Human Factors Engineering emphasizes designing medical devices based on understanding human capabilities, limitations, and behaviors to enhance safety and performance. Usability Engineering focuses on evaluating and improving the interaction between users and medical devices through systematic testing and iterative design processes. Both disciplines are essential for creating effective medical devices that reduce user errors and improve patient outcomes.
Table of Comparison
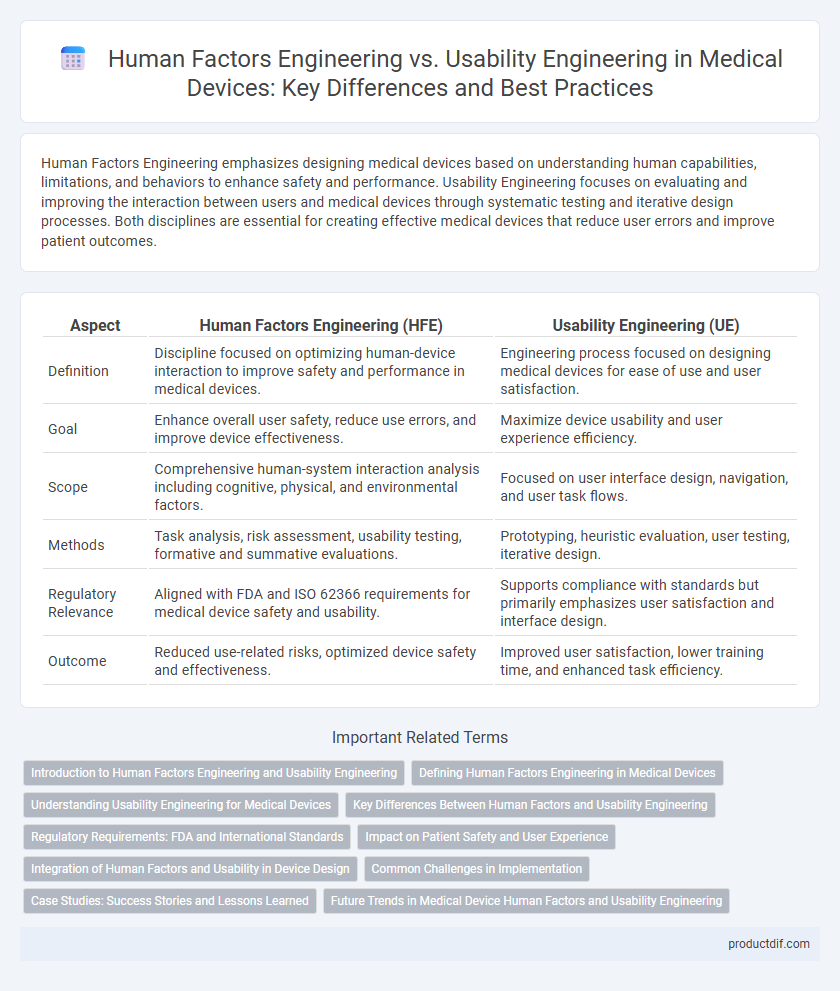
| Aspect | Human Factors Engineering (HFE) | Usability Engineering (UE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Discipline focused on optimizing human-device interaction to improve safety and performance in medical devices. | Engineering process focused on designing medical devices for ease of use and user satisfaction. |
| Goal | Enhance overall user safety, reduce use errors, and improve device effectiveness. | Maximize device usability and user experience efficiency. |
| Scope | Comprehensive human-system interaction analysis including cognitive, physical, and environmental factors. | Focused on user interface design, navigation, and user task flows. |
| Methods | Task analysis, risk assessment, usability testing, formative and summative evaluations. | Prototyping, heuristic evaluation, user testing, iterative design. |
| Regulatory Relevance | Aligned with FDA and ISO 62366 requirements for medical device safety and usability. | Supports compliance with standards but primarily emphasizes user satisfaction and interface design. |
| Outcome | Reduced use-related risks, optimized device safety and effectiveness. | Improved user satisfaction, lower training time, and enhanced task efficiency. |
Introduction to Human Factors Engineering and Usability Engineering
Human Factors Engineering in medical devices focuses on optimizing device design by understanding the interactions between users and technology to enhance safety and performance. Usability Engineering emphasizes systematic evaluation methods to ensure devices are intuitive, efficient, and reduce user errors. Both disciplines integrate ergonomic principles and user-centered design to improve clinical outcomes and regulatory compliance.
