A 3D printer builds objects layer by layer from digital models, excelling at creating complex, detailed shapes with minimal material waste. In contrast, a CNC machine removes material from a solid block using precise cutting tools, making it ideal for producing parts with high strength and tight tolerances. Choosing between a 3D printer and a CNC machine depends on the specific requirements of precision, material type, and production volume.
Table of Comparison
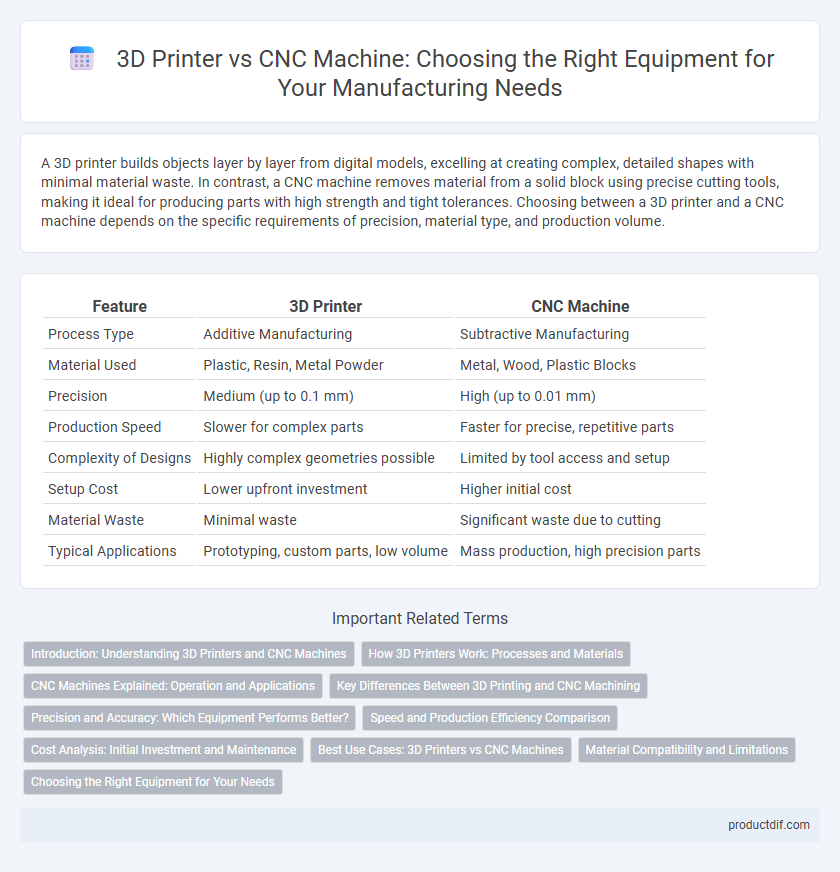
| Feature | 3D Printer | CNC Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Additive Manufacturing | Subtractive Manufacturing |
| Material Used | Plastic, Resin, Metal Powder | Metal, Wood, Plastic Blocks |
| Precision | Medium (up to 0.1 mm) | High (up to 0.01 mm) |
| Production Speed | Slower for complex parts | Faster for precise, repetitive parts |
| Complexity of Designs | Highly complex geometries possible | Limited by tool access and setup |
| Setup Cost | Lower upfront investment | Higher initial cost |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste | Significant waste due to cutting |
| Typical Applications | Prototyping, custom parts, low volume | Mass production, high precision parts |
Introduction: Understanding 3D Printers and CNC Machines
3D printers create objects by adding material layer by layer using digital files, enabling complex geometries and rapid prototyping. CNC machines remove material from solid blocks through computer-controlled cutting, providing high precision and strength for manufacturing parts. Both technologies revolutionize equipment fabrication but serve different production needs based on material type, complexity, and volume.
