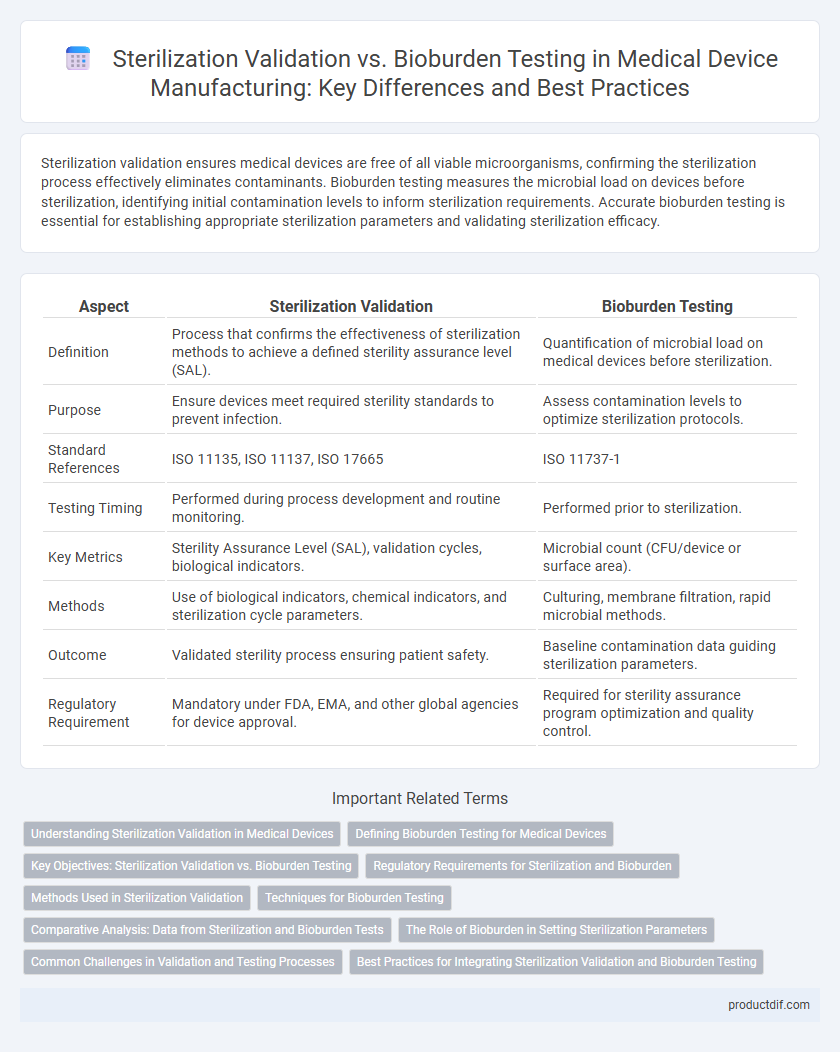
Sterilization validation ensures medical devices are free of all viable microorganisms, confirming the sterilization process effectively eliminates contaminants. Bioburden testing measures the microbial load on devices before sterilization, identifying initial contamination levels to inform sterilization requirements. Accurate bioburden testing is essential for establishing appropriate sterilization parameters and validating sterilization efficacy.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sterilization Validation | Bioburden Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process that confirms the effectiveness of sterilization methods to achieve a defined sterility assurance level (SAL). | Quantification of microbial load on medical devices before sterilization. |
| Purpose | Ensure devices meet required sterility standards to prevent infection. | Assess contamination levels to optimize sterilization protocols. |
| Standard References | ISO 11135, ISO 11137, ISO 17665 | ISO 11737-1 |
| Testing Timing | Performed during process development and routine monitoring. | Performed prior to sterilization. |
| Key Metrics | Sterility Assurance Level (SAL), validation cycles, biological indicators. | Microbial count (CFU/device or surface area). |
| Methods | Use of biological indicators, chemical indicators, and sterilization cycle parameters. | Culturing, membrane filtration, rapid microbial methods. |
| Outcome | Validated sterility process ensuring patient safety. | Baseline contamination data guiding sterilization parameters. |
| Regulatory Requirement | Mandatory under FDA, EMA, and other global agencies for device approval. | Required for sterility assurance program optimization and quality control. |
Understanding Sterilization Validation in Medical Devices
Sterilization validation in medical devices ensures the complete elimination of microbial contaminants, confirming the sterilization process meets predetermined safety standards. It involves rigorous testing protocols including establishing the sterilization cycle parameters, worst-case scenario assessments, and biological indicator evaluations. Bioburden testing, by quantifying the microbial load on devices before sterilization, supports sterilization validation by identifying contamination levels and guiding process adjustments.
