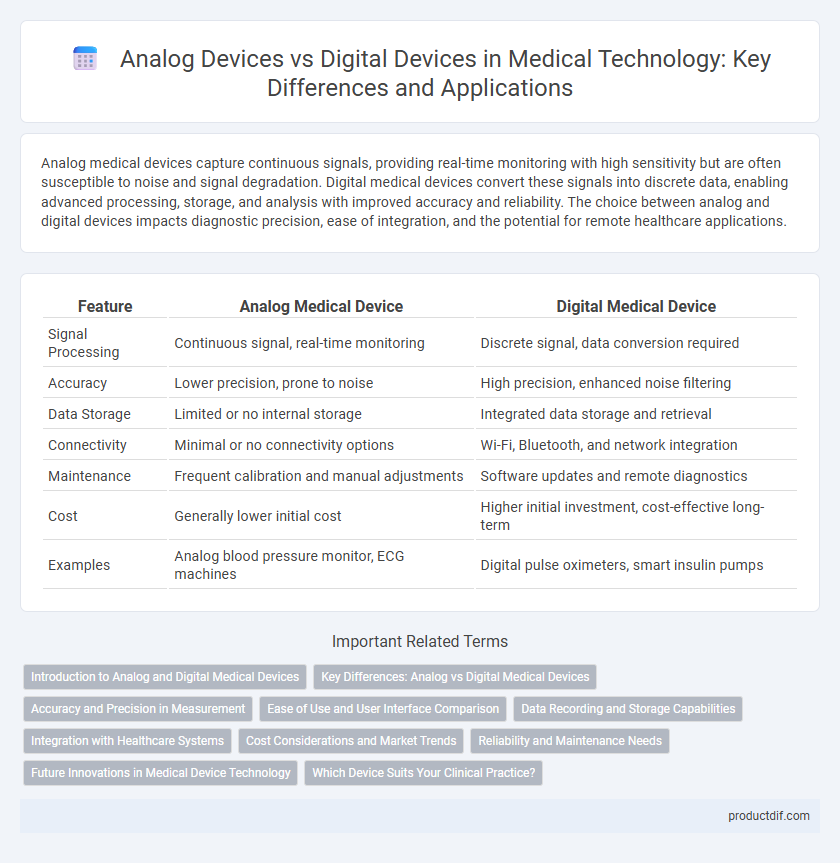
Analog medical devices capture continuous signals, providing real-time monitoring with high sensitivity but are often susceptible to noise and signal degradation. Digital medical devices convert these signals into discrete data, enabling advanced processing, storage, and analysis with improved accuracy and reliability. The choice between analog and digital devices impacts diagnostic precision, ease of integration, and the potential for remote healthcare applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Analog Medical Device | Digital Medical Device |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Processing | Continuous signal, real-time monitoring | Discrete signal, data conversion required |
| Accuracy | Lower precision, prone to noise | High precision, enhanced noise filtering |
| Data Storage | Limited or no internal storage | Integrated data storage and retrieval |
| Connectivity | Minimal or no connectivity options | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and network integration |
| Maintenance | Frequent calibration and manual adjustments | Software updates and remote diagnostics |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial investment, cost-effective long-term |
| Examples | Analog blood pressure monitor, ECG machines | Digital pulse oximeters, smart insulin pumps |
Introduction to Analog and Digital Medical Devices
Analog medical devices capture continuous physiological signals such as heart rate and blood pressure in real-time, providing precise, uninterrupted data crucial for monitoring gradual changes. Digital medical devices convert these analog signals into discrete numerical data through analog-to-digital converters, enabling advanced data processing, storage, and interpretation by healthcare software. Understanding the differences in signal handling and data output between analog and digital devices is essential for selecting appropriate medical technology in diagnostics and patient care.
Key Differences: Analog vs Digital Medical Devices
Analog medical devices process continuous signals representing physiological data, offering real-time monitoring with high fidelity but limited noise resistance. Digital medical devices convert signals into discrete digital values, enabling advanced data analysis, storage, and integration with electronic health records, enhancing accuracy and functionality. Key differences include signal processing methods, data precision, and compatibility with modern healthcare IT systems.
Accuracy and Precision in Measurement
Analog medical devices provide continuous signal representation, allowing high-resolution readings but are susceptible to signal noise affecting accuracy. Digital medical devices convert analog inputs into discrete values, offering improved precision through error correction algorithms and consistent repeatability in measurements. Accuracy in digital systems often surpasses analog counterparts due to enhanced calibration capabilities and noise reduction technologies.
Ease of Use and User Interface Comparison
Analog medical devices offer intuitive controls with tactile feedback, making them easier to operate for users familiar with traditional equipment. Digital devices provide customizable interfaces with clear visual displays, enabling precise adjustments and real-time data monitoring that enhance user experience. User interface design in digital devices supports integration with electronic health records, streamlining workflow and improving overall ease of use in clinical settings.
Data Recording and Storage Capabilities
Analog medical devices capture physiological data continuously in real-time, offering high-fidelity signal representation but limited data storage capacity, typically relying on magnetic tapes or paper charts. Digital medical devices convert analog signals into discrete digital data, enabling extensive data recording, efficient storage, and easy retrieval through electronic health records and cloud-based systems. Digital storage supports advanced analytics, long-term data preservation, and seamless integration with other medical software, significantly enhancing clinical decision-making.
Integration with Healthcare Systems
Analog medical devices transmit continuous, real-time physiological signals but face challenges integrating seamlessly with modern healthcare systems due to limited digital compatibility. Digital devices convert patient data into precise, standardized formats, enabling real-time interoperability with electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine platforms, and clinical decision support systems. Enhanced integration of digital medical devices improves data accuracy, facilitates remote patient monitoring, and supports advanced analytics for personalized treatment plans.
Cost Considerations and Market Trends
Analog medical devices generally incur lower upfront costs due to simpler design and manufacturing processes, making them accessible for basic diagnostic applications. Digital devices, while initially more expensive, offer enhanced precision, data integration, and remote monitoring capabilities, driving higher long-term value and adoption in telemedicine and advanced diagnostics. Market trends indicate growing investment in digital technology innovation, fueled by increasing demand for AI-driven healthcare solutions and interoperability with electronic health records (EHR).
Reliability and Maintenance Needs
Analog devices in medical settings offer continuous signal monitoring with simpler maintenance requirements but may suffer from signal degradation over time, impacting reliability. Digital devices provide enhanced precision, data storage, and error correction, resulting in higher reliability but often demand more complex maintenance and software updates. Choosing between analog and digital medical devices depends on balancing the need for consistent performance with the facility's capacity for ongoing technical support.
Future Innovations in Medical Device Technology
Future innovations in medical device technology increasingly favor digital devices due to their superior data processing, real-time monitoring, and connectivity capabilities compared to analog devices. Enhanced artificial intelligence algorithms and advanced sensors integrated into digital medical devices enable more precise diagnostics and personalized treatment plans. Emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled wearable devices and cloud-based health platforms are revolutionizing patient care by facilitating continuous health tracking and remote medical interventions.
Which Device Suits Your Clinical Practice?
Analog devices offer continuous signal measurement, providing high-resolution data ideal for monitoring subtle physiological changes in real-time clinical settings. Digital devices convert signals into discrete numerical values, enhancing data storage, processing accuracy, and integration with electronic health records, making them suitable for diagnostic precision and remote patient monitoring. Choosing between analog and digital medical devices depends on the clinical need for real-time responsiveness versus data analysis, interoperability, and long-term record keeping.
Analog Device vs Digital Device Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com