Diagnostic catheters are primarily designed for imaging and assessment purposes, enabling detailed visualization of blood vessels and cardiac chambers to identify abnormalities. Therapeutic catheters, in contrast, are specialized for intervention, such as delivering medications, removing blockages, or performing procedures like angioplasty. Understanding the distinct functions of diagnostic versus therapeutic catheters is crucial for selecting the appropriate device to optimize patient outcomes in cardiovascular care.
Table of Comparison
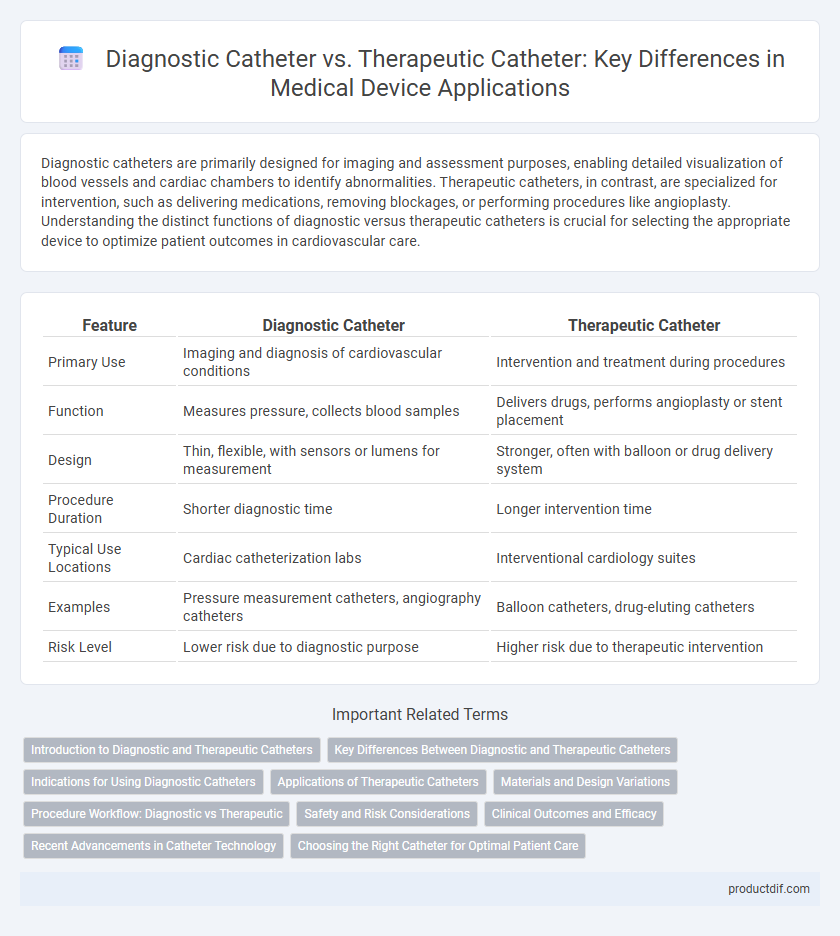
| Feature | Diagnostic Catheter | Therapeutic Catheter |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Imaging and diagnosis of cardiovascular conditions | Intervention and treatment during procedures |
| Function | Measures pressure, collects blood samples | Delivers drugs, performs angioplasty or stent placement |
| Design | Thin, flexible, with sensors or lumens for measurement | Stronger, often with balloon or drug delivery system |
| Procedure Duration | Shorter diagnostic time | Longer intervention time |
| Typical Use Locations | Cardiac catheterization labs | Interventional cardiology suites |
| Examples | Pressure measurement catheters, angiography catheters | Balloon catheters, drug-eluting catheters |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to diagnostic purpose | Higher risk due to therapeutic intervention |
Introduction to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Catheters
Diagnostic catheters are designed primarily for imaging and monitoring within the vascular system to assist in identifying abnormalities, such as blockages or malformations. Therapeutic catheters, on the other hand, are utilized to deliver treatments including medication administration, clot removal, or vessel dilation directly to the affected site. Both types play crucial roles in interventional cardiology and radiology, improving patient outcomes through minimally invasive procedures.
