Electromagnetic interference (EMI) refers to the disruption of medical device performance caused by external electromagnetic signals, which can compromise patient safety and device functionality. Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) ensures that medical devices operate correctly in their electromagnetic environment without producing unacceptable interference with other equipment. Achieving EMC involves rigorous testing and design modifications to minimize susceptibility to EMI and guarantee reliable device operation in clinical settings.
Table of Comparison
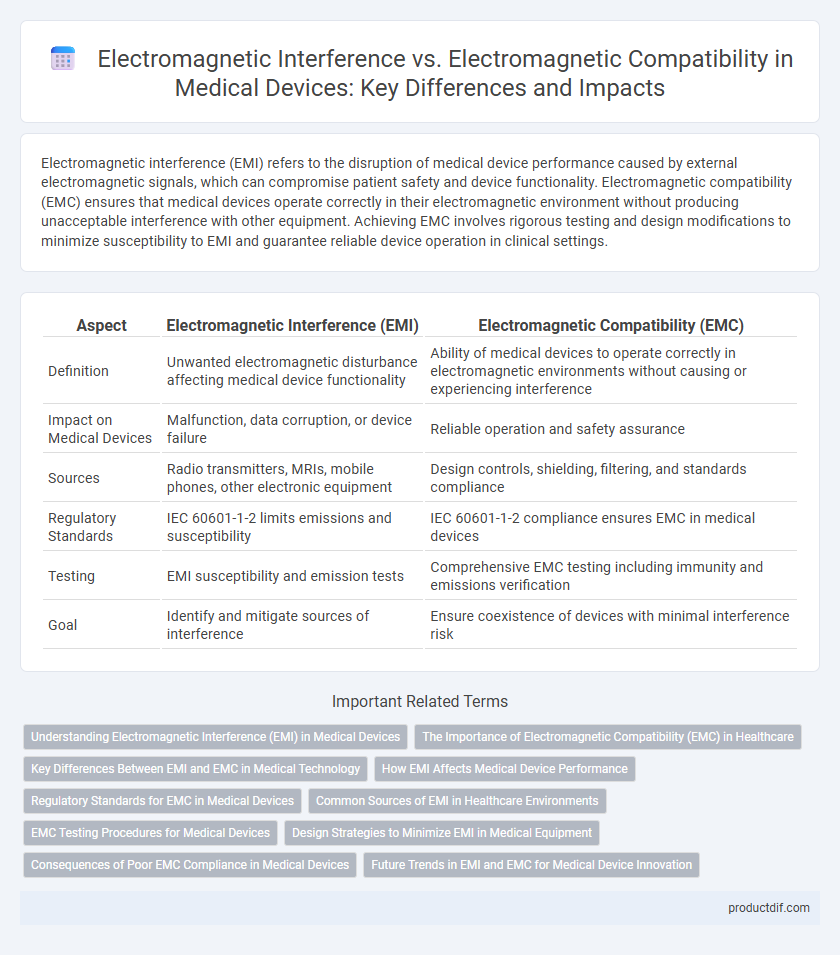
| Aspect | Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) | Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwanted electromagnetic disturbance affecting medical device functionality | Ability of medical devices to operate correctly in electromagnetic environments without causing or experiencing interference |
| Impact on Medical Devices | Malfunction, data corruption, or device failure | Reliable operation and safety assurance |
| Sources | Radio transmitters, MRIs, mobile phones, other electronic equipment | Design controls, shielding, filtering, and standards compliance |
| Regulatory Standards | IEC 60601-1-2 limits emissions and susceptibility | IEC 60601-1-2 compliance ensures EMC in medical devices |
| Testing | EMI susceptibility and emission tests | Comprehensive EMC testing including immunity and emissions verification |
| Goal | Identify and mitigate sources of interference | Ensure coexistence of devices with minimal interference risk |
Understanding Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) in Medical Devices
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) in medical devices occurs when external electromagnetic fields disrupt the normal operation of electronic equipment, potentially leading to malfunction or inaccurate readings. Understanding the sources of EMI, such as radio frequency waves, power lines, and other medical devices, is crucial for designing devices that maintain reliability and patient safety. Effective EMI management involves shielding, filtering, and grounding techniques to minimize interference and ensure electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) in clinical environments.
