Wireless telemetry offers enhanced patient mobility and reduces infection risks by eliminating physical cables, making it ideal for continuous remote monitoring in medical settings. Wired monitoring provides reliable data transmission with minimal signal interference and is often preferred in critical situations where consistent connectivity is paramount. Choosing between wireless and wired systems depends on the clinical environment, patient condition, and required data accuracy.
Table of Comparison
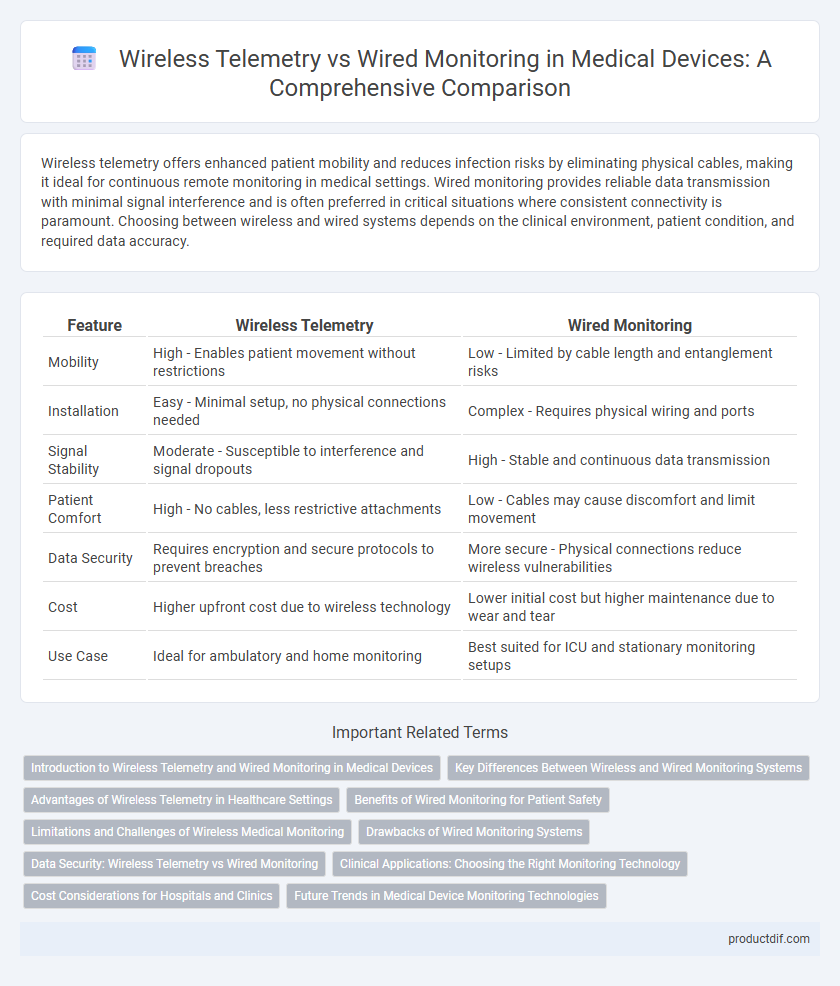
| Feature | Wireless Telemetry | Wired Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | High - Enables patient movement without restrictions | Low - Limited by cable length and entanglement risks |
| Installation | Easy - Minimal setup, no physical connections needed | Complex - Requires physical wiring and ports |
| Signal Stability | Moderate - Susceptible to interference and signal dropouts | High - Stable and continuous data transmission |
| Patient Comfort | High - No cables, less restrictive attachments | Low - Cables may cause discomfort and limit movement |
| Data Security | Requires encryption and secure protocols to prevent breaches | More secure - Physical connections reduce wireless vulnerabilities |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to wireless technology | Lower initial cost but higher maintenance due to wear and tear |
| Use Case | Ideal for ambulatory and home monitoring | Best suited for ICU and stationary monitoring setups |
Introduction to Wireless Telemetry and Wired Monitoring in Medical Devices
Wireless telemetry in medical devices enables real-time patient data transmission without physical cables, enhancing mobility and reducing infection risks. Wired monitoring relies on direct physical connections for continuous data accuracy and stable signal quality, often preferred in critical care settings. Advances in wireless technology now offer comparable reliability and security, expanding its use in diverse clinical environments.
