Heavy-duty equipment is designed for demanding tasks requiring high strength, durability, and long operational hours, ideal for construction, mining, and industrial applications. Light-duty equipment is better suited for smaller-scale jobs, offering greater maneuverability, lower weight, and ease of use in residential or light commercial settings. Choosing between heavy-duty and light-duty equipment depends on the project's scale, intensity, and specific operational requirements.
Table of Comparison
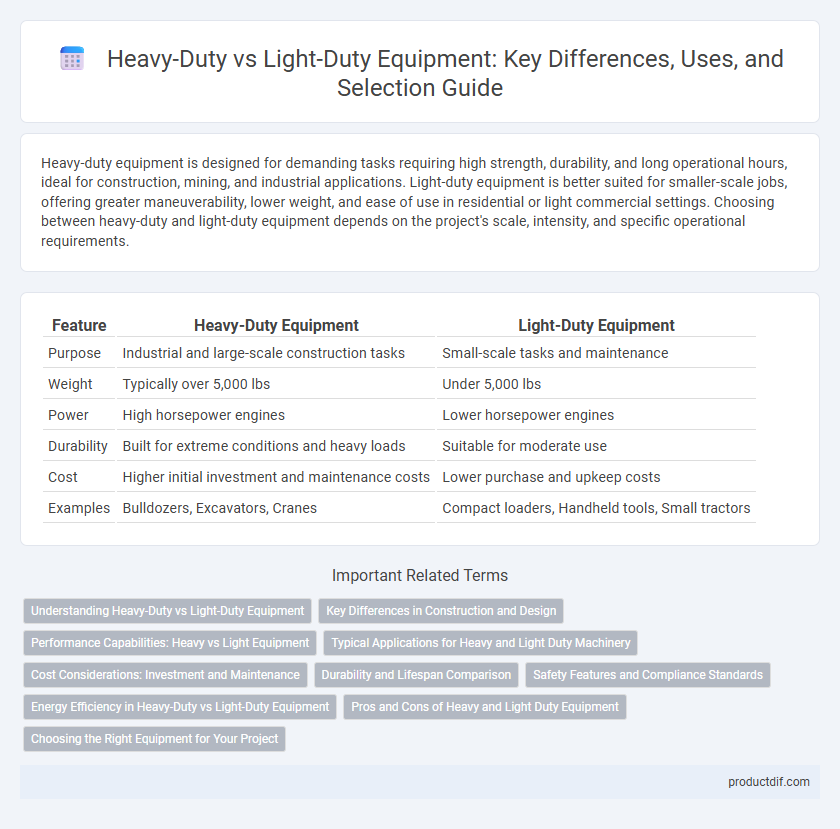
| Feature | Heavy-Duty Equipment | Light-Duty Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Industrial and large-scale construction tasks | Small-scale tasks and maintenance |
| Weight | Typically over 5,000 lbs | Under 5,000 lbs |
| Power | High horsepower engines | Lower horsepower engines |
| Durability | Built for extreme conditions and heavy loads | Suitable for moderate use |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and maintenance costs | Lower purchase and upkeep costs |
| Examples | Bulldozers, Excavators, Cranes | Compact loaders, Handheld tools, Small tractors |
Understanding Heavy-Duty vs Light-Duty Equipment
Heavy-duty equipment is designed for rigorous tasks requiring high power, durability, and extended operational capacity in industries like construction and mining. Light-duty equipment offers greater portability and ease of use, ideal for less intensive applications such as landscaping or small-scale repairs. Selecting the appropriate equipment depends on job requirements, material specifications, and expected workload intensity.
Key Differences in Construction and Design
Heavy-duty equipment features reinforced frames and high-strength materials to withstand intense operational stress and heavy loads, whereas light-duty equipment uses lighter materials optimized for agility and ease of use. Heavy machinery includes robust hydraulic systems and larger engines designed for prolonged, demanding tasks, while light-duty models prioritize fuel efficiency and portability. The design of heavy-duty equipment emphasizes durability and power, contrasting with the more compact, versatile construction of light-duty counterparts.
