An endoscope is a flexible or rigid instrument equipped with a camera used to examine internal organs through natural body openings, enabling minimally invasive diagnostics and biopsies. A laparoscope, a specialized type of endoscope, is primarily employed in abdominal surgeries through small incisions, allowing surgeons to perform procedures with enhanced precision and reduced recovery time. Both devices revolutionize medical interventions by minimizing patient trauma and improving visualization during examinations and surgeries.
Table of Comparison
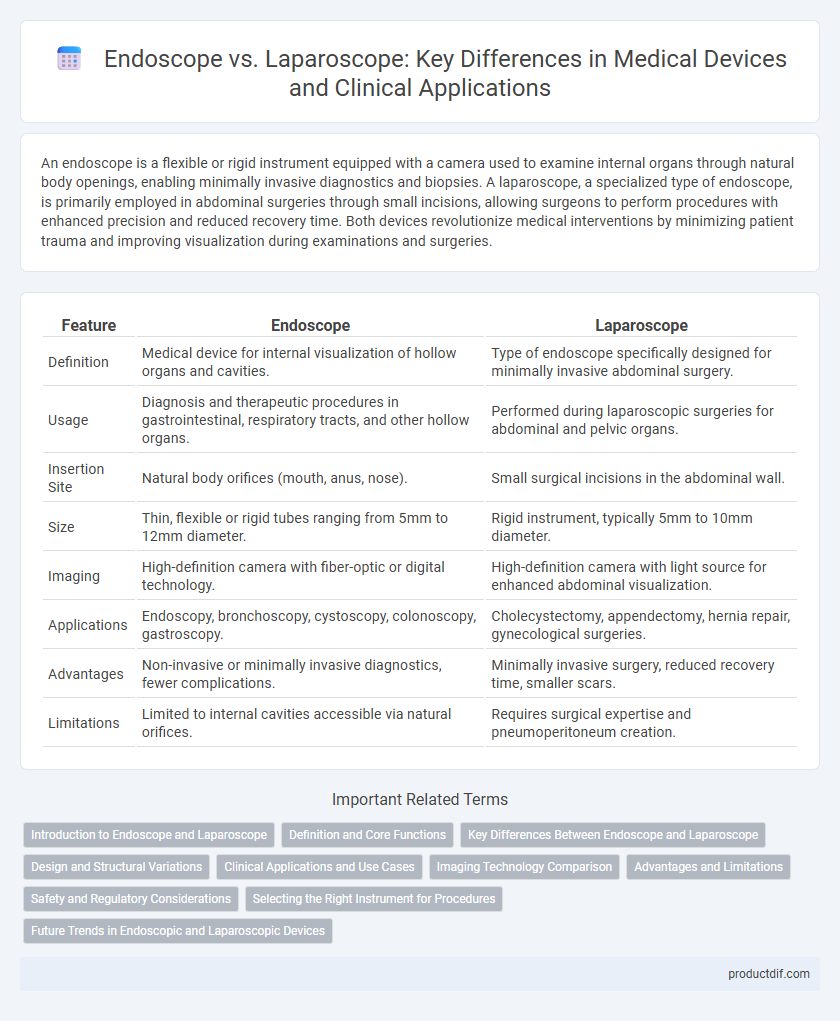
| Feature | Endoscope | Laparoscope |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Medical device for internal visualization of hollow organs and cavities. | Type of endoscope specifically designed for minimally invasive abdominal surgery. |
| Usage | Diagnosis and therapeutic procedures in gastrointestinal, respiratory tracts, and other hollow organs. | Performed during laparoscopic surgeries for abdominal and pelvic organs. |
| Insertion Site | Natural body orifices (mouth, anus, nose). | Small surgical incisions in the abdominal wall. |
| Size | Thin, flexible or rigid tubes ranging from 5mm to 12mm diameter. | Rigid instrument, typically 5mm to 10mm diameter. |
| Imaging | High-definition camera with fiber-optic or digital technology. | High-definition camera with light source for enhanced abdominal visualization. |
| Applications | Endoscopy, bronchoscopy, cystoscopy, colonoscopy, gastroscopy. | Cholecystectomy, appendectomy, hernia repair, gynecological surgeries. |
| Advantages | Non-invasive or minimally invasive diagnostics, fewer complications. | Minimally invasive surgery, reduced recovery time, smaller scars. |
| Limitations | Limited to internal cavities accessible via natural orifices. | Requires surgical expertise and pneumoperitoneum creation. |
Introduction to Endoscope and Laparoscope
Endoscopes are flexible or rigid medical instruments equipped with a light source and camera, designed to visualize internal organs and cavities through natural body openings or small incisions. Laparoscopes, a specialized type of endoscope, are primarily used for minimally invasive abdominal and pelvic surgeries, providing high-resolution imaging through small incisions in the abdominal wall. Both devices revolutionize diagnostic and therapeutic procedures by minimizing patient trauma, enhancing precision, and reducing recovery time.
