Medical robots encompass a broad range of automated devices designed to assist in various healthcare tasks, including diagnostics, rehabilitation, and patient care, while surgical robots specifically refer to advanced robotic systems used to perform or enhance precision in surgical procedures. Surgical robots provide surgeons with enhanced dexterity, control, and visualization during operations, often improving patient outcomes through minimally invasive techniques. The distinction lies in their application scope, with medical robots serving general medical functions and surgical robots tailored specifically for operative interventions.
Table of Comparison
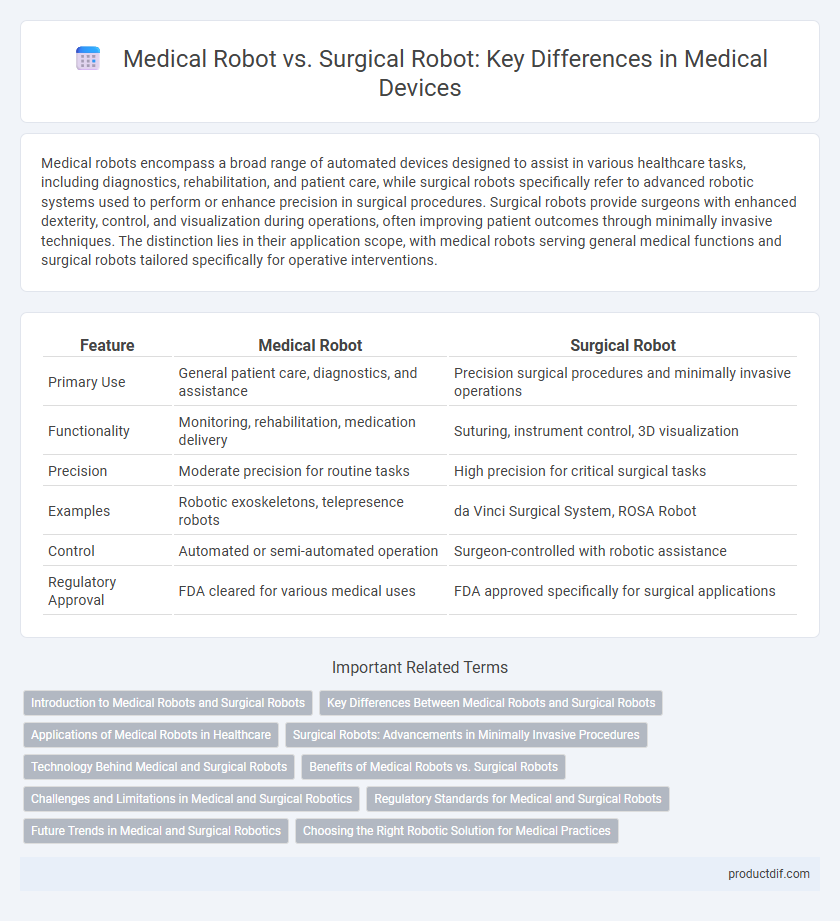
| Feature | Medical Robot | Surgical Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General patient care, diagnostics, and assistance | Precision surgical procedures and minimally invasive operations |
| Functionality | Monitoring, rehabilitation, medication delivery | Suturing, instrument control, 3D visualization |
| Precision | Moderate precision for routine tasks | High precision for critical surgical tasks |
| Examples | Robotic exoskeletons, telepresence robots | da Vinci Surgical System, ROSA Robot |
| Control | Automated or semi-automated operation | Surgeon-controlled with robotic assistance |
| Regulatory Approval | FDA cleared for various medical uses | FDA approved specifically for surgical applications |
Introduction to Medical Robots and Surgical Robots
Medical robots encompass a broad range of automated machines designed to assist in various healthcare tasks, including diagnostics, rehabilitation, and patient care. Surgical robots represent a specialized subset of medical robots, engineered specifically to enhance precision and control during surgical procedures through minimally invasive techniques. These advanced robotic systems improve surgical outcomes by enabling greater dexterity, reducing human error, and facilitating complex operations with enhanced visualization and tremor filtration.
