Proprietary equipment offers enhanced security and dedicated technical support, ensuring reliable performance tailored to specific industry standards. Open-source equipment provides greater flexibility and customization, enabling users to modify hardware and software to meet unique operational needs. Choosing between the two depends on balancing control, cost, and adaptability for optimized equipment management.
Table of Comparison
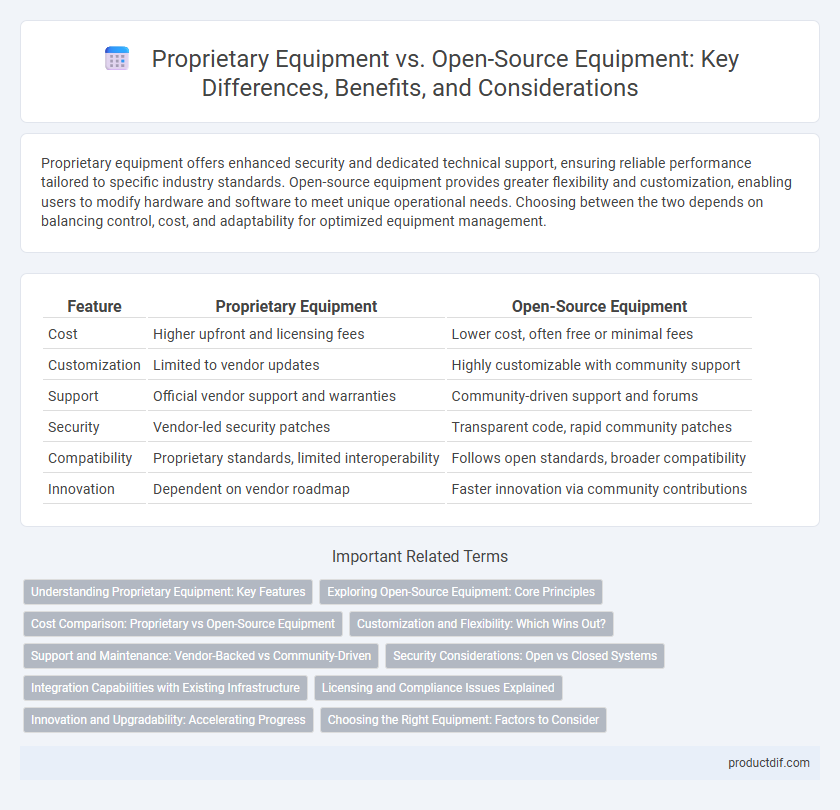
| Feature | Proprietary Equipment | Open-Source Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher upfront and licensing fees | Lower cost, often free or minimal fees |
| Customization | Limited to vendor updates | Highly customizable with community support |
| Support | Official vendor support and warranties | Community-driven support and forums |
| Security | Vendor-led security patches | Transparent code, rapid community patches |
| Compatibility | Proprietary standards, limited interoperability | Follows open standards, broader compatibility |
| Innovation | Dependent on vendor roadmap | Faster innovation via community contributions |
Understanding Proprietary Equipment: Key Features
Proprietary equipment is designed with exclusive technology and software controlled by a single company, ensuring compatibility and optimized performance within its ecosystem. Key features include restricted access to design specifications, limited customization options, and support services provided solely by the manufacturer. This type of equipment often offers enhanced security measures and integrated components, delivering reliability and consistency tailored to specific user needs.
Exploring Open-Source Equipment: Core Principles
Open-source equipment prioritizes transparency, modularity, and community collaboration, enabling users to access, modify, and improve hardware designs freely. Unlike proprietary equipment, which restricts access through patents and closed systems, open-source equipment fosters innovation and reduces costs by leveraging collective expertise. Key principles include open documentation, interoperability standards, and shared development platforms that empower users to customize solutions effectively.
Cost Comparison: Proprietary vs Open-Source Equipment
Proprietary equipment often carries higher upfront costs due to licensing fees and vendor lock-in, while open-source equipment typically offers lower initial expenses and greater budget flexibility by eliminating costly licenses. Maintenance and upgrade costs for proprietary systems tend to be more expensive as they require vendor-specific services, whereas open-source equipment benefits from community-driven support and customizable updates that reduce long-term expenditures. Cost comparison reveals that open-source equipment can significantly lower total cost of ownership in environments prioritizing scalability and adaptability.
Customization and Flexibility: Which Wins Out?
Proprietary equipment often provides tailored features with manufacturer-backed support but limits user customization and flexibility due to closed architectures. Open-source equipment enables extensive customization and adaptability, allowing users to modify hardware and software to fit specific needs, fostering innovation and cost-efficiency. For industries requiring specialized solutions and rapid iteration, open-source equipment generally wins in customization and flexibility.
Support and Maintenance: Vendor-Backed vs Community-Driven
Vendor-backed proprietary equipment offers dedicated support and regular maintenance updates, ensuring reliability and quick issue resolution through professional service teams. Open-source equipment relies on community-driven support, where maintenance and troubleshooting depend on user contributions and shared knowledge, potentially resulting in varied response times and expertise levels. Enterprises prioritize vendor-backed options for critical operations due to guaranteed service agreements, while open-source solutions appeal to those valuing flexibility and collaborative problem-solving.
Security Considerations: Open vs Closed Systems
Proprietary equipment often features closed systems with restricted access to hardware and software, reducing vulnerabilities by limiting modifications and unauthorized access. Open-source equipment allows transparency in code and design, enabling extensive community scrutiny and rapid identification of security flaws but potentially exposing more attack vectors. Security considerations hinge on the trade-off between controlled environments in closed systems and collaborative oversight in open-source platforms.
Integration Capabilities with Existing Infrastructure
Proprietary equipment often features tailored integration capabilities designed to seamlessly connect with specific existing infrastructure, leveraging vendor-supported protocols and standardized interfaces. Open-source equipment provides greater flexibility by enabling customization and compatibility with a wider range of systems through open standards and community-driven updates. Organizations prioritizing efficient infrastructure integration must evaluate proprietary solutions for turnkey compatibility and open-source options for adaptability and interoperability.
Licensing and Compliance Issues Explained
Proprietary equipment typically involves strict licensing agreements that restrict usage, modification, and redistribution, often requiring compliance with vendor-imposed terms to avoid legal penalties. Open-source equipment, governed by licenses such as GPL or MIT, promotes transparency and flexibility but mandates adherence to specific conditions like source code disclosure and attribution. Understanding these licensing frameworks is crucial for ensuring compliance, minimizing legal risks, and managing intellectual property rights in equipment deployment.
Innovation and Upgradability: Accelerating Progress
Proprietary equipment often features tightly controlled design and software, limiting user modifications but ensuring consistent innovation driven by dedicated R&D teams. Open-source equipment promotes rapid innovation and upgradability through collaborative development, enabling users to customize hardware and firmware to meet evolving needs. The choice between proprietary and open-source equipment significantly impacts the pace of technological progress and adaptability in dynamic industries.
Choosing the Right Equipment: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right equipment involves evaluating proprietary equipment's reliability, specialized features, and manufacturer support against open-source equipment's adaptability, cost-effectiveness, and community-driven innovation. Key factors include compatibility with existing systems, total cost of ownership, scalability, and the level of technical support available. Decision-makers should also consider security implications and long-term maintenance requirements aligned with project goals.
Proprietary equipment vs open-source equipment Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com