Post-market surveillance involves the continuous monitoring of a medical device's safety and performance after it has been released to the market, ensuring any emerging risks are identified and managed promptly. Post-market clinical follow-up is a specific subset of surveillance that collects and evaluates clinical data related to the device over time to confirm long-term effectiveness and safety. Both processes are essential for compliance with regulatory requirements and for maintaining patient safety in real-world use scenarios.
Table of Comparison
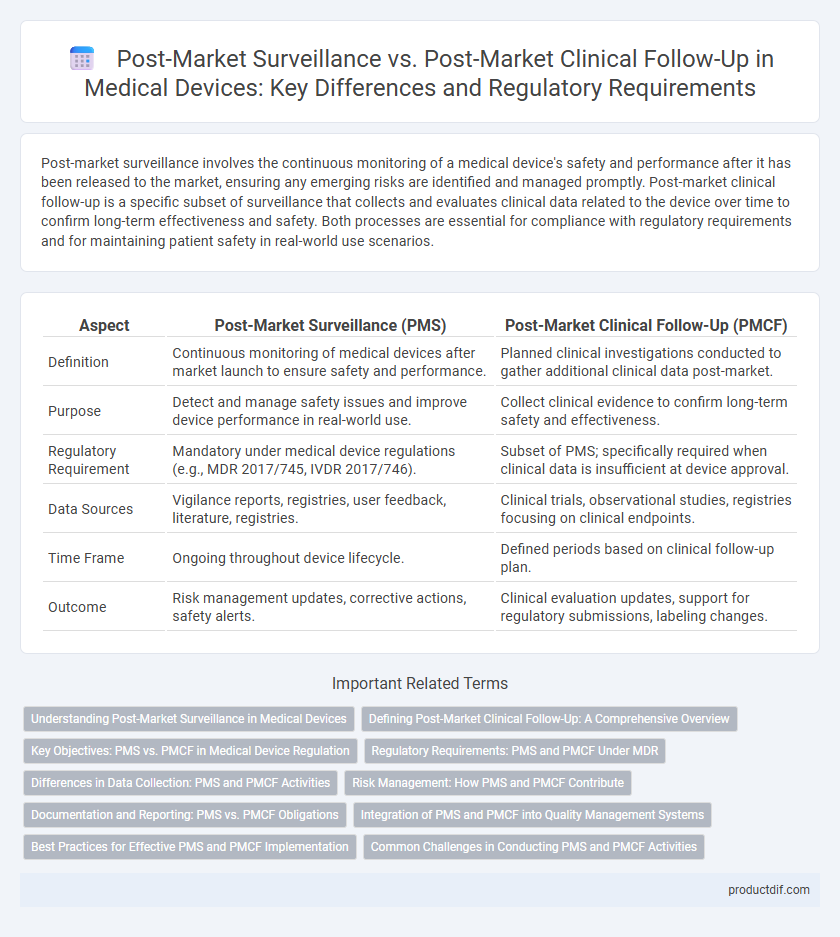
| Aspect | Post-Market Surveillance (PMS) | Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up (PMCF) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous monitoring of medical devices after market launch to ensure safety and performance. | Planned clinical investigations conducted to gather additional clinical data post-market. |
| Purpose | Detect and manage safety issues and improve device performance in real-world use. | Collect clinical evidence to confirm long-term safety and effectiveness. |
| Regulatory Requirement | Mandatory under medical device regulations (e.g., MDR 2017/745, IVDR 2017/746). | Subset of PMS; specifically required when clinical data is insufficient at device approval. |
| Data Sources | Vigilance reports, registries, user feedback, literature, registries. | Clinical trials, observational studies, registries focusing on clinical endpoints. |
| Time Frame | Ongoing throughout device lifecycle. | Defined periods based on clinical follow-up plan. |
| Outcome | Risk management updates, corrective actions, safety alerts. | Clinical evaluation updates, support for regulatory submissions, labeling changes. |
Understanding Post-Market Surveillance in Medical Devices
Post-market surveillance in medical devices involves continuous monitoring of device performance and safety after market approval to detect, assess, and prevent potential risks. It encompasses activities such as data collection, analysis of adverse events, and real-world evidence gathering to ensure ongoing regulatory compliance and patient safety. Post-market clinical follow-up specifically refers to systematic clinical investigations post-market to provide additional safety and effectiveness data, forming a critical subset within the broader surveillance framework.
