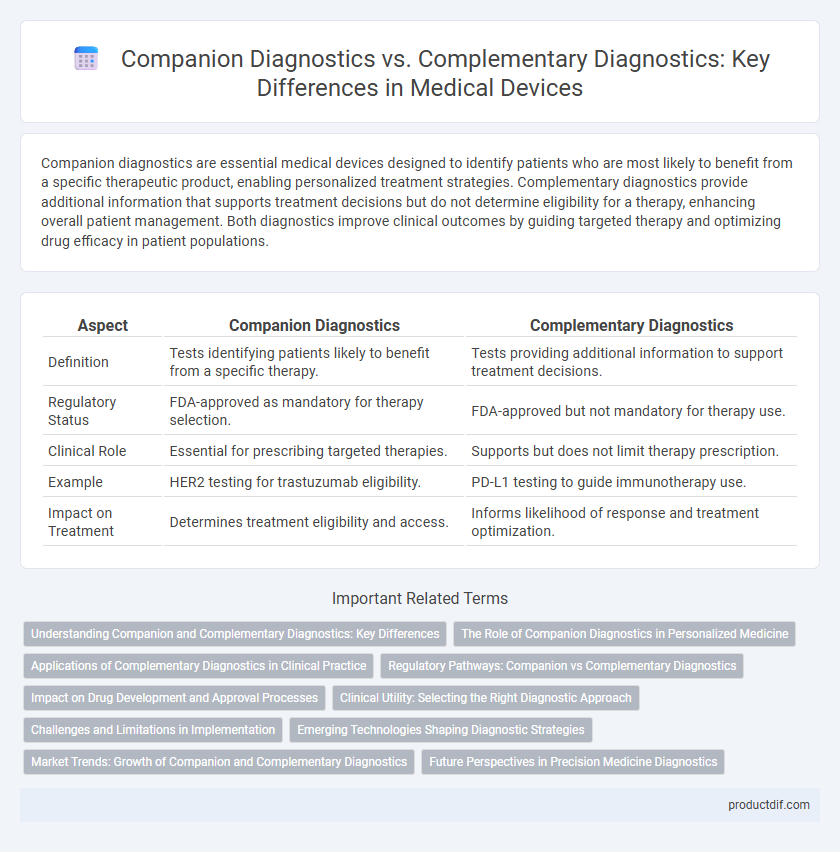
Companion diagnostics are essential medical devices designed to identify patients who are most likely to benefit from a specific therapeutic product, enabling personalized treatment strategies. Complementary diagnostics provide additional information that supports treatment decisions but do not determine eligibility for a therapy, enhancing overall patient management. Both diagnostics improve clinical outcomes by guiding targeted therapy and optimizing drug efficacy in patient populations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Companion Diagnostics | Complementary Diagnostics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tests identifying patients likely to benefit from a specific therapy. | Tests providing additional information to support treatment decisions. |
| Regulatory Status | FDA-approved as mandatory for therapy selection. | FDA-approved but not mandatory for therapy use. |
| Clinical Role | Essential for prescribing targeted therapies. | Supports but does not limit therapy prescription. |
| Example | HER2 testing for trastuzumab eligibility. | PD-L1 testing to guide immunotherapy use. |
| Impact on Treatment | Determines treatment eligibility and access. | Informs likelihood of response and treatment optimization. |
Understanding Companion and Complementary Diagnostics: Key Differences
Companion diagnostics are essential medical tests that identify patients who are most likely to benefit from a specific therapy by detecting biomarkers, ensuring personalized treatment efficacy and safety. Complementary diagnostics, meanwhile, provide additional information about treatment response and can guide therapy decisions but are not mandatory for drug use approval. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for optimizing targeted therapies and enhancing patient outcomes in precision medicine.
The Role of Companion Diagnostics in Personalized Medicine
Companion diagnostics play a crucial role in personalized medicine by identifying patients most likely to benefit from a specific therapeutic product, enhancing treatment efficacy and safety. These tests enable targeted therapies based on genetic, proteomic, or metabolic biomarkers, optimizing drug selection and dosing. Unlike complementary diagnostics, which provide additional information without determining treatment eligibility, companion diagnostics directly inform clinical decisions and regulatory approvals.
