Portable equipment offers flexibility and ease of transportation, ideal for tasks requiring mobility or limited workspace. Stationary equipment provides enhanced stability and durability, making it suitable for heavy-duty operations and long-term installations. Selecting the right option depends on the specific operational needs, site conditions, and the frequency of equipment movement.
Table of Comparison
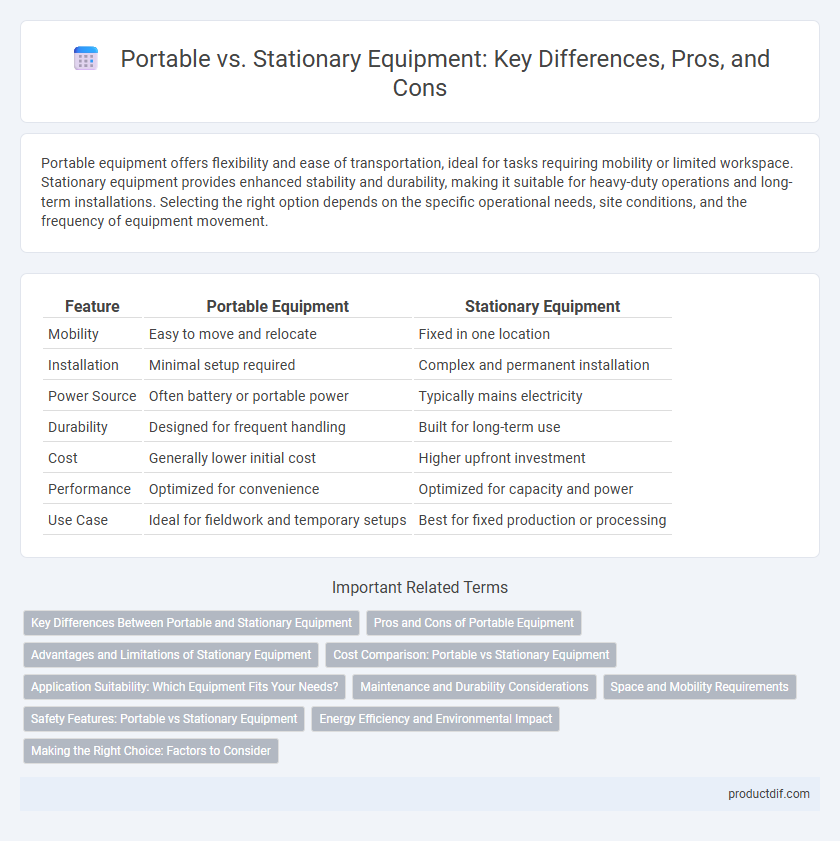
| Feature | Portable Equipment | Stationary Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | Easy to move and relocate | Fixed in one location |
| Installation | Minimal setup required | Complex and permanent installation |
| Power Source | Often battery or portable power | Typically mains electricity |
| Durability | Designed for frequent handling | Built for long-term use |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Performance | Optimized for convenience | Optimized for capacity and power |
| Use Case | Ideal for fieldwork and temporary setups | Best for fixed production or processing |
Key Differences Between Portable and Stationary Equipment
Portable equipment offers mobility and convenience, enabling use in various locations without complex installation, while stationary equipment provides stability, higher capacity, and enhanced performance for fixed-site operations. Portable units usually have lower weight, compact design, and are powered by batteries or lightweight sources, contrasting with stationary equipment that relies on permanent power connections and robust structural support. Key differences include operational flexibility, durability, maintenance requirements, and suitability for diverse industrial or commercial applications.
Pros and Cons of Portable Equipment
Portable equipment offers unmatched flexibility and convenience, enabling on-site operations and easy transportation across various locations, which significantly reduces downtime. However, these devices often sacrifice durability and power compared to stationary equipment, potentially leading to higher maintenance costs and limited performance in heavy-duty tasks. Nevertheless, the compact size and lightweight design of portable equipment make it ideal for industries requiring mobility, such as construction, agriculture, and emergency services.
Advantages and Limitations of Stationary Equipment
Stationary equipment offers superior stability and durability, making it ideal for high-precision tasks and heavy-duty industrial applications. It typically supports larger capacity and continuous operation but lacks mobility, restricting its use to a fixed location. Maintenance and setup costs can be higher compared to portable alternatives, impacting initial investment and operational flexibility.
Cost Comparison: Portable vs Stationary Equipment
Portable equipment generally incurs higher upfront costs due to compact design and added mobility features, but it reduces transportation and installation expenses. Stationary equipment, while often less expensive initially, involves higher costs in installation, space allocation, and long-term maintenance. When evaluating total cost of ownership, factors such as usage frequency, mobility needs, and operational efficiency must be considered to determine the most cost-effective option.
Application Suitability: Which Equipment Fits Your Needs?
Portable equipment excels in applications requiring mobility and flexibility, such as onsite repairs, fieldwork, and temporary setups. Stationary equipment suits environments with consistent, high-volume operations like manufacturing plants and fixed installations, offering stability and enhanced performance. Choosing between portable and stationary equipment depends on factors like operational scale, location stability, and specific task requirements to ensure optimal efficiency and productivity.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Portable equipment typically requires more frequent maintenance due to increased exposure to environmental factors and handling stress, which can accelerate wear and tear. Stationary equipment benefits from stable installation conditions, resulting in enhanced durability and less frequent maintenance needs. Choosing between portable and stationary equipment depends on balancing operational flexibility with long-term maintenance costs and equipment lifespan.
Space and Mobility Requirements
Portable equipment offers superior mobility and requires minimal space, ideal for dynamic work environments and frequent relocation. Stationary equipment demands a fixed, often larger footprint but provides enhanced stability and capacity for heavy-duty operations. Choosing between portable and stationary depends on balancing spatial constraints with mobility needs in the specific application.
Safety Features: Portable vs Stationary Equipment
Portable equipment often incorporates safety features such as automatic shutoff, insulated handles, and lightweight designs to minimize user injury during transport and operation. Stationary equipment typically includes fixed safety guards, emergency stop buttons, and reinforced structural components to ensure stability and protect operators in high-intensity industrial environments. Understanding the distinct safety mechanisms of portable versus stationary equipment is crucial for selecting devices that meet specific operational hazards and compliance standards.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Portable equipment typically consumes less energy due to smaller power requirements and often incorporates energy-saving features, reducing operational costs and environmental footprint. Stationary equipment, while generally more powerful and capable of handling larger workloads, can lead to higher energy consumption and increased emissions if not optimized for efficiency. Choosing energy-efficient models and using smart controls can significantly mitigate the environmental impact of both portable and stationary equipment.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Choosing between portable and stationary equipment depends on factors such as space availability, frequency of use, and mobility requirements. Portable equipment offers flexibility and ease of transport, making it ideal for temporary or remote applications, while stationary equipment provides greater durability and capacity for heavy-duty, continuous tasks. Assessing budget constraints, maintenance needs, and operational environment ensures selecting the equipment type that maximizes efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Portable vs Stationary Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com