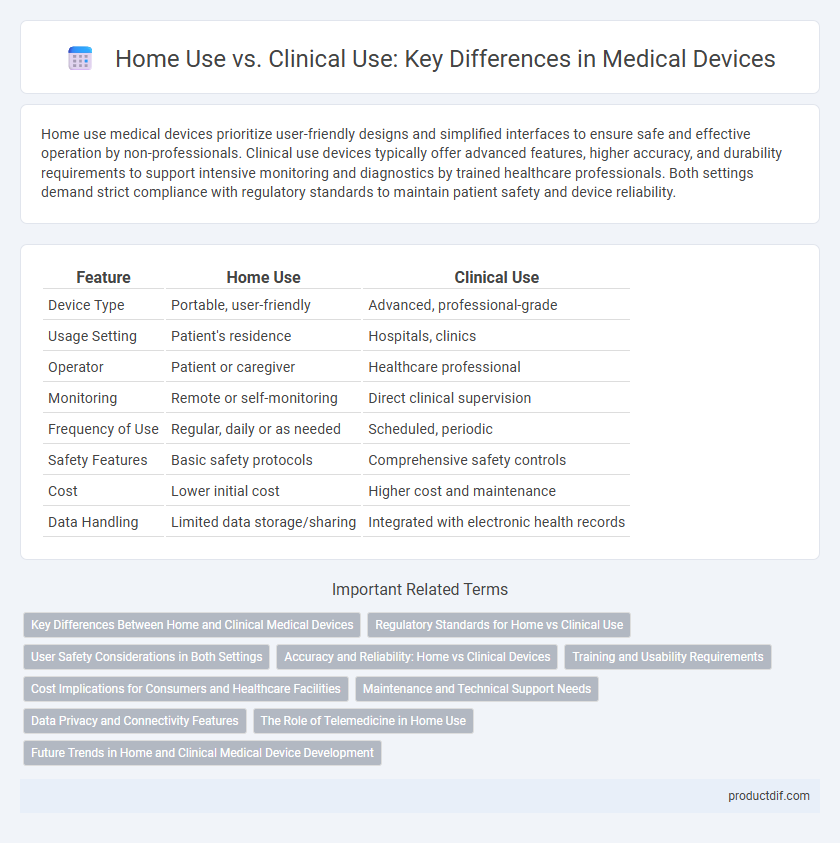
Home use medical devices prioritize user-friendly designs and simplified interfaces to ensure safe and effective operation by non-professionals. Clinical use devices typically offer advanced features, higher accuracy, and durability requirements to support intensive monitoring and diagnostics by trained healthcare professionals. Both settings demand strict compliance with regulatory standards to maintain patient safety and device reliability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Home Use | Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Device Type | Portable, user-friendly | Advanced, professional-grade |
| Usage Setting | Patient's residence | Hospitals, clinics |
| Operator | Patient or caregiver | Healthcare professional |
| Monitoring | Remote or self-monitoring | Direct clinical supervision |
| Frequency of Use | Regular, daily or as needed | Scheduled, periodic |
| Safety Features | Basic safety protocols | Comprehensive safety controls |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost and maintenance |
| Data Handling | Limited data storage/sharing | Integrated with electronic health records |
Key Differences Between Home and Clinical Medical Devices
Home medical devices prioritize ease of use, portability, and patient safety, featuring simplified interfaces and clear instructions to accommodate non-professional users. Clinical medical devices often provide advanced functionalities, higher accuracy, and robust durability, designed for use by trained healthcare professionals in controlled environments. Regulatory standards for home devices emphasize user-friendliness and safety, whereas clinical devices must meet stricter performance and sterilization requirements to ensure reliability in medical settings.
