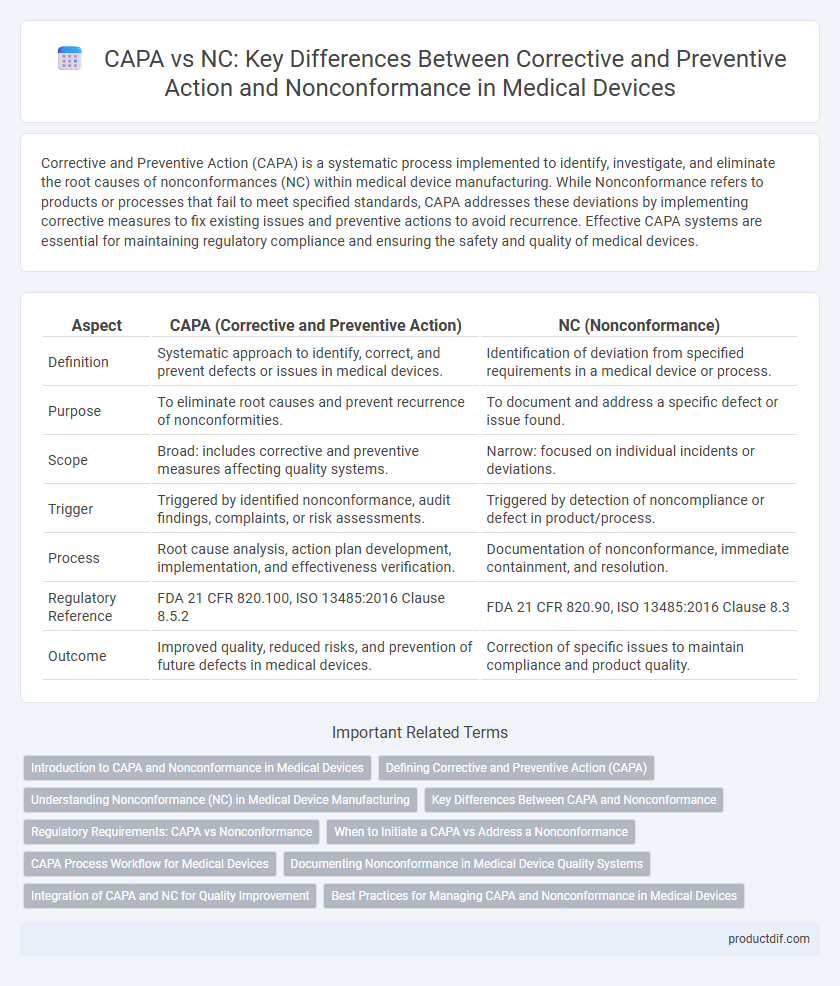
Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) is a systematic process implemented to identify, investigate, and eliminate the root causes of nonconformances (NC) within medical device manufacturing. While Nonconformance refers to products or processes that fail to meet specified standards, CAPA addresses these deviations by implementing corrective measures to fix existing issues and preventive actions to avoid recurrence. Effective CAPA systems are essential for maintaining regulatory compliance and ensuring the safety and quality of medical devices.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) | NC (Nonconformance) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic approach to identify, correct, and prevent defects or issues in medical devices. | Identification of deviation from specified requirements in a medical device or process. |
| Purpose | To eliminate root causes and prevent recurrence of nonconformities. | To document and address a specific defect or issue found. |
| Scope | Broad: includes corrective and preventive measures affecting quality systems. | Narrow: focused on individual incidents or deviations. |
| Trigger | Triggered by identified nonconformance, audit findings, complaints, or risk assessments. | Triggered by detection of noncompliance or defect in product/process. |
| Process | Root cause analysis, action plan development, implementation, and effectiveness verification. | Documentation of nonconformance, immediate containment, and resolution. |
| Regulatory Reference | FDA 21 CFR 820.100, ISO 13485:2016 Clause 8.5.2 | FDA 21 CFR 820.90, ISO 13485:2016 Clause 8.3 |
| Outcome | Improved quality, reduced risks, and prevention of future defects in medical devices. | Correction of specific issues to maintain compliance and product quality. |
Introduction to CAPA and Nonconformance in Medical Devices
Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) in medical devices is a systematic approach to identifying, investigating, and resolving nonconformances to prevent recurrence and enhance product quality. Nonconformance refers to any deviation from specified requirements, standards, or regulations that impact the safety, efficacy, or performance of a medical device. Implementing effective CAPA ensures regulatory compliance and continuous improvement in medical device manufacturing and quality management systems.
