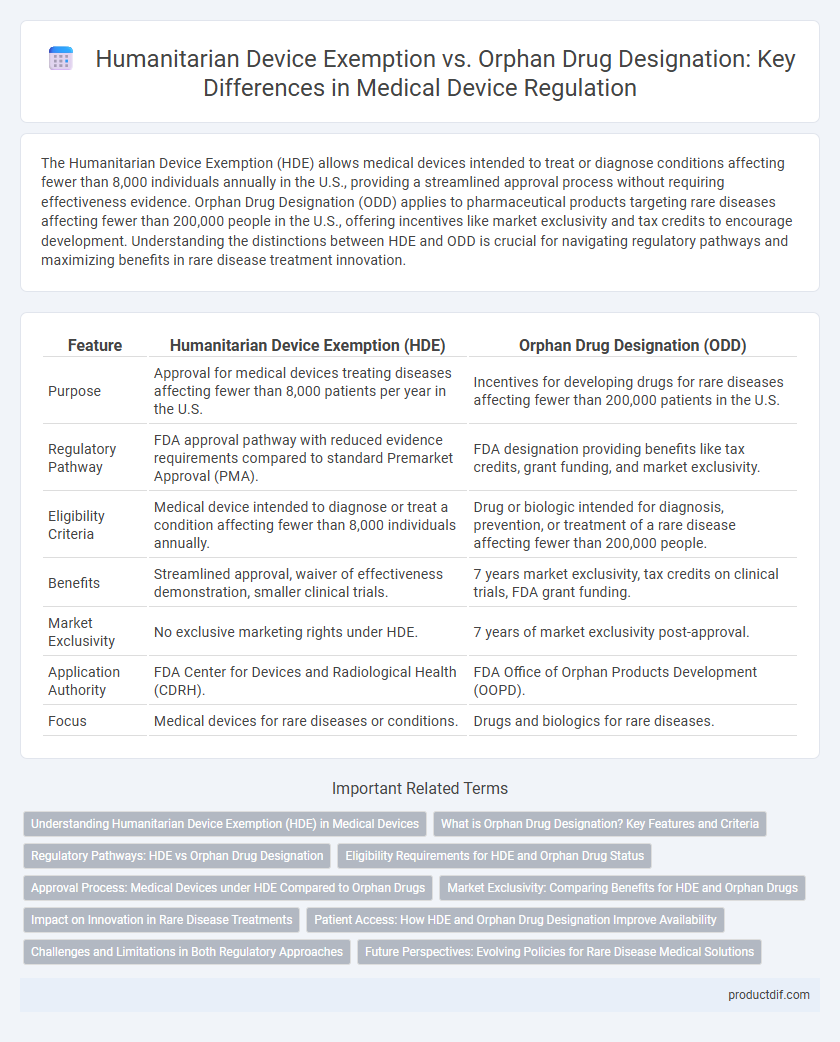
The Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) allows medical devices intended to treat or diagnose conditions affecting fewer than 8,000 individuals annually in the U.S., providing a streamlined approval process without requiring effectiveness evidence. Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) applies to pharmaceutical products targeting rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 people in the U.S., offering incentives like market exclusivity and tax credits to encourage development. Understanding the distinctions between HDE and ODD is crucial for navigating regulatory pathways and maximizing benefits in rare disease treatment innovation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) | Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Approval for medical devices treating diseases affecting fewer than 8,000 patients per year in the U.S. | Incentives for developing drugs for rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 patients in the U.S. |
| Regulatory Pathway | FDA approval pathway with reduced evidence requirements compared to standard Premarket Approval (PMA). | FDA designation providing benefits like tax credits, grant funding, and market exclusivity. |
| Eligibility Criteria | Medical device intended to diagnose or treat a condition affecting fewer than 8,000 individuals annually. | Drug or biologic intended for diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of a rare disease affecting fewer than 200,000 people. |
| Benefits | Streamlined approval, waiver of effectiveness demonstration, smaller clinical trials. | 7 years market exclusivity, tax credits on clinical trials, FDA grant funding. |
| Market Exclusivity | No exclusive marketing rights under HDE. | 7 years of market exclusivity post-approval. |
| Application Authority | FDA Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH). | FDA Office of Orphan Products Development (OOPD). |
| Focus | Medical devices for rare diseases or conditions. | Drugs and biologics for rare diseases. |
Understanding Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) in Medical Devices
Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) allows medical devices designed for diseases or conditions affecting fewer than 8,000 individuals annually in the U.S. to bypass effectiveness requirements typical of standard FDA approval, facilitating faster access to critical treatments. Unlike Orphan Drug Designation, which provides incentives for drug development targeting rare diseases, HDE focuses exclusively on medical devices, enabling innovators to address unmet needs in small patient populations. The HDE pathway ensures safety while promoting innovation for rare conditions, emphasizing the balance between risk mitigation and access to life-saving technology.
