Portable equipment offers flexibility and ease of transportation, making it ideal for tasks that require mobility and quick relocation. Stationary equipment typically provides greater power and stability, suited for heavy-duty or continuous operations in a fixed location. Choosing between portable and stationary equipment depends on the specific needs of the job, including space constraints, frequency of movement, and intensity of use.
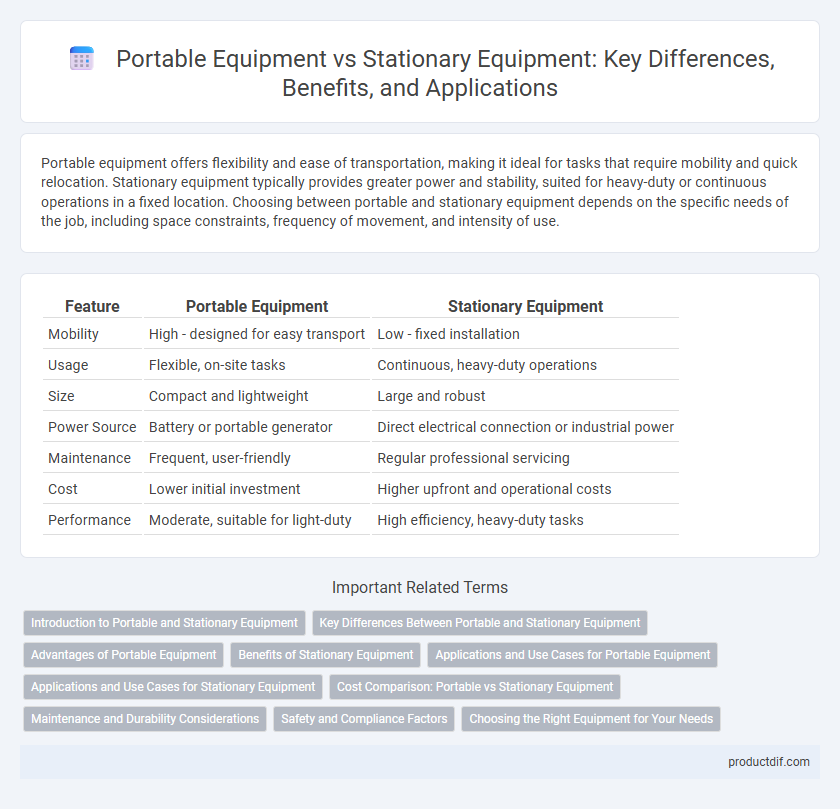
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Portable Equipment | Stationary Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | High - designed for easy transport | Low - fixed installation |
| Usage | Flexible, on-site tasks | Continuous, heavy-duty operations |
| Size | Compact and lightweight | Large and robust |
| Power Source | Battery or portable generator | Direct electrical connection or industrial power |
| Maintenance | Frequent, user-friendly | Regular professional servicing |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher upfront and operational costs |
| Performance | Moderate, suitable for light-duty | High efficiency, heavy-duty tasks |
Introduction to Portable and Stationary Equipment
Portable equipment offers flexibility and ease of transport, making it ideal for on-site tasks and varying work environments, whereas stationary equipment provides stable, high-capacity performance suited for fixed installations. Portable tools often emphasize lightweight design, battery power, and compactness, while stationary machinery focuses on durability, continuous operation, and integration into production lines. Understanding the distinct applications and benefits of each type enables informed decisions for efficiency and productivity in industrial and commercial settings.
Key Differences Between Portable and Stationary Equipment
Portable equipment offers mobility and flexibility, allowing users to transport tools and devices across various locations, making them ideal for on-site tasks and temporary setups. Stationary equipment, designed for fixed installations, provides greater stability, power, and durability, suitable for continuous or heavy-duty operations in a dedicated workspace. Key differences include size, weight, power source, and intended usage environment, influencing efficiency and usability in different industrial or operational contexts.
Advantages of Portable Equipment
Portable equipment offers significant advantages such as enhanced mobility, allowing users to operate in diverse locations without the need for fixed installations. Its compact design facilitates easy transportation and rapid deployment, improving operational efficiency and reducing setup time. Additionally, portable equipment often requires less maintenance and lower initial investment compared to stationary alternatives.
Benefits of Stationary Equipment
Stationary equipment offers enhanced stability and durability for heavy-duty industrial applications, ensuring consistent performance and safety in fixed locations. It typically provides higher power capacity and precision, making it ideal for manufacturing, processing, and large-scale operations. The reduced need for frequent relocation minimizes wear and maintenance costs, improving long-term operational efficiency.
Applications and Use Cases for Portable Equipment
Portable equipment is essential in industries requiring mobility, such as construction, field research, and emergency services, enabling on-site diagnostics, repairs, and data collection. Its compact design and ease of transport allow workers to perform tasks in remote or confined locations where stationary equipment is impractical. Common applications include handheld power tools, portable medical devices, and mobile communication units, which enhance operational efficiency and flexibility.
Applications and Use Cases for Stationary Equipment
Stationary equipment is predominantly used in industrial manufacturing, chemical processing, and power generation due to its ability to handle large-scale, continuous operations with high stability and precision. Applications include fixed machinery such as HVAC systems in commercial buildings, assembly lines in automotive plants, and boilers in energy facilities, where reliable, long-term operation is critical. This equipment supports complex production processes, ensuring consistent output quality and minimizing downtime through robust installation.
Cost Comparison: Portable vs Stationary Equipment
Portable equipment generally incurs lower initial costs compared to stationary equipment due to reduced installation and infrastructure requirements. Maintenance expenses for portable equipment tend to be higher over time because of increased wear from frequent relocation and transport. Stationary equipment, while requiring significant upfront investment, often benefits from greater durability and lower ongoing operational costs, making it more cost-effective for long-term use.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Portable equipment requires more frequent maintenance due to exposure to varying environmental conditions and increased wear from mobility. Stationary equipment generally benefits from a stable operating environment, resulting in longer durability and reduced maintenance intervals. Selecting equipment depends on balancing maintenance schedules and durability requirements based on specific operational demands.
Safety and Compliance Factors
Portable equipment requires rigorous safety inspections and adherence to portable-specific standards such as ANSI/UL certifications to prevent hazards during frequent relocation and use in varied environments. Stationary equipment demands compliance with fixed safety codes, including OSHA regulations and local building codes, emphasizing installation integrity and long-term operational safety. Both types must incorporate regular maintenance schedules and user training to ensure continuous compliance and minimize accident risks.
Choosing the Right Equipment for Your Needs
Portable equipment offers flexibility and ease of movement, ideal for tasks requiring frequent relocation or limited workspace. Stationary equipment provides higher power capacity and stability, making it suitable for intensive, continuous operations in fixed locations. Selecting the right equipment depends on factors such as job requirements, workspace availability, and the need for mobility versus performance.
Portable equipment vs stationary equipment Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com