Defining Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA)
Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) in medical device manufacturing refers to systematic procedures used to identify, investigate, and resolve nonconformities or potential issues that impact product quality and patient safety. CAPA processes involve root cause analysis, implementation of corrective measures to address existing problems, and preventive strategies to avoid recurrence or occurrence of defects. Effective CAPA ensures compliance with regulatory standards such as FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and ISO 13485 by maintaining robust quality management systems.
Understanding Nonconformance (NC) in Medical Device Manufacturing
Nonconformance (NC) in medical device manufacturing refers to any deviation from specified requirements, standards, or procedures that may impact product quality or patient safety. Identifying and documenting NC is critical for triggering Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) to investigate root causes and implement solutions that prevent recurrence. Effective NC management ensures compliance with regulatory standards such as ISO 13485 and FDA 21 CFR Part 820, maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process and the safety of medical devices.
Key Differences Between CAPA and Nonconformance
CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) is a systemic process designed to identify, investigate, and address the root causes of quality issues to prevent recurrence, while Nonconformance (NC) refers to any deviation from specified requirements or standards in medical device manufacturing. CAPA involves a structured approach, including evaluation, corrective action implementation, and preventive measures, whereas Nonconformance mainly focuses on the identification and documentation of defects or deviations. Effective CAPA emphasizes long-term quality improvement and compliance, whereas Nonconformance provides a basis for initiating CAPA activities by highlighting specific failures.
Regulatory Requirements: CAPA vs Nonconformance
CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) systems are mandated by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and ISO 13485 to identify, investigate, and resolve both current and potential nonconformances to ensure sustained compliance in medical device manufacturing. Nonconformance refers to deviations from specified requirements detected during production or quality control processes and must be documented and evaluated to determine risk and impact on device safety and effectiveness. Regulatory standards require CAPA processes to implement corrective measures that address root causes of nonconformance and preventive strategies to avoid recurrence, ensuring product quality and patient safety.
When to Initiate a CAPA vs Address a Nonconformance
Initiate a CAPA when a systemic issue or trend affecting product quality or patient safety is identified, requiring investigation and long-term corrective and preventive measures. Address a nonconformance when a specific, isolated deviation from established specifications or regulations is detected that necessitates immediate correction but may not indicate a broader systemic problem. Distinguishing between CAPA and nonconformance ensures efficient compliance with FDA and ISO 13485 standards, optimizing risk management and quality assurance processes in medical device manufacturing.
CAPA Process Workflow for Medical Devices
The CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) process workflow for medical devices involves identifying the root cause of nonconformance (NC), implementing corrective actions to address existing issues, and preventive actions to avoid recurrence. This systematic approach includes steps such as detection, investigation, action planning, implementation, and effectiveness verification to ensure compliance with regulatory standards like FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and ISO 13485. Efficient CAPA management improves product quality, reduces risk, and supports continuous improvement in medical device manufacturing and post-market surveillance.
Documenting Nonconformance in Medical Device Quality Systems
Documenting nonconformance in medical device quality systems involves accurately identifying, recording, and analyzing instances where products or processes fail to meet established specifications or regulatory requirements. Effective documentation supports traceability and facilitates timely investigation and resolution within the Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) framework. Maintaining comprehensive nonconformance records ensures regulatory compliance, drives continuous improvement, and helps mitigate risks associated with defective devices.
Integration of CAPA and NC for Quality Improvement
Integrating Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) with Nonconformance (NC) processes enhances medical device quality management by enabling systematic identification, analysis, and resolution of defects or deviations. This integration ensures real-time tracking of nonconformances and facilitates proactive implementation of corrective actions, reducing recurrence rates and improving product safety. Leveraging data from both CAPA and NC systems supports continuous quality improvement and regulatory compliance in the medical device industry.
Best Practices for Managing CAPA and Nonconformance in Medical Devices
Effective management of CAPA and Nonconformance in medical devices requires thorough documentation, root cause analysis, and timely implementation of corrective and preventive measures. Utilizing integrated quality management systems (QMS) enhances traceability and accountability, ensuring compliance with FDA and ISO 13485 standards. Regular training and audit reviews optimize CAPA processes, minimizing risks and improving device safety and efficacy.
CAPA vs NC (Corrective and Preventive Action vs Nonconformance) Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com