The Importance of Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) in Healthcare
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) in medical devices ensures reliable operation by minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can disrupt critical healthcare equipment. Compliance with EMC standards like IEC 60601-1-2 is crucial for maintaining patient safety and preventing malfunction in diagnostic or therapeutic devices such as MRI machines and pacemakers. Effective EMC management reduces the risk of data corruption and operational failures, thereby supporting accurate medical diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
Key Differences Between EMI and EMC in Medical Technology
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) in medical devices refers to unwanted electromagnetic signals that disrupt the functioning of equipment, potentially leading to inaccurate diagnostics or device malfunction. Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) ensures medical devices operate correctly in their electromagnetic environment without causing or falling victim to interference. Key differences include EMI representing the disturbance itself, while EMC encompasses the design standards and testing protocols that prevent such disruptions, ensuring patient safety and device reliability in clinical settings.
How EMI Affects Medical Device Performance
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) disrupts the normal operation of medical devices by inducing unwanted electromagnetic signals that can cause malfunctions, inaccurate readings, or device failure. Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) ensures that medical devices operate reliably within their electromagnetic environment without emitting or being affected by EMI. Effective EMC design minimizes EMI impact, safeguarding device performance and patient safety in critical healthcare settings.
Regulatory Standards for EMC in Medical Devices
Regulatory standards for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) in medical devices, such as IEC 60601-1-2, set strict limits to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can disrupt device performance and patient safety. These standards require medical devices to undergo rigorous EMC testing to ensure immunity to external electromagnetic disturbances and control emissions to prevent interference with other equipment. Compliance with EMC standards is essential for market approval and ensures reliable operation of medical devices in complex electromagnetic environments.
Common Sources of EMI in Healthcare Environments
Common sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI) in healthcare environments include medical imaging equipment, such as MRI machines and X-ray systems, which emit strong electromagnetic fields that can disrupt nearby devices. Other frequent contributors are wireless communication devices, including mobile phones and hospital telemetry systems, which generate radiofrequency signals that may interfere with sensitive medical instruments. Understanding these sources is crucial for ensuring electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), allowing medical devices to function correctly without mutual electromagnetic disruption in clinical settings.
EMC Testing Procedures for Medical Devices
EMC testing procedures for medical devices ensure electromagnetic compatibility by evaluating the device's ability to function correctly in its electromagnetic environment without causing or suffering from electromagnetic interference. These tests include emission measurements to assess radiated and conducted disturbances, as well as immunity tests such as electrostatic discharge, radiated RF electromagnetic fields, and transient burst pulses. Compliance with standards like IEC 60601-1-2 guarantees that medical devices maintain safety and performance despite electromagnetic challenges in clinical settings.
Design Strategies to Minimize EMI in Medical Equipment
Design strategies to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) in medical equipment emphasize electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) through careful circuit layout, shielding, and grounding techniques. Using twisted pair cables, ferrite beads, and high-quality filters reduces susceptibility to external electromagnetic noise and prevents device malfunction. Adopting rigorous EMC testing standards such as IEC 60601-1-2 ensures medical devices operate safely within electromagnetic environments.
Consequences of Poor EMC Compliance in Medical Devices
Poor electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) compliance in medical devices can lead to electromagnetic interference (EMI), causing malfunctions such as inaccurate readings, delayed responses, or complete device failure. These disruptions jeopardize patient safety by impairing critical functions in life-supporting equipment like pacemakers, infusion pumps, and diagnostic instruments. Regulatory bodies like the FDA and IEC enforce strict EMC standards to minimize risks and ensure reliable medical device performance in diverse electromagnetic environments.
Future Trends in EMI and EMC for Medical Device Innovation
Future trends in electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) for medical devices emphasize advanced shielding materials and adaptive filtering technologies to enhance device reliability. Integration of machine learning algorithms enables real-time detection and mitigation of EMI sources, ensuring consistent device performance in complex electromagnetic environments. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to address emerging wireless communication protocols, promoting safer and more interoperable medical innovations.
Electromagnetic interference vs electromagnetic compatibility Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com