Defining Human Factors Engineering in Medical Devices
Human Factors Engineering in medical devices focuses on understanding how users interact with devices to enhance safety, effectiveness, and user satisfaction by minimizing use-related risks. It incorporates ergonomic principles, cognitive psychology, and user experience research to design devices that accommodate human limitations and capabilities. Key activities include task analysis, usability testing, and risk assessment to ensure device design aligns with real-world clinical environments and user needs.
Understanding Usability Engineering for Medical Devices
Usability Engineering for medical devices focuses on systematically optimizing device interfaces to enhance user interaction, minimize use errors, and improve patient safety. It involves rigorous user research, iterative design, and validation testing aligned with regulatory standards such as IEC 62366 to ensure devices meet real-world usability requirements. Understanding these principles is critical for developing medical devices that cater to diverse clinical environments and user capabilities.
Key Differences Between Human Factors and Usability Engineering
Human Factors Engineering emphasizes understanding human capabilities and limitations to design safe, effective medical devices, while Usability Engineering primarily focuses on optimizing the interaction between users and devices to enhance ease of use. Human Factors involves comprehensive analysis of user behavior, environmental conditions, and safety risks, whereas Usability centers on task efficiency, error reduction, and user satisfaction during operation. Both disciplines aim to improve medical device performance but differ in scope, with Human Factors encompassing broader cognitive and ergonomic considerations and Usability Engineering targeting practical user interface improvements.
Regulatory Requirements: FDA and International Standards
Human Factors Engineering (HFE) and Usability Engineering both address user interaction with medical devices, but HFE emphasizes comprehensive risk management aligned with FDA guidance such as FDA's Human Factors and Usability Engineering Design Control Guidance, while Usability Engineering often focuses on optimizing device interfaces per IEC 62366 standards. FDA mandates submission of usability validation data demonstrating minimized use-related risks, whereas international standards like ISO 14971 integrate risk management with human factors considerations for global regulatory compliance. Compliance with both FDA and international requirements ensures medical devices meet safety, effectiveness, and usability criteria critical for market approval and patient safety.
Impact on Patient Safety and User Experience
Human Factors Engineering systematically integrates human capabilities and limitations into medical device design, significantly reducing user errors and enhancing patient safety by optimizing device interaction. Usability Engineering focuses on evaluating and improving the device's interface and functionality through user-centric testing, directly influencing user satisfaction and minimizing operational risks. Both disciplines collaborate to create medical devices that are intuitive, safe, and effective, thereby improving clinical outcomes and patient care quality.
Integration of Human Factors and Usability in Device Design
Human Factors Engineering focuses on understanding user interactions, cognitive load, and ergonomic aspects to enhance safety and effectiveness in medical device design. Usability Engineering emphasizes systematic evaluation of user interfaces and tasks to optimize intuitive operation and reduce errors. Integrating Human Factors and Usability Engineering ensures comprehensive insight into user needs, aligning ergonomic principles with interface design for improved device performance and patient outcomes.
Common Challenges in Implementation
Human Factors Engineering and Usability Engineering in medical device development face common challenges such as integrating user feedback early in the design process, addressing diverse user needs across clinical environments, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards like FDA's Human Factors Guidance. Balancing device complexity with intuitive interface design often leads to iterative testing and redesign, which can prolong development timelines. Both disciplines require multidisciplinary collaboration to mitigate risks related to user errors and enhance patient safety effectively.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Human Factors Engineering (HFE) and Usability Engineering (UE) play pivotal roles in medical device design, with HFE focusing on optimizing user interactions to enhance safety, while UE emphasizes intuitive interfaces that improve efficiency and satisfaction. Case studies from leading medical device manufacturers reveal that integrating HFE principles reduced user errors by 30%, whereas UX improvements led to a 25% increase in task completion speed. Key lessons highlight the importance of iterative testing with real users and early-stage integration of both engineering approaches to ensure regulatory compliance and maximize patient safety.
Future Trends in Medical Device Human Factors and Usability Engineering
Future trends in medical device human factors and usability engineering emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance user interaction and device adaptability. Immersive technologies such as augmented reality are being explored to improve training and real-time device operation, reducing user errors. Regulatory bodies increasingly mandate comprehensive usability testing, driving innovation toward more intuitive, user-centered design processes in medical device development.
Human Factors Engineering vs Usability Engineering Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com