design freeze in medical device development mandate the finalization and documentation of design inputs, specifications, and validation results to ensure product safety and effectiveness before production. Design transfer involves the formal handoff of design documentation and specifications to manufacturing, requiring strict compliance with quality management systems such as ISO 13485 and FDA 21 CFR Part 820 to confirm that the device can be produced consistently according to the approved design. Both processes must maintain traceability and control changes to meet regulatory standards and support device approval and market release.
Timing: When to Initiate Design Freeze vs Design Transfer
Design freeze occurs after finalizing the medical device design to lock specifications, preventing further changes, typically initiated before regulatory submissions. Design transfer begins once the design freeze is complete, focusing on transferring detailed design documentation to manufacturing teams for production. Proper timing ensures design integrity and manufacturing readiness, minimizing risks in product development.
Documentation Required for Design Freeze and Design Transfer
Design freeze requires comprehensive documentation including finalized design specifications, validation and verification reports, risk assessments, and design change records to ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Design transfer documentation demands detailed device master records, manufacturing instructions, quality assurance protocols, and supplier qualifications to facilitate accurate production handoff. Both stages emphasize traceability and control to maintain device safety and efficacy throughout development and manufacturing.
Challenges and Risks in Design Freeze and Design Transfer
Design freeze in medical device development poses challenges such as incomplete validation of design inputs and unresolved regulatory requirements, leading to risks of non-compliance and costly post-freeze changes. Design transfer involves translating design documentation into manufacturing processes, with risks including miscommunication between engineering and production teams, inaccuracies in device specifications, and inadequate quality control measures, which can result in production delays and product recalls. Effective management of these phases is critical to ensure device safety, regulatory compliance, and successful commercialization.
Impact on Product Quality and Regulatory Compliance
Design freeze marks the point where design outputs are finalized, ensuring stability and reducing variability that could compromise product quality. Design transfer involves accurately conveying design specifications to manufacturing, critical for maintaining regulatory compliance and consistent production standards. Effective management of both phases directly influences the reliability, safety, and regulatory approval of the medical device.
Best Practices for Managing Design Freeze and Design Transfer
Establishing a comprehensive design freeze checklist characterized by finalized specifications, validated test results, and regulatory compliance documentation ensures a controlled transition to manufacturing. Maintaining clear communication channels between design, engineering, quality, and production teams minimizes errors and accelerates the design transfer process. Implementing version control systems and formal approval workflows guarantees traceability and accountability throughout design freeze and transfer phases.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them in Medical Device Development
Common pitfalls in design freeze versus design transfer in medical device development include premature design lock without thorough validation, leading to costly revisions and regulatory non-compliance. Failure to establish clear criteria for design completion often results in incomplete documentation and gaps during the transfer to manufacturing, increasing risk of production errors. Avoid these issues by implementing rigorous design verification protocols and cross-functional reviews to ensure design integrity before transfer.
Design freeze vs Design transfer Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com