Bench testing offers rapid, controlled evaluation of medical devices using mechanical and electronic simulations, ensuring precise measurement of performance and safety parameters. Animal testing provides crucial biological insights by mimicking physiological responses, enabling assessment of device interaction within living tissues and identification of potential adverse effects. Combining bench testing and animal testing enhances device validation by balancing reproducibility with biological relevance, accelerating regulatory approval and clinical readiness.
Table of Comparison
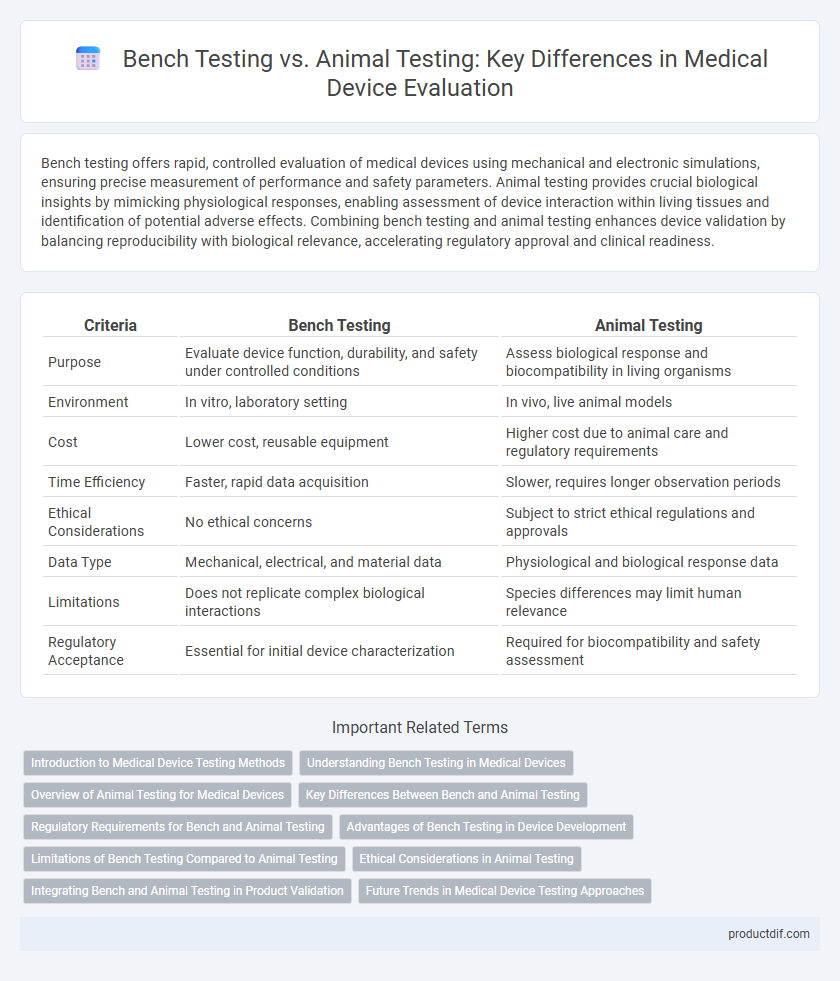
| Criteria | Bench Testing | Animal Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate device function, durability, and safety under controlled conditions | Assess biological response and biocompatibility in living organisms |
| Environment | In vitro, laboratory setting | In vivo, live animal models |
| Cost | Lower cost, reusable equipment | Higher cost due to animal care and regulatory requirements |
| Time Efficiency | Faster, rapid data acquisition | Slower, requires longer observation periods |
| Ethical Considerations | No ethical concerns | Subject to strict ethical regulations and approvals |
| Data Type | Mechanical, electrical, and material data | Physiological and biological response data |
| Limitations | Does not replicate complex biological interactions | Species differences may limit human relevance |
| Regulatory Acceptance | Essential for initial device characterization | Required for biocompatibility and safety assessment |
Introduction to Medical Device Testing Methods
Medical device testing methods include bench testing and animal testing, each serving a critical role in device development. Bench testing uses controlled laboratory settings to evaluate mechanical, electrical, and performance characteristics, ensuring safety and functionality before moving to biological assessments. Animal testing follows to assess biocompatibility, physiological response, and potential side effects, providing essential data on how the device interacts with living tissues.
