High-capacity equipment handles larger volumes and increased workloads, significantly boosting productivity in industrial and manufacturing settings. Low-capacity equipment offers greater flexibility and lower initial costs, making it suitable for small-scale operations or tasks with less demand. Choosing between the two depends on operational needs, budget constraints, and the scale of production required.
Table of Comparison
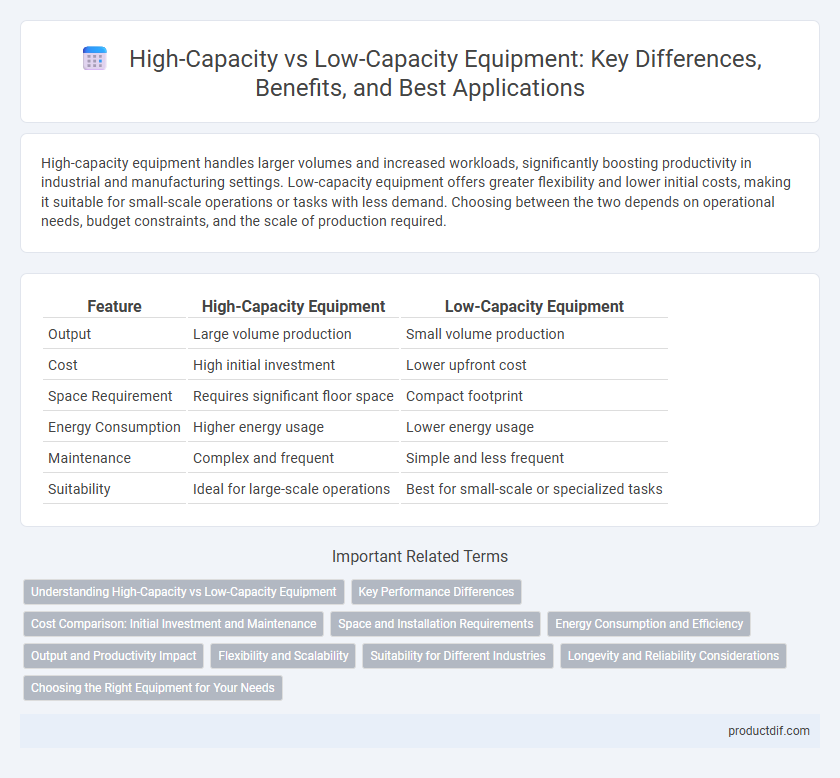
| Feature | High-Capacity Equipment | Low-Capacity Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Output | Large volume production | Small volume production |
| Cost | High initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Space Requirement | Requires significant floor space | Compact footprint |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy usage | Lower energy usage |
| Maintenance | Complex and frequent | Simple and less frequent |
| Suitability | Ideal for large-scale operations | Best for small-scale or specialized tasks |
Understanding High-Capacity vs Low-Capacity Equipment
High-capacity equipment handles larger volumes or loads, improving operational efficiency in industries like manufacturing, construction, and logistics. Low-capacity equipment is ideal for smaller tasks, offering greater precision and lower energy consumption. Understanding the differences helps businesses select the right machinery to optimize performance and reduce costs.
Key Performance Differences
High-capacity equipment delivers significantly higher throughput, enabling increased operational efficiency and reduced production time compared to low-capacity equipment. It often features advanced technology for enhanced durability and software integration, resulting in superior precision and consistent output quality. Maintenance frequency and energy consumption tend to be optimized in high-capacity models, providing lower downtime and cost-effectiveness in large-scale industrial applications.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Maintenance
High-capacity equipment demands a significantly higher initial investment due to advanced technology and larger scale components, whereas low-capacity equipment offers budget-friendly entry costs suitable for smaller operations. Maintenance expenses for high-capacity equipment often include specialized parts and skilled labor, leading to increased ongoing costs compared to the simpler and more accessible upkeep of low-capacity machinery. Evaluating cost efficiency requires balancing upfront capital with long-term maintenance budgets tailored to operational scale and productivity goals.
Space and Installation Requirements
High-capacity equipment demands significantly more physical space for installation due to larger dimensions and heavier weight, often requiring reinforced flooring and specialized handling equipment. Low-capacity equipment typically occupies compact footprints, enabling easier integration into existing facilities with minimal space modification and simpler installation processes. Efficient space planning must consider these factors to optimize workflow and reduce infrastructure costs.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
High-capacity equipment typically consumes more energy due to its larger operational scale, but it often delivers higher productivity per unit of power, resulting in better overall energy efficiency compared to low-capacity equipment. Energy consumption in low-capacity equipment may be lower in absolute terms, but inefficiencies in power usage can lead to higher energy costs per output unit. Optimizing the balance between capacity and energy efficiency is crucial for reducing operational expenses and environmental impact in industrial applications.
Output and Productivity Impact
High-capacity equipment significantly boosts output by processing larger volumes within shorter time frames, directly enhancing productivity levels in industrial and manufacturing settings. Low-capacity equipment, while often more cost-effective initially, may lead to bottlenecks and slower production cycles, reducing overall operational efficiency. Optimizing equipment capacity to align with production demands is critical for maximizing throughput and maintaining competitive advantage.
Flexibility and Scalability
High-capacity equipment offers superior scalability, enabling businesses to handle increased workloads without compromising performance. Low-capacity equipment provides greater flexibility, allowing easy adaptation to varying operational demands and diverse application requirements. Choosing between the two depends on balancing future growth potential against immediate, dynamic operational needs.
Suitability for Different Industries
High-capacity equipment is ideal for industries with large-scale production needs such as manufacturing, mining, and agriculture, where processing high volumes efficiently is critical. Low-capacity equipment suits small to medium enterprises or specialized sectors like artisanal crafts and boutique food production, offering flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Selecting the appropriate equipment depends on industry-specific demands, production scale, and operational budget constraints.
Longevity and Reliability Considerations
High-capacity equipment typically offers enhanced longevity due to robust construction and industrial-grade components designed to withstand intense usage, leading to reduced downtime and maintenance costs. In contrast, low-capacity equipment may experience faster wear and increased failure rates under heavy workloads, impacting overall reliability and operational efficiency. Investing in high-capacity machinery ensures consistent performance and durability, especially in demanding environments where equipment lifespan and dependability directly affect productivity.
Choosing the Right Equipment for Your Needs
High-capacity equipment delivers greater output and efficiency, making it ideal for large-scale industrial operations with high production demands. Low-capacity equipment suits smaller projects or businesses with limited budgets and lower operational requirements due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance. Evaluating project size, budget constraints, and future scalability ensures selecting equipment that aligns with specific operational needs and maximizes productivity.
High-capacity equipment vs low-capacity equipment Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com