Definition and Core Functions
An endoscope is a medical device equipped with a flexible or rigid tube and a camera used for visual examination and diagnosis inside the body's hollow organs and cavities. A laparoscope is a specialized type of endoscope designed primarily for minimally invasive surgery within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, enabling surgeons to perform procedures with small incisions. Both devices are critical in enhancing medical visualization, but laparoscopes additionally facilitate surgical intervention alongside diagnostic capabilities.
Key Differences Between Endoscope and Laparoscope
Endoscopes are flexible or rigid instruments used for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures within hollow organs or cavities, while laparoscopes are a type of rigid endoscope specifically designed for minimally invasive abdominal and pelvic surgeries. Endoscopes provide real-time visualization and access to areas such as the gastrointestinal tract, whereas laparoscopes facilitate surgical interventions with specialized tools through small incisions. Key differences include the target anatomical regions, instrument flexibility, and typical applications in diagnostic versus operative procedures.
Design and Structural Variations
Endoscopes feature a flexible, slender tube equipped with a light source and camera, enabling navigation through natural body openings for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Laparoscopes are rigid instruments with a straight, tubular design and integrated optics, optimized for minimally invasive surgeries via small abdominal incisions. Structural variations include endoscopes' flexibility for accessing complex anatomical pathways, contrasting with laparoscopes' fixed shape that provides stability and precision in the peritoneal cavity.
Clinical Applications and Use Cases
Endoscopes are primarily utilized for diagnostic procedures such as gastrointestinal examinations, bronchoscopy, and cystoscopy to visualize internal organs with minimal invasiveness. Laparoscopes are specialized endoscopes designed for abdominal and pelvic surgeries, enabling procedures like cholecystectomy, appendectomy, and gynecological surgeries through small incisions. Both devices enhance surgical precision and reduce patient recovery time, but laparoscopes are more focused on operative interventions while endoscopes provide broader diagnostic capabilities.
Imaging Technology Comparison
Endoscopes utilize fiber-optic or digital cameras to provide high-resolution, real-time images primarily of internal organs and cavities, enabling diagnosis and minor procedures. Laparoscopes, a specialized type of endoscope, incorporate advanced imaging technologies such as HD or 4K cameras with integrated light sources to offer enhanced visualization of the abdominal and pelvic regions during minimally invasive surgeries. The superior imaging clarity and depth perception in laparoscopes improve surgical precision and patient outcomes compared to standard endoscopic devices.
Advantages and Limitations
Endoscopes offer superior flexibility and are ideal for diagnostic procedures due to their ability to navigate complex internal pathways and provide real-time imaging with minimal invasiveness. Laparoscopes excel in surgical applications by enabling precise tissue manipulation and access to the abdominal cavity through small incisions, which reduces patient recovery time. However, endoscopes can be limited by their range of motion and depth, while laparoscopes require general anesthesia and carry risks associated with surgical interventions.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Endoscopes and laparoscopes adhere to stringent regulatory standards set by bodies such as the FDA and EMA, ensuring biocompatibility and sterilization protocols vital for patient safety. Both devices undergo rigorous risk assessments and validation processes to minimize infection risks and mechanical failures during procedures. Continuous monitoring and reporting of adverse events are mandated to maintain compliance and enhance device safety profiles.
Selecting the Right Instrument for Procedures
Endoscopes provide detailed internal imaging for diagnostic and minimally invasive procedures across various organ systems, while laparoscopes are specifically designed for abdominal and pelvic surgeries, offering enhanced maneuverability and precision. Selecting the right instrument depends on the clinical application, required visualization depth, and surgical access, with endoscopes favored for flexible navigation and laparoscopes preferred for rigid, stable interventions. Understanding the specific features and limitations of each device ensures optimal patient outcomes and procedural efficiency.
Future Trends in Endoscopic and Laparoscopic Devices
Emerging innovations in endoscopic and laparoscopic devices emphasize enhanced imaging technologies such as ultra-high-definition cameras and 3D visualization, improving diagnostic accuracy and surgical precision. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms is driving real-time analysis and decision support, transforming minimally invasive procedures. Advances in flexible instrumentation and robotic-assisted platforms are expanding the range of treatable conditions and optimizing patient outcomes in endoscopic and laparoscopic surgery.
Endoscope vs Laparoscope Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com