Wired pet equipment offers a reliable and consistent connection, ensuring uninterrupted performance and eliminating concerns about battery life. Wireless pet devices provide enhanced mobility and ease of use, allowing pets greater freedom without being tethered by cords. Choosing between wired and wireless options depends on the balance of convenience versus dependability required for your pet's specific needs.
Table of Comparison
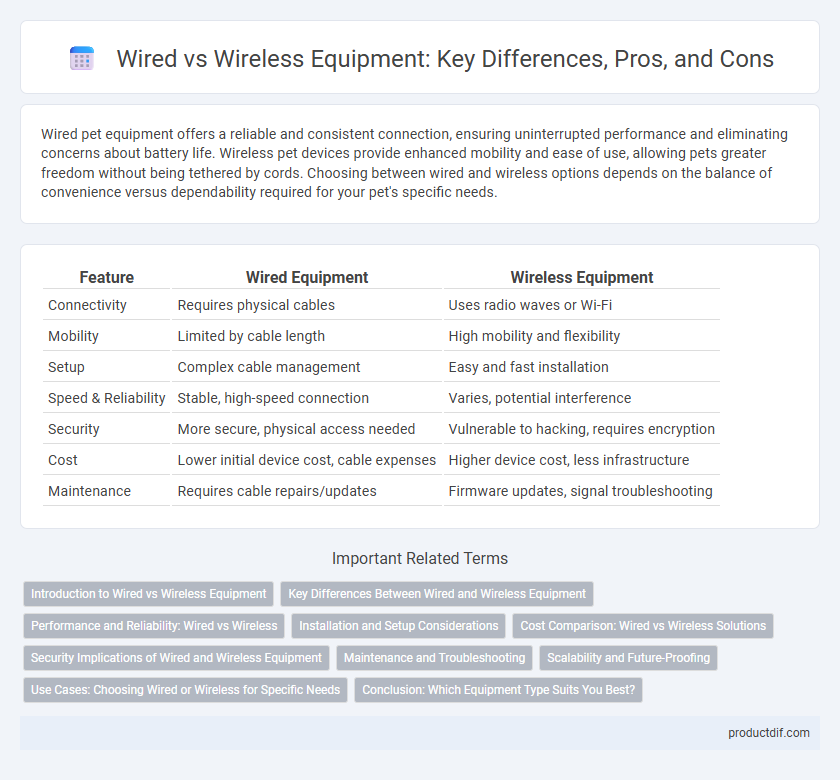
| Feature | Wired Equipment | Wireless Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Requires physical cables | Uses radio waves or Wi-Fi |
| Mobility | Limited by cable length | High mobility and flexibility |
| Setup | Complex cable management | Easy and fast installation |
| Speed & Reliability | Stable, high-speed connection | Varies, potential interference |
| Security | More secure, physical access needed | Vulnerable to hacking, requires encryption |
| Cost | Lower initial device cost, cable expenses | Higher device cost, less infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Requires cable repairs/updates | Firmware updates, signal troubleshooting |
Introduction to Wired vs Wireless Equipment
Wired equipment relies on physical cables such as Ethernet or coaxial to transmit data, providing stable and high-speed connections ideal for environments requiring consistent performance like data centers. Wireless equipment uses radio frequency signals including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, offering greater mobility and ease of installation, suited for dynamic and flexible setups. Choosing between wired and wireless equipment depends on factors like network speed requirements, security considerations, and the physical layout of the space.
Key Differences Between Wired and Wireless Equipment
Wired equipment relies on physical cables such as Ethernet for data transmission, offering consistent speeds and lower latency, essential for environments demanding stable connections like data centers and large offices. Wireless equipment operates via radio frequencies, providing greater mobility and easier installation but can face interference, signal attenuation, and generally higher latency compared to wired counterparts. Key differences include installation complexity, network reliability, speed consistency, security levels, and flexibility in device placement.
Performance and Reliability: Wired vs Wireless
Wired equipment generally offers superior performance and reliability due to stable, high-speed connections and minimal signal interference. Wireless devices provide flexibility and mobility but may face latency issues and susceptibility to signal disruptions from physical obstructions or electromagnetic interference. Choosing wired technology ensures consistent data transfer rates and reduced downtime, critical for mission-critical applications.
Installation and Setup Considerations
Wired equipment installation requires precise cable management and access to physical connection points, often resulting in longer setup times and limited flexibility in positioning. Wireless devices offer easier installation with minimal physical infrastructure, allowing for quick setup and repositioning without the need for extensive cabling. However, wired setups generally provide more stable and interference-free connections, which can be critical for environments demanding reliable performance.
Cost Comparison: Wired vs Wireless Solutions
Wired equipment solutions typically involve higher upfront installation costs due to extensive cabling and labor requirements but offer lower maintenance expenses over time. Wireless systems often have lower initial deployment costs and greater flexibility but may incur higher operational costs related to network upgrades, signal interference, and security measures. Evaluating total cost of ownership for wired versus wireless solutions depends on specific use cases, infrastructure complexity, and long-term scalability requirements.
Security Implications of Wired and Wireless Equipment
Wired equipment offers enhanced security by minimizing exposure to external interception through physical cables, reducing risks associated with unauthorized access and eavesdropping. Wireless equipment, while providing greater flexibility and mobility, is inherently vulnerable to security threats such as signal interception, unauthorized access, and interference, demanding robust encryption protocols like WPA3 and regular firmware updates. Implementing stringent security measures and network segmentation is critical to mitigating vulnerabilities unique to both wired and wireless environments.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Wired equipment typically requires less frequent maintenance due to stable connections and fewer interference issues, simplifying troubleshooting processes. Wireless equipment often demands regular firmware updates and signal optimization to maintain performance, with troubleshooting focused on connectivity problems and signal interference sources. Effective maintenance strategies for both involve proactive monitoring and timely hardware inspections to minimize downtime.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
Wired equipment offers consistent scalability through stable bandwidth and minimal interference, making it ideal for expanding infrastructure without compromising performance. Wireless solutions provide flexibility and ease of deployment but may face limitations in range and signal congestion as networks grow. Future-proofing favors hybrid systems that integrate wired backbone stability with wireless adaptability to accommodate evolving technology demands.
Use Cases: Choosing Wired or Wireless for Specific Needs
Wired equipment excels in environments requiring stable, high-speed connections, such as data centers and professional studios where low latency and consistent performance are critical. Wireless solutions offer flexibility and mobility, ideal for home offices, retail spaces, and IoT devices where ease of installation and portability outweigh maximum speed. Selecting wired or wireless depends on factors like network reliability, distance constraints, and specific operational demands.
Conclusion: Which Equipment Type Suits You Best?
Wired equipment provides stable, high-speed connections ideal for environments demanding consistent performance, such as data centers or professional studios. Wireless equipment offers flexibility and convenience, making it suitable for mobile setups or locations where cabling is impractical. Choosing between wired and wireless depends on your specific needs for reliability, mobility, and installation constraints.
Wired vs Wireless Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com