Pilot batches are small-scale production runs designed to test manufacturing processes and ensure product quality before full-scale commercialization. Commercial batches involve large-scale production aimed at meeting market demand while adhering to regulatory standards and quality control measures. Comparing pilot and commercial batches helps identify process improvements and validate consistency in medical device manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
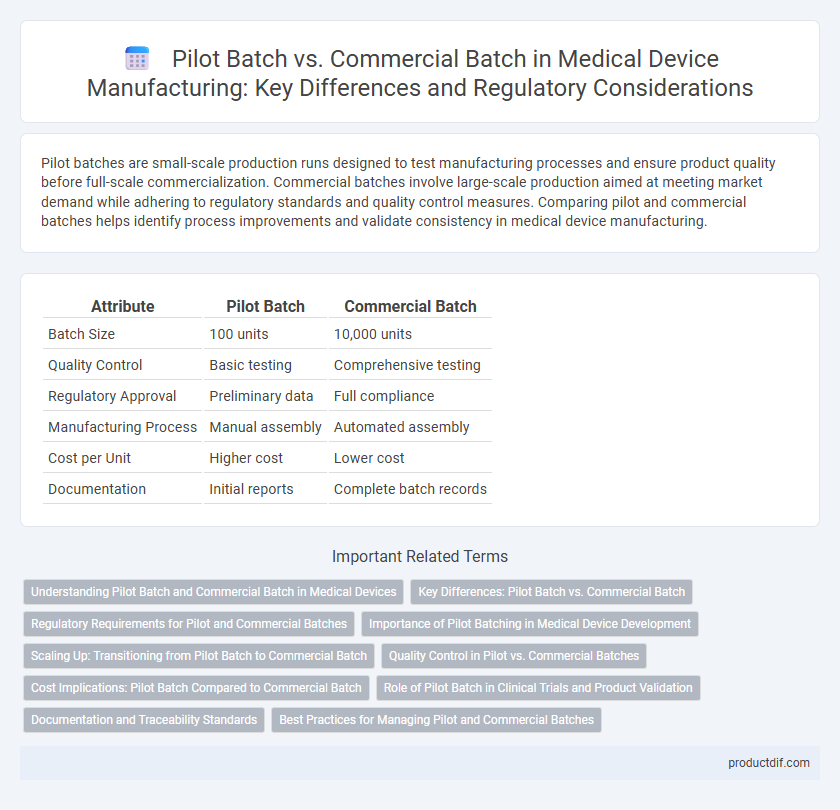
| Attribute | Pilot Batch | Commercial Batch |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Size | 100 units | 10,000 units |
| Quality Control | Basic testing | Comprehensive testing |
| Regulatory Approval | Preliminary data | Full compliance |
| Manufacturing Process | Manual assembly | Automated assembly |
| Cost per Unit | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Documentation | Initial reports | Complete batch records |
Understanding Pilot Batch and Commercial Batch in Medical Devices
Pilot batch in medical device manufacturing refers to a small-scale production run used to validate processes, test equipment, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards before full-scale manufacturing begins. Commercial batch represents the large-scale production intended for market distribution, meeting all quality assurance and regulatory requirements for widespread use. Understanding the differences between pilot and commercial batches is crucial for ensuring product consistency, safety, and adherence to FDA or ISO standards in medical device development.
Key Differences: Pilot Batch vs. Commercial Batch
Pilot batches in medical device manufacturing serve as small-scale production runs to validate processes, equipment, and quality control before full-scale manufacturing. Commercial batches involve large-scale production aimed at meeting market demand, ensuring consistent product quality, regulatory compliance, and cost efficiency. Key differences include batch size, purpose, regulatory scrutiny, and scalability of production processes.
Regulatory Requirements for Pilot and Commercial Batches
Pilot batches in medical device manufacturing are primarily used to validate processes and ensure compliance with regulatory standards such as ISO 13485 and FDA's QSR before scaling production. Commercial batches must meet stringent regulatory requirements involving complete documentation, traceability, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to guarantee product consistency and patient safety. Regulatory bodies often require robust batch records, validation protocols, and risk management documentation for commercial production to support product registration and market approval.
Importance of Pilot Batching in Medical Device Development
Pilot batching in medical device development is crucial for identifying manufacturing flaws and ensuring product consistency before scaling to commercial batch production. It enables the validation of production processes, quality control measures, and regulatory compliance, minimizing the risk of costly recalls or failures. Data gathered from pilot batches informs process optimization, improving reliability and safety in the final commercial batches.
Scaling Up: Transitioning from Pilot Batch to Commercial Batch
Scaling up from a pilot batch to a commercial batch in medical device manufacturing involves increasing production volume while maintaining strict compliance with regulatory standards such as FDA and ISO 13485. The transition requires thorough validation of processes, equipment, and quality control systems to ensure consistency, safety, and efficacy of the devices. Robust documentation and risk management strategies are critical to address potential scale-related challenges and ensure successful market entry.
Quality Control in Pilot vs. Commercial Batches
Quality control in pilot batches emphasizes iterative testing to refine manufacturing processes and validate device performance under controlled conditions, often employing tighter specifications to identify potential defects early. Commercial batches require robust quality control systems that ensure consistent compliance with regulatory standards and production scalability, utilizing statistical process control and comprehensive documentation for traceability. Effective transition from pilot to commercial batch quality control mitigates risks, enhances device reliability, and supports regulatory approval.
Cost Implications: Pilot Batch Compared to Commercial Batch
Pilot batches in medical device manufacturing typically incur higher per-unit costs due to small-scale production, specialized setup requirements, and extensive quality testing protocols. Commercial batches benefit from economies of scale, reducing material, labor, and overhead expenses per unit, thus lowering overall cost implications. Understanding cost differentials between pilot and commercial batches is crucial for budgeting, regulatory compliance, and strategic pricing in product launch phases.
Role of Pilot Batch in Clinical Trials and Product Validation
Pilot batches play a crucial role in clinical trials by providing initial product samples to validate manufacturing processes and ensure consistency in quality before large-scale production. These batches help identify potential issues in device design, materials, or production techniques, enabling refinement to meet regulatory standards and performance specifications. Validation through pilot batches supports risk mitigation, regulatory submissions, and establishes the foundation for scaling up to commercial batches with reproducible safety and efficacy.
Documentation and Traceability Standards
Pilot batches in medical device manufacturing require detailed documentation to validate processes and ensure traceability, often following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and ISO 13485 standards. Commercial batches demand even stricter documentation and traceability with comprehensive batch records, lot traceability, and quality control data to comply with regulatory bodies such as the FDA and MDR. Maintaining meticulous traceability from raw materials to finished products is critical for risk management, post-market surveillance, and ensuring patient safety throughout the device lifecycle.
Best Practices for Managing Pilot and Commercial Batches
Effective management of pilot and commercial batches in medical device manufacturing requires strict adherence to validated protocols and comprehensive documentation to ensure product quality and regulatory compliance. Pilot batches serve as critical validation tools to optimize manufacturing processes, while commercial batches must consistently meet defined quality standards to ensure patient safety. Implementing robust quality control measures and continuous monitoring throughout both phases minimizes risks and supports successful scale-up from development to market launch.
Pilot batch vs Commercial batch Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com