In vitro diagnostics (IVD) offer comprehensive laboratory-based analysis with high accuracy and a wide range of test options, supporting detailed clinical decision-making. Point-of-care testing (POCT) provides rapid results directly at the patient's location, enhancing immediate treatment decisions and improving patient outcomes. Both IVD and POCT technologies are integral to modern healthcare, balancing precision with speed to optimize diagnostic workflows.
Table of Comparison
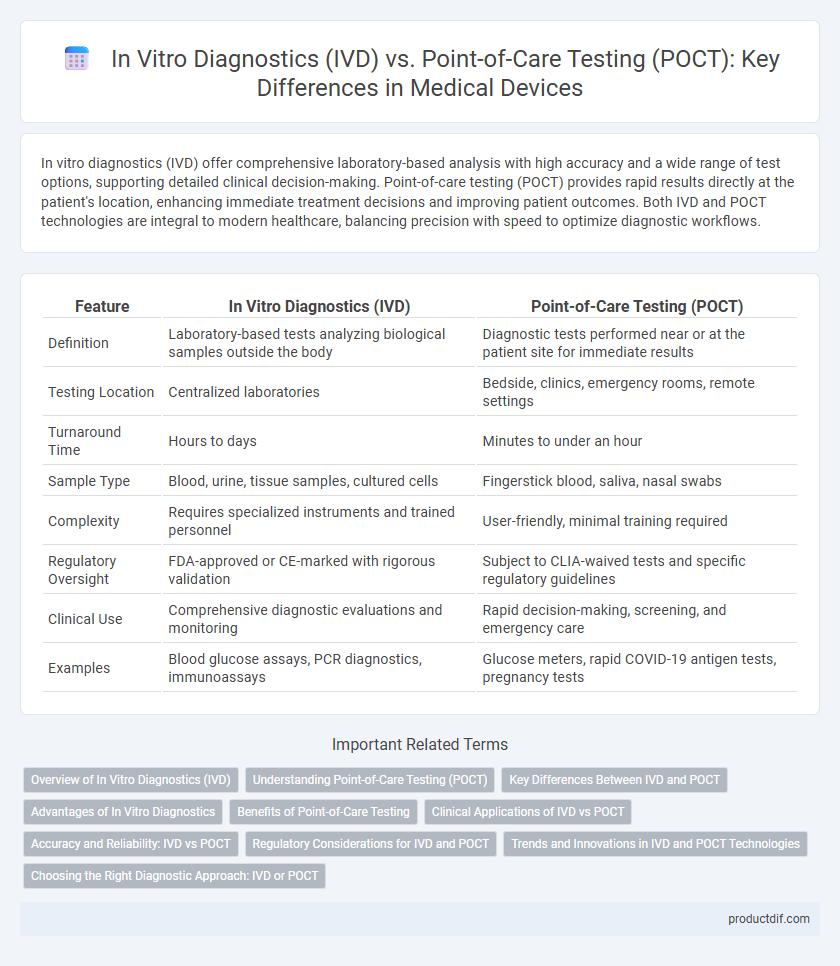
| Feature | In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) | Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Laboratory-based tests analyzing biological samples outside the body | Diagnostic tests performed near or at the patient site for immediate results |
| Testing Location | Centralized laboratories | Bedside, clinics, emergency rooms, remote settings |
| Turnaround Time | Hours to days | Minutes to under an hour |
| Sample Type | Blood, urine, tissue samples, cultured cells | Fingerstick blood, saliva, nasal swabs |
| Complexity | Requires specialized instruments and trained personnel | User-friendly, minimal training required |
| Regulatory Oversight | FDA-approved or CE-marked with rigorous validation | Subject to CLIA-waived tests and specific regulatory guidelines |
| Clinical Use | Comprehensive diagnostic evaluations and monitoring | Rapid decision-making, screening, and emergency care |
| Examples | Blood glucose assays, PCR diagnostics, immunoassays | Glucose meters, rapid COVID-19 antigen tests, pregnancy tests |
Overview of In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD)
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) involve analyzing biological samples such as blood, urine, or tissue outside the human body to detect diseases, monitor health conditions, or guide treatment decisions. IVD devices include reagents, instruments, and systems used in clinical laboratories to provide accurate and reliable diagnostic results. Unlike point-of-care testing (POCT), which offers rapid testing at or near the patient, IVD relies on centralized laboratory settings for comprehensive analysis and higher throughput.
