Non-invasive medical devices for pets offer diagnostic and therapeutic benefits without breaking the skin, reducing the risk of infection and promoting quicker recovery. Minimally-invasive devices involve small incisions or punctures, allowing targeted treatment with less trauma compared to traditional surgery, enhancing precision and minimizing discomfort. Selecting between non-invasive and minimally-invasive options depends on the specific condition, desired outcomes, and pet welfare considerations.
Table of Comparison
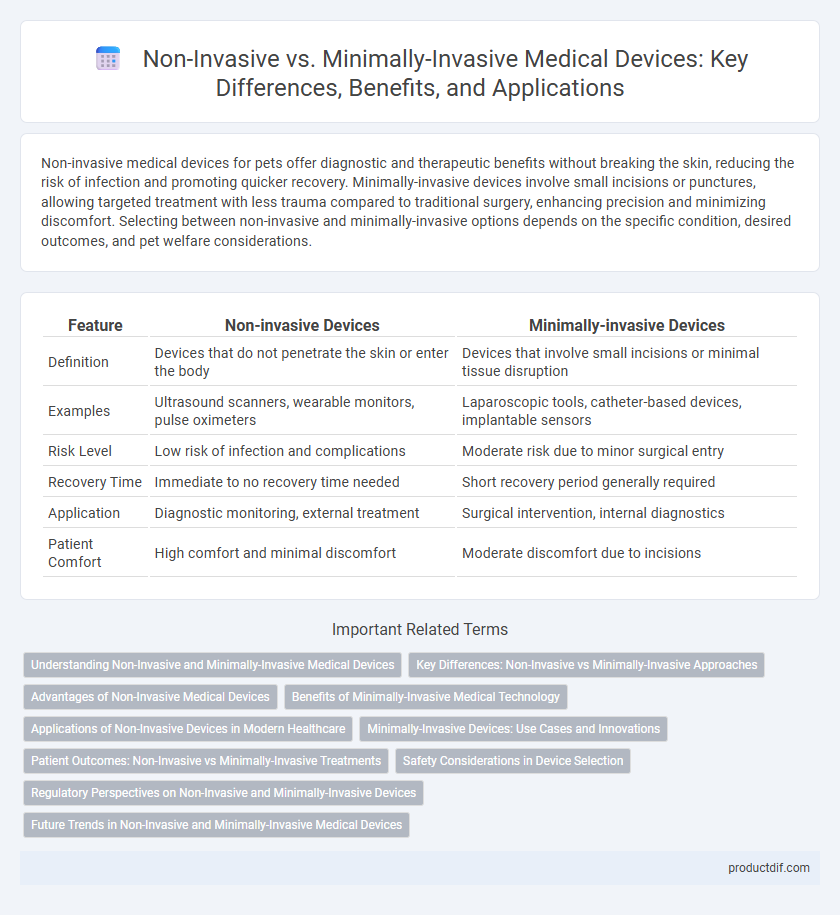
| Feature | Non-invasive Devices | Minimally-invasive Devices |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Devices that do not penetrate the skin or enter the body | Devices that involve small incisions or minimal tissue disruption |
| Examples | Ultrasound scanners, wearable monitors, pulse oximeters | Laparoscopic tools, catheter-based devices, implantable sensors |
| Risk Level | Low risk of infection and complications | Moderate risk due to minor surgical entry |
| Recovery Time | Immediate to no recovery time needed | Short recovery period generally required |
| Application | Diagnostic monitoring, external treatment | Surgical intervention, internal diagnostics |
| Patient Comfort | High comfort and minimal discomfort | Moderate discomfort due to incisions |
Understanding Non-Invasive and Minimally-Invasive Medical Devices
Non-invasive medical devices perform diagnostics or treatments without penetrating the skin or entering the body, minimizing risk and recovery time. Minimally-invasive devices involve small incisions or natural body openings, allowing access to internal structures with reduced trauma compared to traditional surgery. Understanding the distinctions aids in selecting appropriate tools for patient safety, efficiency, and targeted clinical outcomes.