Understanding Bench Testing in Medical Devices
Bench testing in medical devices involves controlled, reproducible laboratory experiments designed to evaluate device performance, safety, and reliability under simulated clinical conditions. This method provides quantitative data on mechanical, electrical, and software functions, enabling early identification of potential failures without ethical concerns related to live subjects. Compared to animal testing, bench testing offers faster iterations and detailed analysis, contributing to streamlined regulatory approval processes by demonstrating adherence to standards like ISO 13485 and IEC 60601.
Overview of Animal Testing for Medical Devices
Animal testing for medical devices involves evaluating biocompatibility, safety, and functionality by implanting or applying devices to animal models, typically rodents or pigs, to predict human responses. This method provides critical data on tissue reactions, toxicity, and mechanical performance under physiological conditions that cannot be fully replicated in vitro or through bench testing. While regulatory agencies often require animal testing to ensure device safety before clinical trials, ethical concerns and advancements in alternative methods are driving a shift toward reduced animal use in medical device evaluation.
Key Differences Between Bench and Animal Testing
Bench testing in medical devices involves controlled laboratory experiments on synthetic models or components to assess functionality, durability, and safety, providing precise, repeatable data. Animal testing evaluates biological interactions and systemic effects in living organisms, offering insights into biocompatibility and physiological responses that bench testing cannot replicate. Bench testing is faster, less expensive, and avoids ethical concerns, while animal testing is critical for understanding in vivo effects crucial for regulatory approval.
Regulatory Requirements for Bench and Animal Testing
Regulatory requirements for bench testing emphasize precise simulation of human physiological conditions using advanced in vitro models to validate safety and performance of medical devices before clinical trials. Animal testing regulations demand strict adherence to ethical standards, minimizing animal use and ensuring relevance to human biology for accurate biocompatibility and toxicity assessments. Compliance with FDA, ISO 10993, and EMA guidelines is critical for both testing methods to support device approval and market entry.
Advantages of Bench Testing in Device Development
Bench testing in medical device development offers precise control over experimental conditions, enabling consistent and reproducible results that accelerate design optimization. Unlike animal testing, bench testing reduces ethical concerns and lowers costs while providing rapid feedback on device performance under simulated physiological environments. This method enhances early identification of mechanical failures and material compatibility issues, facilitating safer and more efficient product iterations.
Limitations of Bench Testing Compared to Animal Testing
Bench testing in medical device evaluation often lacks the ability to replicate complex biological interactions and physiological conditions found in living organisms. This limitation restricts the assessment of device biocompatibility, immune response, and long-term functionality, which are critical parameters better observed in animal testing. Consequently, bench testing may fail to predict real-world performance and safety, necessitating supplementary animal studies for comprehensive risk assessment.
Ethical Considerations in Animal Testing
Animal testing in medical device development raises significant ethical concerns due to potential pain and distress inflicted on sentient beings. Bench testing offers a humane alternative by using in vitro models and computer simulations to evaluate device safety and performance without involving live subjects. Ethical frameworks increasingly promote reducing, refining, and replacing animal testing to minimize animal suffering in biomedical research.
Integrating Bench and Animal Testing in Product Validation
Integrating bench testing and animal testing in medical device validation enhances the accuracy of safety and performance assessments by combining controlled laboratory simulations with biological responses observed in vivo. Bench testing provides precise mechanical and functional data under standardized conditions, while animal testing offers critical insights into biocompatibility, physiological interactions, and potential adverse effects. Leveraging both methods accelerates regulatory approval processes and ensures comprehensive evaluation of device efficacy and safety before clinical trials.
Future Trends in Medical Device Testing Approaches
Future trends in medical device testing emphasize integrating advanced bench testing with computational models and in vitro systems to reduce reliance on animal testing. Innovations such as microfluidic organ-on-a-chip platforms and 3D bioprinting enable more precise simulation of human physiological responses, enhancing predictive accuracy. Regulatory bodies increasingly support these alternative methods, accelerating the shift toward ethical and efficient validation techniques.
Bench testing vs animal testing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com