Understanding Point-of-Care Testing (POCT)
Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) enables rapid diagnostic results at or near the patient site, facilitating immediate clinical decisions and treatment adjustments. Unlike traditional In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) performed in centralized laboratories, POCT devices are designed for ease of use, portability, and quick turnaround times, enhancing patient care in critical settings. Key POCT applications include glucose monitoring, coagulation testing, and infectious disease detection, which improve workflow efficiency and patient outcomes.
Key Differences Between IVD and POCT
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) involve laboratory-based testing of biological samples to detect diseases or conditions, typically requiring specialized equipment and skilled personnel for accurate results. Point-of-care testing (POCT) offers rapid diagnostic results near the patient, enabling immediate clinical decisions with portable devices designed for ease of use and minimal training. Key differences include the testing environment, turnaround time for results, and the level of user expertise required, with IVD emphasizing accuracy and comprehensive analysis, while POCT prioritizes speed and convenience.
Advantages of In Vitro Diagnostics
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) offer high analytical accuracy and comprehensive laboratory testing capabilities, enabling precise disease detection and monitoring. IVD devices support a wide range of tests, from molecular assays to immunoassays, providing detailed diagnostic information critical for personalized treatment plans. These devices often comply with stringent regulatory standards, ensuring reliable and reproducible results across diverse clinical settings.
Benefits of Point-of-Care Testing
Point-of-care testing (POCT) delivers rapid diagnostic results directly at the site of patient care, significantly reducing turnaround times compared to traditional in vitro diagnostics (IVD) performed in centralized laboratories. POCT enhances clinical decision-making by enabling immediate treatment adjustments, improving patient outcomes, and minimizing hospital stay durations. The portability and ease of use of POCT devices facilitate broader access in diverse healthcare settings, including remote and resource-limited areas, supporting timely disease management and control.
Clinical Applications of IVD vs POCT
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) enable comprehensive laboratory analysis for detecting diseases, monitoring chronic conditions, and guiding therapeutic decisions with high accuracy and throughput in centralized labs. Point-of-care testing (POCT) offers rapid, on-site diagnostic results for emergency care, infectious disease screening, and critical patient monitoring, facilitating immediate clinical decision-making. The clinical application of IVD is ideal for detailed, confirmatory testing while POCT enhances patient management through timely, accessible diagnostics in diverse healthcare settings.
Accuracy and Reliability: IVD vs POCT
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) offer higher accuracy and reliability due to standardized laboratory conditions and advanced equipment, which minimizes variability and ensures consistent results. Point-of-care testing (POCT) provides rapid results at the patient's location but may sacrifice some accuracy and reliability due to simpler devices and operator-dependent factors. Despite this, POCT remains valuable for immediate clinical decisions, while IVD is preferred for confirmatory diagnostics and comprehensive analysis.
Regulatory Considerations for IVD and POCT
Regulatory considerations for In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) involve stringent compliance with standards set by agencies such as the FDA, CE marking in Europe, and ISO 13485 certification to ensure device safety, accuracy, and reliability. Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) devices face additional regulatory scrutiny due to their usage in decentralized environments, requiring rigorous evaluation of user-friendliness, rapid turnaround times, and consistent performance under diverse conditions. Both IVD and POCT devices must undergo clinical validation and risk assessment to meet regulatory requirements, but POCT devices often require tailored guidelines addressing on-site testing challenges.
Trends and Innovations in IVD and POCT Technologies
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) technologies are rapidly advancing with innovations such as multiplex assays, digital PCR, and microfluidic platforms that enhance sensitivity and throughput in clinical laboratories. Point-of-care testing (POCT) devices are increasingly integrating wireless connectivity, real-time data analytics, and smartphone compatibility to deliver faster, decentralized diagnostic results at the patient's bedside or remote locations. Emerging trends in both IVD and POCT emphasize automation, miniaturization, and artificial intelligence-driven interpretation to improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce turnaround times, and support precision medicine initiatives.
Choosing the Right Diagnostic Approach: IVD or POCT
Selecting the appropriate diagnostic method depends on clinical needs, test complexity, and turnaround time requirements, with in vitro diagnostics (IVD) offering high-throughput and precise analysis typically performed in centralized laboratories. Point-of-care testing (POCT) provides rapid, on-site results critical for immediate clinical decision-making, especially in emergency or remote settings. Evaluating factors such as accuracy, accessibility, cost, and sample type ensures optimal diagnostic effectiveness for patient care.
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) vs Point-of-care testing (POCT) Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com