Defining Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up: A Comprehensive Overview
Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up (PMCF) is a proactive, continuous process designed to collect and evaluate clinical data on a medical device after its market release, ensuring its ongoing safety, effectiveness, and performance in real-world use. PMCF supplements Post-Market Surveillance (PMS) by focusing specifically on clinical aspects, gathering evidence through clinical investigations, registries, or observational studies to monitor potential risks and identify new clinical benefits. This systematic approach supports regulatory compliance under MDR and FDA requirements, guiding device manufacturers in optimizing product lifecycle management and enhancing patient safety outcomes.
Key Objectives: PMS vs. PMCF in Medical Device Regulation
Post-market surveillance (PMS) in medical device regulation primarily aims to continuously monitor the safety and performance of devices throughout their lifecycle using collected real-world data. Post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF) focuses specifically on gathering clinical evidence to confirm device safety and efficacy, addressing any residual risks identified during pre-market evaluation. PMS ensures ongoing risk management and compliance, while PMCF provides targeted clinical data to support regulatory decisions and device improvements.
Regulatory Requirements: PMS and PMCF Under MDR
Post-market surveillance (PMS) under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) requires continuous monitoring of medical device performance and safety throughout its lifecycle, ensuring compliance with EU regulatory standards. Post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF) is a proactive component of PMS, focusing specifically on ongoing clinical data collection to confirm device safety and effectiveness after market release. MDR mandates rigorous documentation and reporting for both PMS and PMCF activities, emphasizing risk management and evidence-based updates to clinical evaluation.
Differences in Data Collection: PMS and PMCF Activities
Post-market surveillance (PMS) involves continuous data collection from various sources such as adverse event reports, registries, and user feedback to monitor the overall safety and performance of a medical device in real-world settings. Post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF) specifically targets clinical data collection through structured studies or investigations aimed at evaluating device performance and clinical outcomes over time. PMS gathers broad safety and performance data, while PMCF emphasizes detailed clinical evidence to support ongoing compliance with regulatory requirements.
Risk Management: How PMS and PMCF Contribute
Post-market surveillance (PMS) systematically collects and analyzes data on medical device performance and adverse events to identify potential risks throughout the product lifecycle. Post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF) specifically targets ongoing clinical evaluation to confirm the device's safety and efficacy in real-world conditions, directly supporting risk management by validating risk control measures. Both PMS and PMCF provide essential feedback loops for updating risk assessments, improving device design, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements such as MDR 2017/745.
Documentation and Reporting: PMS vs. PMCF Obligations
Post-market surveillance (PMS) requires continuous documentation and reporting of real-world device performance data, adverse events, and user feedback to ensure ongoing safety and effectiveness. Post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF) focuses specifically on systematic collection and evaluation of clinical data after market approval to confirm long-term benefits and identify risks. PMS obligations mandate periodic safety update reports (PSURs), while PMCF demands detailed clinical evaluation reports that integrate new clinical evidence into device assessment.
Integration of PMS and PMCF into Quality Management Systems
Post-market surveillance (PMS) and post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF) are essential components integrated into medical device Quality Management Systems (QMS) to ensure ongoing safety and performance. PMS encompasses systematic data collection on device use and adverse events, while PMCF focuses specifically on actively gathering clinical evidence after market release. Integrating both processes within QMS frameworks aligns regulatory compliance with continuous risk management and supports improved clinical outcomes throughout the device lifecycle.
Best Practices for Effective PMS and PMCF Implementation
Post-market surveillance (PMS) comprehensively monitors medical device safety and performance using real-world data, while post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF) specifically collects clinical data to verify ongoing device benefits and risks. Best practices for effective PMS and PMCF implementation include establishing robust data collection systems, integrating risk management processes, and ensuring continuous stakeholder engagement for proactive safety monitoring. Leveraging advanced analytics and adhering to regulatory guidelines like MDR (EU) and FDA requirements optimize the accuracy and responsiveness of post-market activities.
Common Challenges in Conducting PMS and PMCF Activities
Post-market surveillance (PMS) and post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF) both face challenges related to data collection, such as ensuring the accuracy and completeness of real-world evidence from diverse patient populations. Managing regulatory compliance across different regions requires harmonizing varied reporting timelines and requirements, complicating the systematic evaluation of device performance. Limited patient engagement and resource constraints further hinder continuous monitoring, leading to potential gaps in detecting long-term safety and efficacy issues.
Post-market surveillance vs Post-market clinical follow-up Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com