Defining Bioburden Testing for Medical Devices
Bioburden testing for medical devices measures the number and types of microorganisms present on a device before sterilization, serving as a critical quality control step. This testing quantifies microbial load to establish sterilization parameters and monitor effectiveness in reducing microbial contamination. Accurate bioburden assessment ensures compliance with ISO 11737 standards and supports validation of sterilization processes such as ethylene oxide, steam, or radiation sterilization.
Key Objectives: Sterilization Validation vs. Bioburden Testing
Sterilization validation aims to confirm that a medical device consistently achieves the required sterility assurance level (SAL) to ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance. Bioburden testing quantifies the number of viable microorganisms present on a device before sterilization, providing critical data to establish effective sterilization parameters. Together, these processes ensure thorough microbial control, minimizing infection risk throughout device lifecycle management.
Regulatory Requirements for Sterilization and Bioburden
Regulatory requirements for sterilization validation mandate comprehensive evidence that the sterilization process effectively eliminates microbial life, ensuring patient safety and compliance with standards such as ISO 11135 and FDA 21 CFR Part 820. Bioburden testing, a critical control measure, quantifies the microbial load on medical devices pre-sterilization, serving as a key input for determining appropriate sterilization parameters under guidelines like ISO 11737-1. Proper documentation and control of both sterilization validation and bioburden testing are essential for regulatory approval and ongoing quality assurance in medical device manufacturing.
Methods Used in Sterilization Validation
Sterilization validation employs methods such as biological indicators, chemical indicators, and physical parameter monitoring to ensure effective microbial inactivation on medical devices. Biological indicators use highly resistant bacterial spores to challenge the sterilization process, providing definitive evidence of sterilization efficacy. Chemical indicators detect exposure to sterilization agents, while physical parameters like temperature, pressure, and time are continuously monitored to verify process consistency and compliance with sterilization standards.
Techniques for Bioburden Testing
Techniques for bioburden testing in medical device sterilization validation include membrane filtration, direct plating, and most probable number (MPN) methods, each offering precise microbial enumeration. Membrane filtration captures microorganisms on a filter, facilitating colony counting, while direct plating involves spreading the sample onto agar plates to detect microbial growth. MPN techniques estimate microbial population statistically, ensuring comprehensive assessment prior to sterilization.
Comparative Analysis: Data from Sterilization and Bioburden Tests
Sterilization validation data and bioburden testing results provide complementary insights critical for ensuring medical device safety and regulatory compliance. Bioburden testing quantifies the microbial load present on devices before sterilization, establishing baseline contamination levels, while sterilization validation confirms the effectiveness of sterilization processes in achieving the required sterility assurance level (SAL). Comparing microbial reduction trends from bioburden data against sterilization efficacy metrics enables precise optimization of sterilization cycles and validation protocols.
The Role of Bioburden in Setting Sterilization Parameters
Bioburden testing quantifies the microbial load on medical devices, providing critical data to establish effective sterilization parameters. Accurate bioburden assessment enables validation of sterilization processes by defining the required sterilant exposure to achieve a predetermined sterility assurance level (SAL). Integrating bioburden results ensures optimized sterilization cycles, enhancing patient safety and regulatory compliance in medical device manufacturing.
Common Challenges in Validation and Testing Processes
Sterilization validation and bioburden testing face common challenges including variability in microbial load, complexity of testing protocols, and ensuring reproducibility across batches. Inconsistent sample collection and environmental conditions can lead to unreliable bioburden data, impacting the accuracy of sterilization effectiveness assessments. Moreover, selecting appropriate validation parameters and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards such as ISO 11737 intensify the difficulty of achieving robust sterilization validation outcomes.
Best Practices for Integrating Sterilization Validation and Bioburden Testing
Integrating sterilization validation with bioburden testing ensures comprehensive microbial control by verifying both the initial microbial load and the efficacy of sterilization processes. Best practices include establishing precise bioburden limits aligned with device material compatibility and selecting validation methods such as ISO 11135 or ISO 17665 standards that match the sterilization mode. Continuous monitoring and trend analysis of bioburden data coupled with regular revalidation enhance process control and product safety in medical device manufacturing.
Sterilization validation vs bioburden testing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com