Key Differences Between Diagnostic and Therapeutic Catheters
Diagnostic catheters are designed primarily for imaging and detecting abnormalities within blood vessels or heart chambers, often equipped with sensors or imaging capabilities such as fluoroscopy or ultrasound. Therapeutic catheters are utilized to deliver treatments directly, including drug administration, tissue ablation, or angioplasty, featuring specialized tips for interventions like balloon inflation or stent deployment. The key differences lie in their functional objectives--diagnostic catheters focus on evaluation and monitoring while therapeutic catheters emphasize active treatment and intervention.
Indications for Using Diagnostic Catheters
Diagnostic catheters are primarily indicated for identifying cardiovascular abnormalities through procedures such as coronary angiography and intracardiac pressure measurements. These catheters facilitate precise visualization and assessment of vascular structures, guiding diagnosis without directly altering the pathology. In contrast, therapeutic catheters are utilized for interventions like angioplasty and stent placement, aimed at treating identified conditions.
Applications of Therapeutic Catheters
Therapeutic catheters are primarily used to deliver treatments directly to targeted sites within the body, facilitating procedures such as angioplasty, thrombolysis, and drug delivery. These catheters enable minimally invasive interventions to restore blood flow, remove clots, or administer medications, improving patient outcomes in cardiovascular, neurological, and oncological care. Their design allows precise navigation to affected areas, enhancing the effectiveness of therapies compared to diagnostic catheters, which are mainly used for imaging and assessment purposes.
Materials and Design Variations
Diagnostic catheters are typically made from flexible polymers like polyurethane or silicone to maximize maneuverability and patient comfort during imaging or sampling procedures. Therapeutic catheters often incorporate reinforced materials such as stainless steel or braided nylon to provide enhanced durability and support for interventions like angioplasty or drug delivery. Design variations include diameter, tip shape, and lumen configuration tailored for specific diagnostic accuracy or therapeutic functionality.
Procedure Workflow: Diagnostic vs Therapeutic
Diagnostic catheters are primarily designed for imaging and pressure measurements, facilitating precise identification of vascular or cardiac abnormalities during procedures such as angiography and electrophysiology studies. Therapeutic catheters enable interventions like angioplasty, stent placement, or ablation, deploying devices or delivering treatments to address identified conditions. The procedure workflow for diagnostic catheters involves detailed assessment and mapping, while therapeutic catheters focus on treatment delivery based on diagnostic findings.
Safety and Risk Considerations
Diagnostic catheters primarily focus on safely accessing and imaging vascular structures, with low risk of vessel trauma due to their smaller size and flexible design. Therapeutic catheters carry higher safety risks including potential vessel perforation, thrombosis, or embolism because they deliver interventions such as angioplasty or drug infusion. Careful monitoring and device selection based on patient-specific anatomy and procedural goals are critical to minimize complications associated with both catheter types.
Clinical Outcomes and Efficacy
Diagnostic catheters enable precise imaging and assessment of vascular conditions, improving the accuracy of diagnoses and guiding treatment decisions. Therapeutic catheters directly deliver medications or perform interventions such as angioplasty, contributing to enhanced clinical outcomes by reducing procedure time and improving patient recovery. Comparative studies indicate that integrating diagnostic and therapeutic catheterization optimizes efficacy, minimizes complications, and increases overall procedural success rates in cardiovascular care.
Recent Advancements in Catheter Technology
Recent advancements in catheter technology have significantly enhanced the functionality of both diagnostic and therapeutic catheters, integrating high-resolution imaging and real-time data transmission capabilities. Innovations such as flexible, biocompatible materials and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) sensors improve navigation accuracy and patient safety during minimally invasive procedures. Enhanced catheter designs now facilitate simultaneous diagnosis and treatment, reducing procedure times and improving clinical outcomes in cardiovascular and neurological interventions.
Choosing the Right Catheter for Optimal Patient Care
Diagnostic catheters are designed primarily for imaging and assessment, enabling precise visualization of vascular structures, while therapeutic catheters deliver treatments such as drug infusion or clot removal directly to targeted sites. Selecting the right catheter involves evaluating patient-specific factors, including vessel size, target location, and the required procedure type to ensure effective intervention and minimize complications. Proper catheter choice enhances procedural success rates and optimizes patient outcomes through tailored, minimally invasive care.
Diagnostic Catheter vs Therapeutic Catheter Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com