CE Mark certification indicates that a medical device complies with European Union safety, health, and environmental protection standards, allowing market access throughout Europe. FDA clearance or approval confirms the device meets stringent regulatory requirements for safety and effectiveness in the United States, often involving a more rigorous review process. Manufacturers targeting global markets must understand the distinct regulatory pathways and documentation requirements for CE Mark and FDA clearance to ensure timely product launch.
Table of Comparison
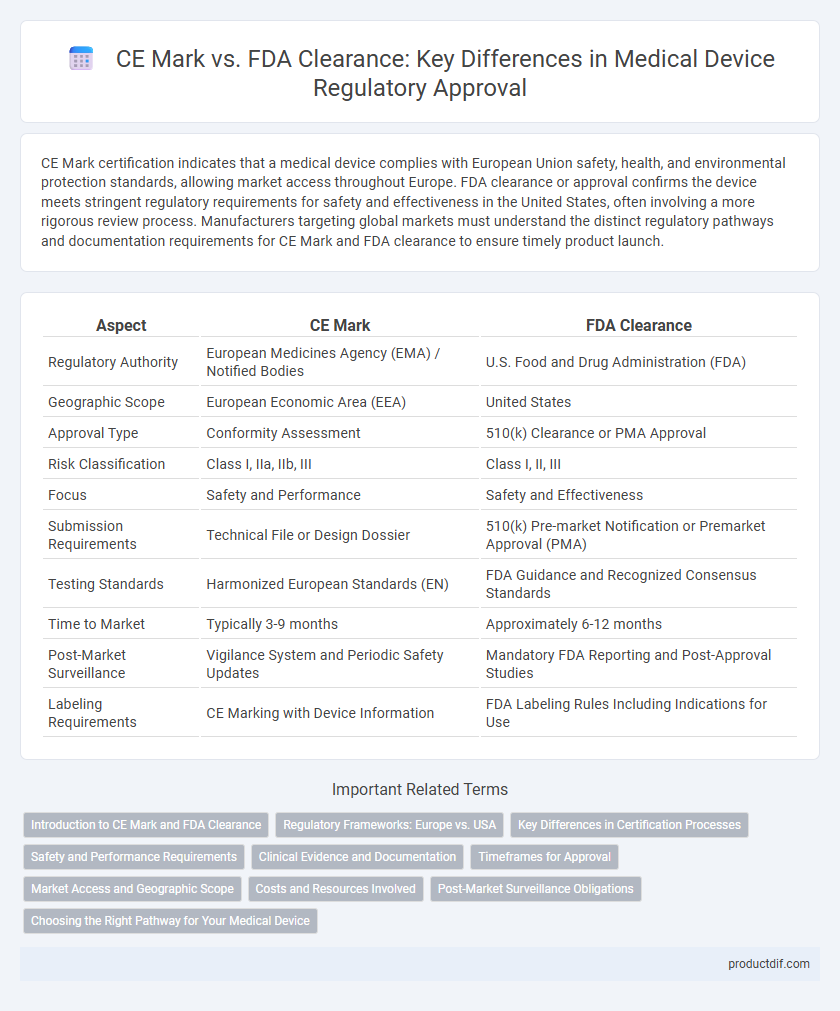
| Aspect | CE Mark | FDA Clearance |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Authority | European Medicines Agency (EMA) / Notified Bodies | U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) |
| Geographic Scope | European Economic Area (EEA) | United States |
| Approval Type | Conformity Assessment | 510(k) Clearance or PMA Approval |
| Risk Classification | Class I, IIa, IIb, III | Class I, II, III |
| Focus | Safety and Performance | Safety and Effectiveness |
| Submission Requirements | Technical File or Design Dossier | 510(k) Pre-market Notification or Premarket Approval (PMA) |
| Testing Standards | Harmonized European Standards (EN) | FDA Guidance and Recognized Consensus Standards |
| Time to Market | Typically 3-9 months | Approximately 6-12 months |
| Post-Market Surveillance | Vigilance System and Periodic Safety Updates | Mandatory FDA Reporting and Post-Approval Studies |
| Labeling Requirements | CE Marking with Device Information | FDA Labeling Rules Including Indications for Use |
Introduction to CE Mark and FDA Clearance
CE Mark certification indicates that a medical device complies with the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR), allowing it to be marketed within the European Economic Area. FDA clearance, granted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, confirms that a device meets safety and efficacy standards under the 510(k) premarket notification process. Both certifications require rigorous documentation and testing but differ in regulatory scope and procedural requirements.