Key Differences Between Wireless and Wired Monitoring Systems
Wireless telemetry in medical devices offers enhanced patient mobility and reduces physical constraints compared to wired monitoring systems, which rely on direct cable connections for data transmission. Wired monitoring typically provides more stable and consistent data streams with lower latency, while wireless systems depend on secure, high-frequency radio waves or Bluetooth technology that may occasionally face interference. The choice between wireless and wired monitoring impacts clinical workflow, patient comfort, data accuracy, and the risk of infection due to cable management.
Advantages of Wireless Telemetry in Healthcare Settings
Wireless telemetry in healthcare settings offers enhanced patient mobility and comfort by eliminating restrictive cables, facilitating continuous monitoring without hindering movement. It enables real-time data transmission to healthcare providers, improving response times and enabling proactive patient care. Wireless systems also reduce infection risks associated with wired equipment and simplify installation and maintenance in clinical environments.
Benefits of Wired Monitoring for Patient Safety
Wired monitoring offers superior reliability and continuous data transmission essential for critical patient safety by eliminating interference and signal loss common in wireless telemetry. It ensures consistent real-time tracking of vital signs, enabling immediate medical intervention when necessary. The stable and secure connection of wired systems reduces the risk of data corruption or breaches, crucial for maintaining patient confidentiality and care accuracy.
Limitations and Challenges of Wireless Medical Monitoring
Wireless medical monitoring faces limitations such as signal interference, limited battery life, and data security vulnerabilities, which can compromise continuous patient care. Environmental factors and physical obstructions often degrade signal quality, leading to potential data loss or delayed alerts. Ensuring reliable, real-time monitoring remains challenging due to these constraints compared to the stable connection of wired systems.
Drawbacks of Wired Monitoring Systems
Wired monitoring systems in medical devices present significant limitations, including restricted patient mobility due to physical cable connections and increased risk of disconnection or signal interference. These systems often lead to patient discomfort and complicate emergency response scenarios in clinical settings. Moreover, wired setups require extensive installation and maintenance efforts, raising overall operational costs and reducing workflow efficiency.
Data Security: Wireless Telemetry vs Wired Monitoring
Wireless telemetry in medical devices offers convenient remote monitoring but poses heightened risks of data breaches and interception due to reliance on wireless signals. Wired monitoring systems provide enhanced data security with direct, physical connections that limit unauthorized access and reduce vulnerability to cyberattacks. Healthcare facilities prioritize wired monitoring when stringent data protection is essential, while employing advanced encryption protocols in wireless telemetry to mitigate security threats.
Clinical Applications: Choosing the Right Monitoring Technology
Wireless telemetry offers enhanced patient mobility and real-time data transmission critical for intensive care units and remote monitoring scenarios, improving clinical outcomes. Wired monitoring provides reliable, uninterrupted data flow with reduced susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, ideal for high-acuity environments requiring continuous ECG and vital sign measurements. Selecting the appropriate technology depends on clinical setting requirements, patient comfort, and the need for data accuracy and transmission stability.
Cost Considerations for Hospitals and Clinics
Wireless telemetry systems in hospitals and clinics reduce installation and maintenance costs by eliminating extensive cabling and infrastructure requirements. Wired monitoring systems may involve higher upfront expenses due to hardware and labor-intensive setup but offer consistent performance with minimal interference. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including long-term reliability and patient mobility benefits, is essential for healthcare facilities when choosing between wireless and wired monitoring solutions.
Future Trends in Medical Device Monitoring Technologies
Wireless telemetry in medical device monitoring is advancing rapidly through integration with IoT and AI, enabling real-time, remote patient data analysis and predictive healthcare insights. Wired monitoring remains essential for critical care due to its reliability and low latency, particularly in intensive care units and surgical environments. Future trends emphasize hybrid systems combining wired stability with wireless mobility, enhanced cybersecurity protocols, and energy-efficient sensor designs to optimize continuous patient monitoring.
Wireless telemetry vs Wired monitoring Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com