OEM devices offer standardized solutions with proven reliability and cost efficiency, ideal for mass production and quick market entry. Custom devices provide tailored functionality and design to meet specific clinical needs or unique patient requirements, enhancing treatment outcomes. Choosing between OEM and custom devices depends on balancing scale, flexibility, and the degree of personalization required.
Table of Comparison
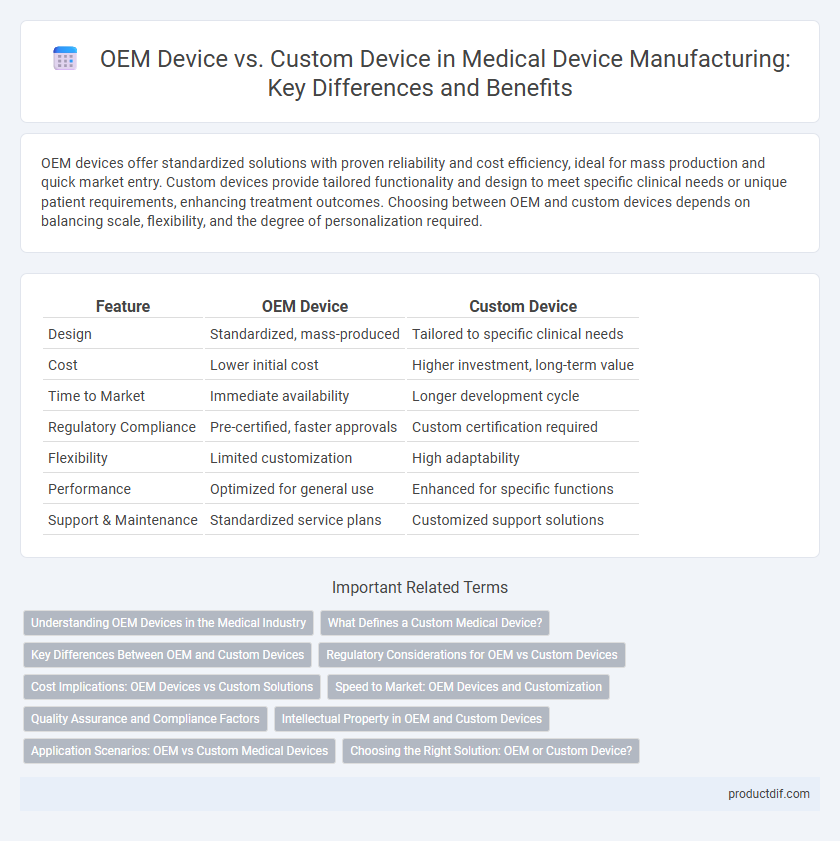
| Feature | OEM Device | Custom Device |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Standardized, mass-produced | Tailored to specific clinical needs |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher investment, long-term value |
| Time to Market | Immediate availability | Longer development cycle |
| Regulatory Compliance | Pre-certified, faster approvals | Custom certification required |
| Flexibility | Limited customization | High adaptability |
| Performance | Optimized for general use | Enhanced for specific functions |
| Support & Maintenance | Standardized service plans | Customized support solutions |
Understanding OEM Devices in the Medical Industry
OEM devices in the medical industry are pre-manufactured components or products designed by an original equipment manufacturer for integration into a larger system or device, offering standardized quality and regulatory compliance. These devices streamline production processes for medical companies, enabling faster time-to-market and cost efficiency while maintaining strict adherence to healthcare regulations such as FDA and ISO 13485 standards. Understanding the role of OEM devices is crucial for medical device manufacturers aiming to balance innovation with proven reliability and scalability in complex healthcare environments.
What Defines a Custom Medical Device?
A custom medical device is specifically designed and manufactured to meet the unique needs of an individual patient, often tailored based on a physician's prescription or an exact anatomical requirement. Unlike OEM devices produced in standardized models for mass distribution, custom devices address specific clinical situations where standard products are inadequate. Regulatory bodies like the FDA define custom devices by their bespoke characteristics, ensuring they comply with stringent safety and effectiveness standards despite their individualized nature.
Key Differences Between OEM and Custom Devices
OEM devices typically involve standardized production with predefined specifications, enabling mass manufacturing and consistent quality control. Custom devices are tailored to specific patient or clinical needs, requiring specialized design and engineering, often resulting in longer development times and higher costs. Key differences include the level of customization, production scale, regulatory complexity, and adaptability to unique medical requirements.
Regulatory Considerations for OEM vs Custom Devices
OEM devices often comply with established regulatory standards such as FDA 510(k) clearance or CE marking due to their mass production and standardized manufacturing processes. Custom devices require rigorous validation and documentation to demonstrate safety and efficacy, often facing more complex regulatory pathways like FDA custom device exemptions or individualized assessments. Understanding the regulatory frameworks for OEM versus custom devices is critical to ensuring timely market approval and maintaining compliance with quality system regulations (QSR) and ISO 13485 standards.
Cost Implications: OEM Devices vs Custom Solutions
OEM medical devices typically offer lower upfront costs due to standardized manufacturing processes and economies of scale, making them cost-effective for common clinical applications. Custom medical devices involve higher initial investment driven by specialized design, development, and regulatory compliance tailored to unique patient needs or market niches. Long-term expenses vary as OEM devices may incur higher modification costs, while custom solutions often reduce maintenance and adaptation expenditures through precise fit and functionality.
Speed to Market: OEM Devices and Customization
OEM medical devices offer faster speed to market due to pre-existing designs and regulatory clearances, enabling quicker deployment in clinical settings. Custom devices, while tailored to specific clinical needs, require extensive design, prototyping, and regulatory approval phases that extend development timelines. Healthcare providers seeking rapid innovation often balance the trade-off between immediate availability of OEM devices and the specificity of custom device solutions.
Quality Assurance and Compliance Factors
OEM medical devices adhere to stringent quality assurance protocols set by the original equipment manufacturer, ensuring consistent compliance with FDA and ISO 13485 standards. Custom medical devices require tailored validation processes to meet specific user needs while maintaining regulatory compliance through rigorous documentation and testing. Both device types demand robust quality management systems to mitigate risks and ensure patient safety in clinical environments.
Intellectual Property in OEM and Custom Devices
OEM devices leverage existing intellectual property licenses from original manufacturers, allowing faster market entry with reduced legal risks. Custom devices require new intellectual property development, offering greater innovation potential but necessitating comprehensive IP protection strategies. Effective management of patents, trademarks, and trade secrets is critical to secure competitive advantages in both OEM and custom device production.
Application Scenarios: OEM vs Custom Medical Devices
OEM medical devices typically serve standardized clinical environments where mass production and cost-efficiency are critical, such as hospitals and diagnostic centers requiring uniform equipment. Custom medical devices are tailored for unique patient needs or specialized clinical applications, including personalized implants and niche therapeutic tools. Choosing between OEM and custom devices depends on the specificity of medical requirements, regulatory compliance, and intended use cases.
Choosing the Right Solution: OEM or Custom Device?
Selecting between an OEM device and a custom medical device hinges on specific project requirements such as budget, timeline, and functionality. OEM devices offer proven reliability and faster deployment with standardized features, while custom devices provide tailored solutions designed to meet unique clinical needs and regulatory demands. Evaluating factors like integration complexity, volume production, and post-market support ensures alignment with healthcare providers' operational goals and patient care standards.
OEM Device vs Custom Device Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com