Regulatory Frameworks: Europe vs. USA
The CE Mark indicates conformity with the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR), requiring manufacturers to demonstrate device safety and performance through a notified body assessment. In contrast, FDA Clearance in the USA follows the 510(k) premarket notification process, emphasizing substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. European regulatory frameworks focus on risk classification and post-market surveillance, while the FDA prioritizes premarket review and compliance with Quality System Regulation (QSR).
Key Differences in Certification Processes
CE Mark certification involves a conformity assessment process aligned with the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR), requiring manufacturers to demonstrate compliance through notified bodies based in the EU. FDA clearance is governed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and centers on premarket notifications, particularly 510(k) submissions that prove substantial equivalence to legally marketed devices. CE Mark approval often emphasizes risk classification and clinical evaluation, while FDA clearance includes rigorous review of safety and effectiveness data specific to the U.S. market.
Safety and Performance Requirements
CE Mark certification emphasizes compliance with the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which mandates rigorous safety and performance requirements, including clinical evaluation and post-market surveillance. FDA clearance under 510(k) focuses on demonstrating substantial equivalence to a legally marketed device, with safety and effectiveness evaluations tailored to U.S. standards. Both regulatory pathways prioritize device safety and performance but differ in documentation, testing protocols, and market surveillance strategies to ensure patient protection.
Clinical Evidence and Documentation
CE Mark requires robust clinical evidence demonstrating conformity with EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) standards, emphasizing clinical evaluation reports and post-market surveillance documentation. FDA Clearance prioritizes substantial clinical data validating safety and effectiveness, with substantial emphasis on premarket submissions like 510(k) or PMA that include detailed clinical trial results. Both regulatory bodies mandate comprehensive documentation, but the FDA demands more rigorous clinical validation and transparency in data submission processes.
Timeframes for Approval
CE Mark approval for medical devices typically takes between 3 to 12 months, depending on the classification and the notified body's review process. FDA clearance, such as 510(k), generally requires around 90 days, but the entire process may extend from 6 months to over a year for more complex devices requiring Premarket Approval (PMA). The faster CE Mark timeframe reflects the conformity assessment focus, while FDA clearance involves more rigorous clinical evaluation and documentation.
Market Access and Geographic Scope
CE Mark certification enables medical devices to access the European Economic Area (EEA) market, covering 27 EU countries plus Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, facilitating swift entry across multiple nations. FDA Clearance applies specifically to the United States, requiring compliance with stringent regulatory standards set by the Food and Drug Administration to legally market medical devices domestically. Understanding the distinct geographic scopes and approval processes of CE Mark and FDA Clearance is critical for manufacturers aiming to expand their medical device market access internationally.
Costs and Resources Involved
CE Marking for medical devices generally involves lower costs and fewer resource requirements compared to FDA clearance, as the European process relies heavily on conformity assessment by notified bodies with fees based on device risk classification. FDA clearance demands extensive premarket submissions such as 510(k) or PMA, which involve significant clinical data, regulatory expertise, and higher financial investment, often spanning months to years. Manufacturers must allocate substantial resources to navigate FDA's stringent documentation, testing, and post-market surveillance, making CE Mark certification a more accessible option for market entry in terms of costs and operational burden.
Post-Market Surveillance Obligations
CE Mark requires manufacturers to implement continuous post-market surveillance systems to monitor device performance and ensure ongoing compliance with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). FDA clearance involves mandatory post-market surveillance activities including Medical Device Reporting (MDR) and, for certain devices, post-approval studies to track safety and effectiveness. Both regulatory frameworks emphasize vigilance but differ in reporting timelines, data requirements, and enforcement mechanisms.
Choosing the Right Pathway for Your Medical Device
Selecting the appropriate regulatory pathway for a medical device depends on target markets and device classification, with CE marking required for European Union sales and FDA clearance mandatory for the U.S. market. CE marking involves compliance with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) or In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) and often requires conformity assessment by a Notified Body. FDA clearance typically entails submitting a 510(k) premarket notification demonstrating substantial equivalence to a legally marketed device or pursuing Premarket Approval (PMA) for higher-risk devices.
CE Mark vs FDA Clearance Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com