How 3D Printers Work: Processes and Materials
3D printers operate by depositing material layer by layer based on digital models, typically using processes such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Common materials include thermoplastics like PLA and ABS, photopolymer resins, and powdered metals or nylon. This additive manufacturing approach allows complex geometries and rapid prototyping compared to the subtractive cutting methods of CNC machines.
CNC Machines Explained: Operation and Applications
CNC machines operate by following precise computer-controlled instructions to cut, carve, or shape materials such as metal, wood, and plastic, achieving high accuracy and repeatability. Unlike 3D printers that build objects layer by layer through additive manufacturing, CNC machines use subtractive processes to remove material, making them ideal for creating complex parts with tight tolerances in industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing. The versatility of CNC machines extends to milling, turning, drilling, and grinding, enabling efficient mass production and prototyping of detailed components.
Key Differences Between 3D Printing and CNC Machining
3D printing builds objects layer by layer using additive manufacturing, ideal for complex geometries and rapid prototyping, while CNC machining removes material from a solid block through subtractive processes, offering high precision and superior surface finish. Material versatility differs as 3D printers commonly use plastics, resins, and some metals, whereas CNC machines can work with a broader range of metals, plastics, and composites. Production speed varies with CNC machining excelling in high-volume manufacturing, and 3D printing better suited for customized, low-volume parts.
Precision and Accuracy: Which Equipment Performs Better?
CNC machines deliver superior precision and accuracy compared to 3D printers, making them ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances and intricate details. 3D printers excel in rapid prototyping and producing complex geometries but generally have layer-based limitations that affect surface finish and dimensional fidelity. In industries demanding micron-level accuracy, CNC machining remains the gold standard for repeatable and high-quality component fabrication.
Speed and Production Efficiency Comparison
3D printers excel in rapid prototyping with the ability to produce complex geometries quickly and with minimal setup time, making them ideal for small batch production and iterative design processes. CNC machines offer superior speed and consistency for high-volume manufacturing, efficiently producing parts with tight tolerances and minimal post-processing. While 3D printing reduces lead time for customized products, CNC machining outperforms in total production efficiency for large-scale runs due to its faster material removal rates and automation capabilities.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
3D printers generally have a lower initial investment cost, ranging from $200 to $5,000 depending on the model and capabilities, while CNC machines typically start at $10,000 and can exceed $100,000 for industrial-grade equipment. Maintenance costs for 3D printers are usually minimal, involving filament replacement and occasional part calibration, whereas CNC machines require regular maintenance, including coolant replacement, tool wear monitoring, and more frequent servicing, contributing to higher long-term expenses. Businesses must evaluate both upfront costs and ongoing maintenance to determine the most cost-effective solution for their manufacturing needs.
Best Use Cases: 3D Printers vs CNC Machines
3D printers excel in creating intricate, customizable prototypes and complex geometries with minimal material waste, ideal for rapid prototyping and low-volume production. CNC machines deliver high precision and consistency for subtractive manufacturing, making them suitable for large-scale production runs of metal or wood components requiring tight tolerances. Selecting between a 3D printer and CNC machine depends on factors like material type, production volume, and complexity of design.
Material Compatibility and Limitations
3D printers excel in working with a variety of thermoplastics, resins, and composite materials, offering complex geometries and intricate details with ease. CNC machines are better suited for harder materials like metals, wood, and plastics, providing high precision and surface finish but limited by the tool geometry and machining accessibility. Material compatibility in CNC machining is constrained by cutting tool wear and rigidity, while 3D printing faces challenges with material strength and thermal properties during layer fusion.
Choosing the Right Equipment for Your Needs
Selecting between a 3D printer and a CNC machine depends on project requirements such as material type, precision, and production volume. 3D printers excel in creating complex, customized parts with minimal waste, ideal for prototyping and small-batch manufacturing using materials like PLA, ABS, or resin. CNC machines offer superior accuracy and durability for cutting metals and dense materials, making them suitable for high-volume production and applications requiring tighter tolerances.
3D printer vs CNC machine Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com