Key Differences: Non-Invasive vs Minimally-Invasive Approaches
Non-invasive medical devices operate without breaking the skin or entering the body, using external methods such as imaging or surface sensors to diagnose or treat conditions. Minimally-invasive devices involve small incisions or natural body openings to reach internal structures, reducing recovery time and minimizing tissue damage compared to traditional surgery. Key differences include the level of bodily intrusion, risk of infection, recovery duration, and procedural complexity, with non-invasive methods generally offering safer, less traumatic alternatives.
Advantages of Non-Invasive Medical Devices
Non-invasive medical devices offer significant advantages including reduced risk of infection, minimal patient discomfort, and faster recovery times compared to minimally-invasive procedures. These devices enable continuous monitoring and diagnostics without the need for incisions or internal instruments, enhancing patient compliance and clinical efficiency. Common examples include wearable heart monitors, ultrasound imaging, and pulse oximeters, which provide real-time data with high accuracy and safety.
Benefits of Minimally-Invasive Medical Technology
Minimally-invasive medical technology offers significant benefits including reduced patient trauma, shorter recovery times, and decreased risk of infection compared to traditional invasive procedures. These techniques utilize advanced tools like laparoscopes and endoscopes to perform precise surgeries with small incisions, preserving surrounding tissues. Enhanced surgical accuracy and minimized hospital stays contribute to improved patient outcomes and overall healthcare efficiency.
Applications of Non-Invasive Devices in Modern Healthcare
Non-invasive medical devices, such as ultrasound imaging, pulse oximeters, and wearable glucose monitors, play a crucial role in early diagnosis, continuous patient monitoring, and preventive care without breaking the skin or entering the body. These devices enhance patient comfort and reduce the risk of infection, making them ideal for managing chronic conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory disorders. Their widespread use in telemedicine and home healthcare settings drives more efficient, cost-effective treatment while improving patient outcomes.
Minimally-Invasive Devices: Use Cases and Innovations
Minimally-invasive medical devices, such as laparoscopic surgical tools and endoscopic imaging systems, enable complex procedures with reduced tissue damage and faster patient recovery compared to traditional surgery. Innovations in robotics, micro-instruments, and real-time imaging have expanded use cases to include cardiovascular interventions, orthopedic surgeries, and neuroendoscopy. These advancements improve precision, decrease hospital stays, and minimize complications, positioning minimally-invasive devices as essential tools in modern healthcare.
Patient Outcomes: Non-Invasive vs Minimally-Invasive Treatments
Non-invasive treatments generally offer faster recovery times and lower risk of complications compared to minimally invasive procedures, enhancing overall patient outcomes especially in outpatient settings. Minimally invasive treatments, while involving small incisions, provide effective therapeutic interventions with reduced trauma and shorter hospitalization than traditional surgery, improving patient comfort and satisfaction. Selecting between non-invasive and minimally invasive options depends on the medical condition, with evidence showing tailored approaches optimize functional recovery and long-term prognosis.
Safety Considerations in Device Selection
Non-invasive medical devices typically present lower risks of infection and faster recovery times compared to minimally-invasive options, making them safer choices for patients with compromised immune systems. Minimally-invasive devices, though involving small incisions, offer enhanced precision and reduced tissue damage, balancing safety with therapeutic efficacy. Evaluating patient-specific factors such as comorbidities and procedural complexity is crucial in optimizing device selection to minimize complications and enhance clinical outcomes.
Regulatory Perspectives on Non-Invasive and Minimally-Invasive Devices
Regulatory frameworks distinguish non-invasive medical devices, which do not breach the body's surface, from minimally-invasive devices that involve small incisions or natural body openings. Non-invasive devices often undergo a more streamlined approval process due to lower risk profiles, while minimally-invasive devices require more rigorous clinical evaluation and compliance with stricter safety standards. Agencies like the FDA and EMA emphasize risk classification, clinical evidence, and post-market surveillance to ensure patient safety and device efficacy across both categories.
Future Trends in Non-Invasive and Minimally-Invasive Medical Devices
Future trends in non-invasive and minimally-invasive medical devices emphasize enhanced precision through integration of AI-powered diagnostics and real-time monitoring systems. Advancements in biocompatible materials and wireless sensor technologies enable safer, more efficient patient outcomes while reducing recovery times and healthcare costs. Emerging wearable and implantable devices continue to drive personalized treatment, expanding applications across chronic disease management and remote patient care.
Non-invasive vs Minimally-invasive Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com