What is Orphan Drug Designation? Key Features and Criteria
Orphan Drug Designation is a regulatory status granted by the FDA to drugs and biologics intended to treat rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 people in the United States. Key features include incentives such as tax credits for clinical research, waiver of FDA application fees, and seven years of market exclusivity upon approval. Criteria for designation require the drug to demonstrate potential to diagnose, prevent, or treat a rare condition with no satisfactory existing treatment alternatives.
Regulatory Pathways: HDE vs Orphan Drug Designation
Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) and Orphan Drug Designation represent distinct regulatory pathways tailored for scarce medical interventions. HDE facilitates marketing approval for medical devices addressing conditions affecting fewer than 8,000 individuals annually in the U.S., bypassing traditional efficacy requirements but ensuring safety. Orphan Drug Designation grants incentives for drug development targeting rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 patients nationwide, supporting clinical trial funding and market exclusivity.
Eligibility Requirements for HDE and Orphan Drug Status
Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) eligibility requires that the device be intended to benefit patients with diseases or conditions affecting fewer than 8,000 individuals annually in the United States, targeting small patient populations lacking sufficient treatment options. Orphan Drug Designation applies to drugs and biologics meant for rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 people in the U.S. or when the sponsor cannot expect to recover research and development costs, emphasizing economic factors in eligibility. Both pathways aim to encourage development for rare conditions but differ in scope, with HDE focused on medical devices and Orphan Drug Status on pharmaceuticals.
Approval Process: Medical Devices under HDE Compared to Orphan Drugs
The Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) approval process requires demonstrating that the medical device is safe and has probable benefit for treating or diagnosing diseases affecting fewer than 8,000 individuals in the U.S. annually, focusing on safety over effectiveness unlike standard premarket approvals. Orphan Drug Designation targets pharmaceuticals for rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 people nationally, facilitating development incentives and expedited FDA review but still requiring substantial evidence of drug efficacy and safety for final marketing approval. While HDE devices bypass the need for clinical efficacy proof, orphan drugs must undergo rigorous clinical trials to confirm therapeutic effects before receiving FDA approval.
Market Exclusivity: Comparing Benefits for HDE and Orphan Drugs
Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) provides market approval without requiring clinical effectiveness evidence, offering limited market exclusivity focused on devices treating conditions affecting fewer than 8,000 individuals annually in the U.S. Orphan Drug Designation grants seven years of market exclusivity upon FDA approval for drugs addressing rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 people nationwide, promoting investment in rare disease therapeutics. While HDE primarily accelerates device availability with less stringent approval, Orphan Drug Designation delivers stronger market protection and incentives for drug development targeting rare diseases.
Impact on Innovation in Rare Disease Treatments
The Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) and Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) both aim to stimulate innovation in rare disease treatments by reducing regulatory barriers and encouraging investment. HDE facilitates development of medical devices for conditions affecting fewer than 8,000 individuals annually, enabling faster market access with limited clinical data requirements. Orphan Drug Designation provides incentives such as market exclusivity and tax credits, significantly boosting pharmaceutical innovation, while HDE primarily accelerates device availability, collectively advancing therapeutic options in rare diseases.
Patient Access: How HDE and Orphan Drug Designation Improve Availability
Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) facilitates patient access by allowing the use of medical devices intended for conditions affecting fewer than 8,000 individuals annually in the United States, bypassing the standard effectiveness evidence requirement. Orphan Drug Designation enhances availability by providing incentives such as market exclusivity and accelerated approval to drugs treating rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 U.S. patients. Both regulatory pathways improve patient access to therapies that would otherwise be commercially nonviable due to limited population sizes.
Challenges and Limitations in Both Regulatory Approaches
Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) faces challenges such as limited patient populations that complicate clinical trial recruitment and post-market surveillance, while Orphan Drug Designation encounters difficulties including high development costs and uncertain market viability due to rare disease prevalence. Both regulatory pathways impose restrictions on profitability and scalability, limiting investment incentives for developers. These constraints create barriers in bringing innovative treatments and devices to patients with rare conditions.
Future Perspectives: Evolving Policies for Rare Disease Medical Solutions
Future perspectives in rare disease medical solutions emphasize evolving policies that enhance access and innovation in both Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) and Orphan Drug Designation pathways. Regulatory agencies are increasingly aligning HDE frameworks with adaptive clinical trial designs and post-market surveillance to accelerate device availability while ensuring safety for small patient populations. Advances in digital health technologies and real-world evidence integration are expected to drive more personalized and effective treatments under these regulatory paradigms.
Humanitarian Device Exemption vs Orphan Drug Designation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com