Horizontal integration involves acquiring or merging with companies at the same stage of production within the equipment industry to increase market share and reduce competition. Vertical integration entails controlling multiple levels of the supply chain, from manufacturing components to final assembly and distribution, enhancing efficiency and reducing dependency on suppliers. Choosing between these strategies depends on whether a company aims to expand market influence or streamline operations through supply chain control.
Table of Comparison
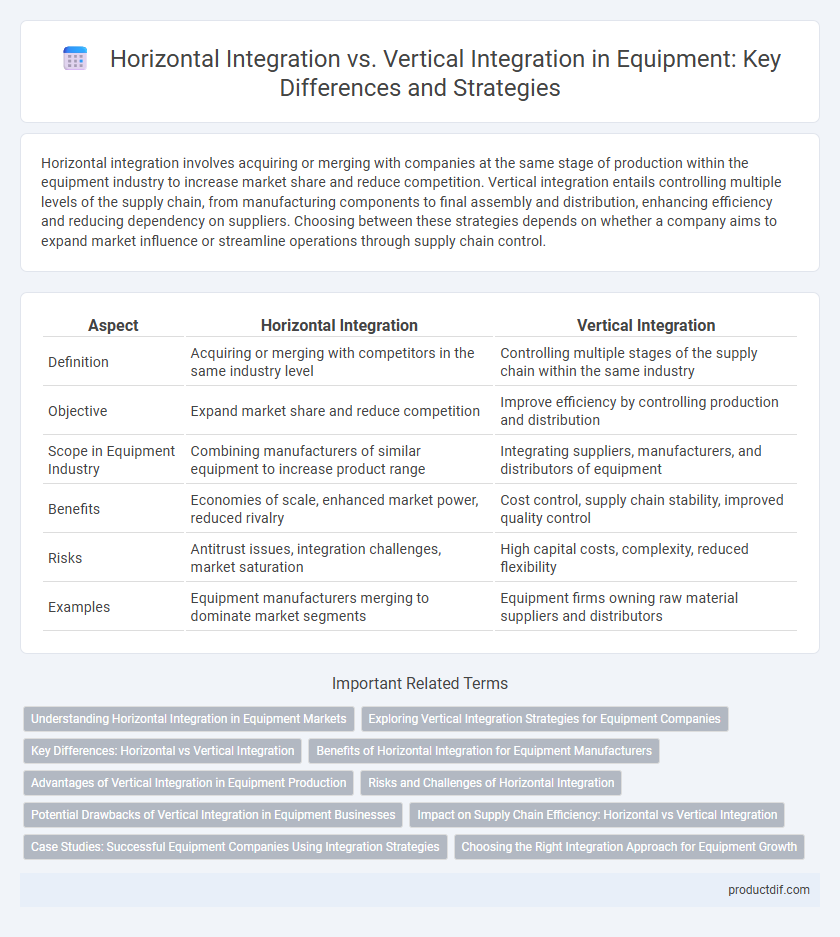
| Aspect | Horizontal Integration | Vertical Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquiring or merging with competitors in the same industry level | Controlling multiple stages of the supply chain within the same industry |
| Objective | Expand market share and reduce competition | Improve efficiency by controlling production and distribution |
| Scope in Equipment Industry | Combining manufacturers of similar equipment to increase product range | Integrating suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors of equipment |
| Benefits | Economies of scale, enhanced market power, reduced rivalry | Cost control, supply chain stability, improved quality control |
| Risks | Antitrust issues, integration challenges, market saturation | High capital costs, complexity, reduced flexibility |
| Examples | Equipment manufacturers merging to dominate market segments | Equipment firms owning raw material suppliers and distributors |
Understanding Horizontal Integration in Equipment Markets
Horizontal integration in equipment markets involves the consolidation of companies that manufacture similar types of machinery or tools, enhancing market share and reducing competition. This strategy enables businesses to achieve economies of scale, streamline production processes, and expand their product offerings within the same equipment category. By acquiring or merging with competitors, firms can leverage shared technologies and customer bases to strengthen their position in the industrial equipment sector.
Exploring Vertical Integration Strategies for Equipment Companies
Vertical integration strategies enable equipment companies to control multiple stages of production, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing and distribution, enhancing supply chain efficiency and reducing costs. By owning suppliers or distributors, companies can increase quality control, accelerate innovation cycles, and respond swiftly to market demands. This approach supports long-term competitive advantage by ensuring consistent equipment quality and fostering closer customer relationships.
Key Differences: Horizontal vs Vertical Integration
Horizontal integration in equipment industries involves acquiring or merging with competitors at the same production stage, enhancing market share and reducing competition. Vertical integration refers to controlling multiple stages of the supply chain, from manufacturing components to final product assembly, improving efficiency and reducing dependency on suppliers. Key differences include horizontal integration's emphasis on market expansion versus vertical integration's focus on supply chain control and cost reduction.
Benefits of Horizontal Integration for Equipment Manufacturers
Horizontal integration allows equipment manufacturers to expand product lines, increase market share, and achieve economies of scale by merging with or acquiring competitors. This strategy enhances operational efficiency and reduces production costs through shared resources and consolidated supply chains. By uniting similar equipment businesses, manufacturers can accelerate innovation and improve customer reach across diverse geographical markets.
Advantages of Vertical Integration in Equipment Production
Vertical integration in equipment production enhances supply chain control, reducing dependency on external suppliers and minimizing delays. It streamlines production processes, leading to cost savings and improved product quality through closer oversight. This strategy also fosters innovation by facilitating better coordination between design, manufacturing, and distribution functions.
Risks and Challenges of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration in equipment manufacturing faces significant risks including regulatory scrutiny for antitrust issues and the challenge of effectively merging corporate cultures and operations. Market saturation can reduce the anticipated economies of scale, while integration inefficiencies may result in increased operational costs and delayed innovation. Dependence on competitors' technologies and potential loss of competitive advantage also complicate long-term strategic positioning in the equipment industry.
Potential Drawbacks of Vertical Integration in Equipment Businesses
Vertical integration in equipment businesses can lead to high capital expenditure and increased operational complexity, which may reduce flexibility in responding to market changes. Relying heavily on internal suppliers or manufacturers might limit innovation and result in inefficiencies compared to specialized external vendors. Furthermore, vertical integration can create dependency risks, as disruptions in one segment of the supply chain can impact the entire production process.
Impact on Supply Chain Efficiency: Horizontal vs Vertical Integration
Horizontal integration in equipment manufacturing enhances supply chain efficiency by consolidating similar production processes and increasing economies of scale, leading to reduced costs and improved bargaining power with suppliers. Vertical integration streamlines supply chain operations by controlling multiple stages from raw material sourcing to final assembly, resulting in better coordination, reduced lead times, and increased quality control. Companies adopting vertical integration often experience stronger supply chain resilience, while horizontal integration drives market share expansion through capacity augmentation.
Case Studies: Successful Equipment Companies Using Integration Strategies
Caterpillar excels through vertical integration by managing its entire supply chain, enhancing quality control and reducing production costs in heavy equipment manufacturing. Komatsu employs horizontal integration by acquiring complementary businesses, expanding product lines and market reach in construction and mining equipment. Deere & Company successfully blends both strategies, integrating key component production while acquiring specialized equipment firms to diversify its portfolio and improve operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Integration Approach for Equipment Growth
Choosing the right integration approach for equipment growth depends on operational goals and market positioning. Horizontal integration expands equipment capacity by acquiring similar manufacturers, increasing market share and reducing competition. Vertical integration enhances control over the supply chain by consolidating equipment production, distribution, and maintenance, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Horizontal integration vs Vertical integration Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com