Key Differences Between Medical Robots and Surgical Robots
Medical robots encompass a broad range of automated machines designed for various healthcare applications, including diagnostics, rehabilitation, and patient care, while surgical robots specifically assist surgeons during operations to enhance precision and control. Surgical robots feature advanced instruments like robotic arms and 3D visualization systems tailored for minimally invasive procedures, distinguishing them from more general-purpose medical robots. Key differences lie in their specialized functionalities, deployment environments, and the critical role of surgical robots in directly influencing patient outcomes during complex surgeries.
Applications of Medical Robots in Healthcare
Medical robots enhance precision and efficiency in complex healthcare procedures by assisting in diagnostics, rehabilitation, and patient monitoring. Surgical robots specifically focus on minimally invasive surgeries, providing superior dexterity, reduced recovery time, and enhanced visualization for surgeons. Applications of medical robots extend to tasks like drug delivery, telemedicine, and automated lab analysis, revolutionizing patient care and operational workflows across healthcare facilities.
Surgical Robots: Advancements in Minimally Invasive Procedures
Surgical robots have revolutionized minimally invasive procedures by enhancing precision, flexibility, and control beyond traditional medical devices. These systems integrate advanced imaging, real-time data analysis, and robotic arms to perform complex surgeries with reduced trauma and faster recovery times. Key examples include the da Vinci Surgical System and the ROSA robot, which continue to drive innovation in robotic-assisted surgery.
Technology Behind Medical and Surgical Robots
Medical robots utilize advanced sensors, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data processing to assist in diagnostics, patient monitoring, and therapeutic interventions. Surgical robots integrate precision robotics, 3D imaging, and haptic feedback systems to enhance surgeon control and improve outcomes during minimally invasive procedures. Both technologies rely on cutting-edge automation and AI to increase accuracy, reduce human error, and enable innovative medical applications.
Benefits of Medical Robots vs. Surgical Robots
Medical robots enhance patient care by automating diagnostic and therapeutic procedures beyond surgery, enabling precision and reducing human error in repetitive tasks like medication dispensing and rehabilitation. Surgical robots specialize in minimally invasive procedures, improving accuracy and reducing recovery time but have limited applications outside the operating room. The versatility of medical robots supports a broader range of healthcare functions, leading to increased efficiency and improved patient outcomes across various medical disciplines.
Challenges and Limitations in Medical and Surgical Robotics
Medical robots often face challenges such as limited dexterity, high costs, and complex integration with existing hospital systems, which restrict their widespread adoption. Surgical robots specifically encounter limitations including the lack of tactile feedback, steep learning curves for surgeons, and increased operation times during initial use. Both medical and surgical robotics require advancements in AI, sensor technology, and real-time data processing to overcome these critical barriers and improve clinical outcomes.
Regulatory Standards for Medical and Surgical Robots
Medical robots and surgical robots are subject to strict regulatory standards such as FDA 510(k) clearance and ISO 13485 certification to ensure safety and efficacy in clinical use. Surgical robots undergo rigorous validation including pre-market approval (PMA) processes due to their direct interaction with patients in invasive procedures. Compliance with IEC 60601 standards for electrical safety and ISO 14971 for risk management is essential for both categories to meet international medical device regulations.
Future Trends in Medical and Surgical Robotics
Future trends in medical and surgical robotics emphasize enhanced precision through AI-driven automation and real-time imaging integration, improving patient outcomes and reducing surgical risks. The development of miniaturized, flexible robotic arms enables minimally invasive procedures with greater dexterity in confined anatomical spaces. Advances in haptic feedback and machine learning algorithms are expected to facilitate more intuitive surgeon-robot collaboration, expanding the scope of robotic-assisted surgeries.
Choosing the Right Robotic Solution for Medical Practices
Medical robots encompass a broad range of automated devices designed for various healthcare applications, while surgical robots specifically target precision and control during operative procedures. Choosing the right robotic solution involves evaluating factors such as the complexity of surgeries, integration with existing medical systems, and the robot's dexterity and imaging capabilities. Cost-effectiveness, training requirements, and regulatory approvals are critical considerations to ensure optimal patient outcomes and workflow efficiency in medical practices.
Medical Robot vs Surgical Robot Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com