Regulatory Standards for Home vs Clinical Use
Medical devices intended for home use must comply with regulatory standards prioritizing user safety, ease of operation, and minimal risk, often requiring additional labeling and instruction clarity compared to clinical devices. Clinical use devices undergo rigorous evaluation for performance, sterility, and biocompatibility, reflecting controlled environments and trained professional operators. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA enforce distinct pathways, including Human Factors Engineering assessments for home devices and stringent clinical trial data for in-hospital devices.
User Safety Considerations in Both Settings
User safety considerations in home use versus clinical use of medical devices significantly differ due to varying levels of professional supervision and environmental control. Home use devices must prioritize intuitive design, clear instructions, and built-in safety features to minimize user errors by non-professionals, while clinical devices benefit from trained personnel to monitor device operation and respond to complications quickly. Regulatory standards such as FDA's 21 CFR 820 and ISO 13485 emphasize rigorous risk management protocols tailored to each setting to ensure patient safety and device efficacy.
Accuracy and Reliability: Home vs Clinical Devices
Home medical devices often prioritize ease of use and convenience, which can lead to variability in accuracy and reliability compared to clinical-grade devices. Clinical devices undergo stringent calibration and validation processes, ensuring higher precision and consistent performance crucial for diagnostic and treatment decisions. While home use devices serve well for routine monitoring, their data may not always match the rigorous accuracy required in clinical settings.
Training and Usability Requirements
Home use medical devices demand intuitive design and simplified interfaces to accommodate users with limited medical knowledge, ensuring safety and ease of operation without professional supervision. Clinical use devices require comprehensive training programs and specialized knowledge to handle complex functions and ensure accurate diagnostics or treatment. The disparity in training intensity and usability features directly impacts device design, regulatory approval, and patient outcomes.
Cost Implications for Consumers and Healthcare Facilities
Home-use medical devices generally offer lower upfront and operational costs for consumers compared to the higher expenses associated with clinical-use equipment, which includes professional maintenance and facility overheads. Healthcare facilities face significant capital investment and ongoing expenses for clinical-grade devices, influencing budget allocations and reimbursement rates. Cost-effective home-use devices can reduce overall healthcare spending by minimizing hospital visits and enabling remote patient monitoring.
Maintenance and Technical Support Needs
Home use medical devices demand user-friendly maintenance protocols and accessible technical support to ensure patient safety and device reliability. Clinical use devices require specialized maintenance by trained biomedical technicians and prompt technical support to minimize downtime and comply with regulatory standards. Efficient maintenance strategies and robust technical support systems are critical for both settings to optimize device performance and patient outcomes.
Data Privacy and Connectivity Features
Home use medical devices prioritize robust data encryption protocols and user-friendly connectivity options like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi to ensure secure transmission of sensitive health information, complying with HIPAA and GDPR standards. Clinical use devices often integrate with hospital information systems (HIS) and electronic health records (EHR), supporting high-throughput data exchange with stringent access controls and audit trails. Both settings emphasize end-to-end security measures and real-time data synchronization to maintain patient privacy and enhance monitoring accuracy.
The Role of Telemedicine in Home Use
Telemedicine significantly enhances home use of medical devices by enabling remote monitoring and real-time data transmission to healthcare providers, improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital visits. Integration of wearable sensors and mobile health apps allows continuous tracking of vital signs and chronic conditions, facilitating timely interventions without the need for clinical visits. This shift supports personalized healthcare management, increases patient engagement, and optimizes resource allocation in medical care delivery.
Future Trends in Home and Clinical Medical Device Development
Future trends in home medical device development emphasize user-friendly interfaces, wireless connectivity, and integration with telemedicine platforms, enhancing patient self-monitoring and real-time data sharing with healthcare providers. Clinical medical devices are advancing toward AI-driven diagnostics, miniaturization, and interoperability with electronic health records (EHR), improving accuracy and workflow efficiency in hospital settings. Both domains prioritize cybersecurity and regulatory compliance to ensure patient safety and data integrity in increasingly connected healthcare environments.
Home use vs Clinical use Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com