Applications of Complementary Diagnostics in Clinical Practice
Complementary diagnostics guide treatment decisions by identifying patients who may benefit from therapy but are not required for drug administration, enhancing personalized medicine strategies. These tests are applied to optimize treatment efficacy and safety in diseases such as cancer, where they help in assessing additional therapeutic options beyond standard protocols. Clinical applications of complementary diagnostics include monitoring drug resistance and tailoring combination therapies to improve patient outcomes.
Regulatory Pathways: Companion vs Complementary Diagnostics
Regulatory pathways for companion diagnostics are typically more stringent, requiring simultaneous approval with the associated therapeutic to ensure safe and effective patient selection for targeted treatments. Complementary diagnostics undergo a less rigorous regulatory process, often receiving approval after the therapeutic, providing additional information to guide treatment decisions without restricting drug use. Understanding these differences is crucial for developers to align regulatory strategies and optimize clinical and commercial outcomes.
Impact on Drug Development and Approval Processes
Companion diagnostics directly influence drug development by enabling targeted therapies, improving clinical trial design, and increasing the likelihood of regulatory approval through biomarker-driven patient selection. Complementary diagnostics provide additional information about drug response or risk, supporting broader patient use but without the necessity for strict patient selection, which may streamline approval in more heterogeneous populations. Both diagnostics impact regulatory pathways, but companion diagnostics usually require simultaneous approval with the therapeutic, intensifying coordination between drug and diagnostic development.
Clinical Utility: Selecting the Right Diagnostic Approach
Companion diagnostics provide essential clinical utility by enabling targeted therapy selection based on specific biomarkers, thereby improving treatment efficacy and patient outcomes. Complementary diagnostics, while not required for drug administration, offer valuable additional information that enhances clinical decision-making and optimizes therapeutic strategies. Choosing the right diagnostic approach depends on the clinical context, biomarker relevance, and the intended therapeutic impact to maximize personalized medicine benefits.
Challenges and Limitations in Implementation
Challenges in implementing companion diagnostics include high development costs, stringent regulatory requirements, and the need for robust clinical validation to ensure accuracy and reliability. Complementary diagnostics face limitations such as limited predictive power for therapy response and difficulties integrating test results into clinical decision-making. Both types require coordinated efforts between diagnostic developers, clinicians, and regulatory bodies to overcome complexities in sample handling, reimbursement, and data interpretation.
Emerging Technologies Shaping Diagnostic Strategies
Companion diagnostics utilize biomarkers to identify patients most likely to benefit from a specific therapeutic product, enabling personalized treatment plans, while complementary diagnostics provide information on drug efficacy and safety but are not mandatory for treatment access. Emerging technologies such as advanced genomics, liquid biopsies, and AI-driven analytics are revolutionizing both companion and complementary diagnostics by enhancing precision, reducing turnaround times, and enabling dynamic monitoring of treatment responses. Integration of next-generation sequencing (NGS) and multiplex assays in companion and complementary diagnostics continues to transform oncology and infectious disease management through highly tailored and real-time diagnostic strategies.
Market Trends: Growth of Companion and Complementary Diagnostics
The market for companion diagnostics is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 12%, driven by the increasing adoption of personalized medicine and targeted therapies. Complementary diagnostics are also experiencing significant expansion as they support the broader use of immunotherapies and enable treatment optimization for diverse patient populations. Key factors fueling this growth include advancements in biomarker discovery, regulatory support, and rising investments in precision medicine technologies.
Future Perspectives in Precision Medicine Diagnostics
Companion diagnostics enable personalized treatment by identifying patients most likely to benefit from specific therapies, driving targeted drug development and regulatory approvals. Complementary diagnostics provide additional information to guide treatment decisions but do not restrict patient eligibility, enhancing therapeutic efficacy in heterogeneous populations. Future perspectives emphasize integrating advanced genomic profiling and AI-driven analytics to refine both diagnostic types, facilitating more precise and adaptive treatment strategies in precision medicine.
Companion diagnostics vs Complementary diagnostics Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com