Performance Capabilities: Heavy vs Light Equipment
Heavy-duty equipment delivers superior performance capabilities for demanding construction and industrial tasks, featuring higher horsepower engines, greater load capacities, and enhanced durability to withstand rigorous use. Light-duty equipment excels in versatility and maneuverability, ideal for smaller projects requiring precision and efficiency with less power and lower operational cost. Choosing between heavy and light equipment depends on the scale of the job, with heavy-duty machines suited for large-scale excavation, lifting, and earthmoving, while light-duty options support landscaping, maintenance, and light material handling.
Typical Applications for Heavy and Light Duty Machinery
Heavy-duty equipment is commonly utilized in construction, mining, and large-scale landscaping projects where tasks require high power, durability, and capacity to handle rough terrain and heavy loads. Light-duty machinery excels in residential landscaping, small-scale farming, and maintenance tasks, providing agility and ease of operation for lighter, repetitive work. Typical applications for heavy-duty equipment include bulldozers, excavators, and loaders, while light-duty equipment includes compact tractors, small skid steers, and portable generators.
Cost Considerations: Investment and Maintenance
Heavy-duty equipment typically demands a higher initial investment due to its robust construction and advanced capabilities, which translates into greater upfront capital expenditure. Maintenance costs for heavy-duty machinery tend to be substantial, driven by the need for specialized parts and frequent servicing to ensure durability under intensive use. In contrast, light-duty equipment generally involves lower purchase prices and reduced maintenance expenses, making it a cost-effective choice for less demanding applications and smaller-scale operations.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Heavy-duty equipment is engineered with robust materials and reinforced components, ensuring exceptional durability and an extended lifespan that can withstand harsh operating conditions and continuous use. Light-duty equipment, while more affordable and easier to maneuver, typically features lighter materials and less reinforced parts, resulting in a shorter lifespan and reduced resistance to wear and tear. Comparing durability, heavy-duty models excel in longevity and maintenance intervals, making them ideal for demanding tasks and long-term investment.
Safety Features and Compliance Standards
Heavy-duty equipment incorporates advanced safety features such as reinforced operator cabins, enhanced rollover protection systems (ROPS), and integrated emergency stop mechanisms, ensuring compliance with stringent standards like OSHA and ISO 3449. Light-duty equipment emphasizes portability and ease of use while maintaining essential safety compliance with standards such as ANSI and CE certification, focusing on features like automatic shutoff and ergonomic controls. Both equipment types undergo rigorous testing to meet specific industry safety regulations, minimizing risk and enhancing operational reliability on job sites.
Energy Efficiency in Heavy-Duty vs Light-Duty Equipment
Heavy-duty equipment typically consumes more energy due to its larger engines and higher operational demands, resulting in lower energy efficiency compared to light-duty equipment designed for smaller tasks and shorter durations. Advances in technology, such as hybrid powertrains and improved fuel management systems, have enhanced energy efficiency in both categories but remain more impactful in light-duty equipment due to their lighter load profiles. Efficient energy use in heavy-duty machines focuses on optimizing fuel consumption during heavy workloads, while light-duty equipment benefits from lower power requirements and reduced idle times.
Pros and Cons of Heavy and Light Duty Equipment
Heavy-duty equipment offers superior durability and higher load capacities, making it ideal for demanding construction and industrial tasks, but it typically involves higher purchase and maintenance costs. Light-duty equipment provides greater maneuverability and lower operating expenses, suitable for smaller projects or less intensive usage, yet it may lack the strength and longevity required for heavy workloads. Selecting between heavy-duty and light-duty equipment depends on project scale, budget constraints, and specific performance requirements.
Choosing the Right Equipment for Your Project
Selecting between heavy-duty equipment and light-duty equipment depends on the scale and complexity of your project; heavy-duty machines like bulldozers and excavators provide power and durability for large construction sites, while light-duty tools such as compact loaders and handheld devices offer flexibility and precision for smaller tasks. Assessing factors like load capacity, terrain, project duration, and budget ensures optimal equipment performance and cost-effectiveness. Matching equipment specifications to project requirements enhances productivity and reduces operational risks.
Heavy-duty equipment vs light-duty equipment Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com