Machinery refers to complex devices composed of multiple parts working together to perform large-scale or automated tasks, often powered by motors or engines. Tooling consists of instruments or devices, such as molds, jigs, or dies, designed to assist in manufacturing processes by shaping, guiding, or assembling components. While machinery drives the primary operation, tooling enhances precision and efficiency within specific stages of production.
Table of Comparison
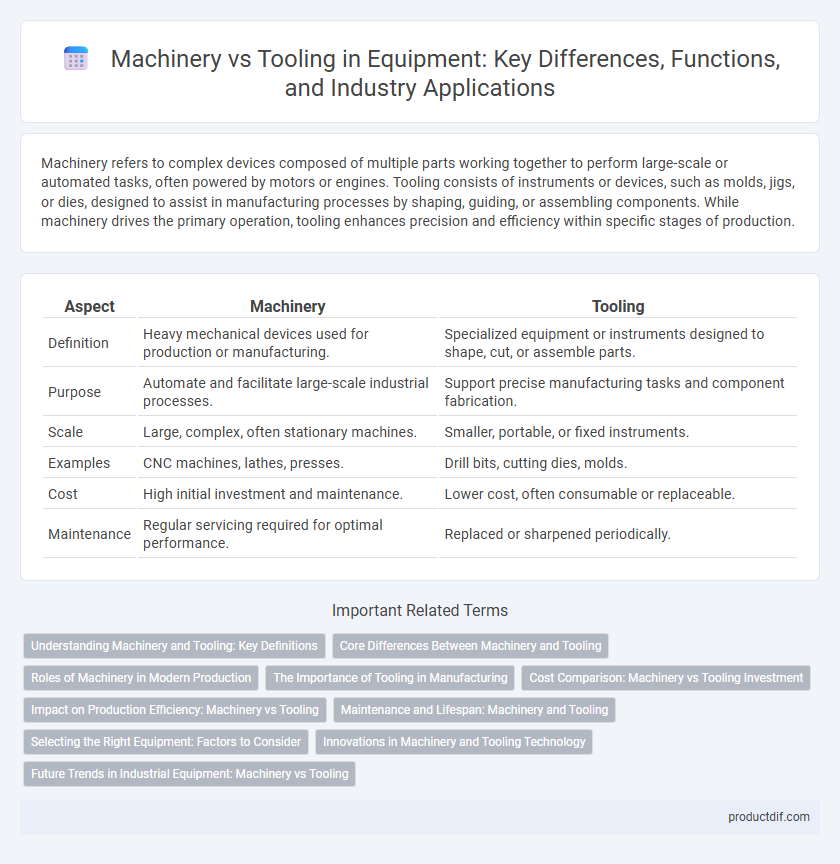
| Aspect | Machinery | Tooling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heavy mechanical devices used for production or manufacturing. | Specialized equipment or instruments designed to shape, cut, or assemble parts. |
| Purpose | Automate and facilitate large-scale industrial processes. | Support precise manufacturing tasks and component fabrication. |
| Scale | Large, complex, often stationary machines. | Smaller, portable, or fixed instruments. |
| Examples | CNC machines, lathes, presses. | Drill bits, cutting dies, molds. |
| Cost | High initial investment and maintenance. | Lower cost, often consumable or replaceable. |
| Maintenance | Regular servicing required for optimal performance. | Replaced or sharpened periodically. |
Understanding Machinery and Tooling: Key Definitions
Machinery refers to complex mechanical devices with moving parts designed to perform specific industrial or manufacturing tasks efficiently, often involving automation or power sources. Tooling encompasses the specialized tools, dies, jigs, and fixtures used to shape, assemble, or modify materials within machinery operations, essential for precision and repeatability. Understanding these definitions clarifies the functional relationship where machinery provides the framework and motion, while tooling directly interacts with the workpiece to achieve desired outcomes.
Core Differences Between Machinery and Tooling
Machinery refers to complex systems composed of multiple mechanical components designed to perform specific industrial tasks, often powered by electricity or hydraulics, while tooling consists of the individual instruments or devices, such as cutting tools, dies, and molds, used to shape, form, or finish materials. Machinery provides the operational framework and motion needed for production processes, whereas tooling directly interacts with the workpiece to achieve precise modifications and specifications. Understanding the core differences between machinery and tooling is crucial for optimizing manufacturing workflows and ensuring equipment compatibility within production environments.
Roles of Machinery in Modern Production
Machinery plays a critical role in modern production by automating complex processes and increasing efficiency across manufacturing lines. Unlike tooling, which consists of specific instruments used for shaping or assembling materials, machinery integrates various tools and components to perform large-scale operations such as cutting, molding, and assembling with precision. This integration reduces manual labor, enhances production speed, and ensures consistent product quality in industries ranging from automotive to electronics.
The Importance of Tooling in Manufacturing
Tooling plays a crucial role in manufacturing by enabling machinery to perform precise and repetitive tasks with high accuracy. While machinery provides the power and automation, tooling directly impacts product quality, efficiency, and customization capabilities. Optimized tooling reduces downtime, minimizes defects, and enhances overall production performance in industrial processes.
Cost Comparison: Machinery vs Tooling Investment
Machinery investments typically require higher upfront capital due to complex engineering, automation capabilities, and larger scale production potential, often exceeding $100,000 for industrial-grade equipment. Tooling costs, while generally lower--ranging from $1,000 to $50,000--can accumulate over time with frequent customization and maintenance, impacting overall operational expenses. Evaluating lifecycle costs and return on investment is crucial, since machinery offers long-term efficiency gains, whereas tooling allows greater flexibility in product variation.
Impact on Production Efficiency: Machinery vs Tooling
Machinery enhances production efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and increasing throughput, significantly reducing manual labor time. Tooling, on the other hand, improves precision and customization, ensuring higher quality outputs and minimizing material waste. Optimizing both machinery and tooling together creates a balanced workflow that maximizes overall production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Maintenance and Lifespan: Machinery and Tooling
Machinery requires regular maintenance such as lubrication, calibration, and parts replacement to extend its operational lifespan, often lasting several years to decades. Tooling, including dies and molds, demands precise upkeep to prevent wear and maintain accuracy, with a lifespan influenced by material hardness and usage frequency. Proper maintenance protocols directly impact the durability and cost-effectiveness of both machinery and tooling in production environments.
Selecting the Right Equipment: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right equipment involves evaluating machinery and tooling based on specific factors such as functionality, precision requirements, and production volume. Machinery often excels in automation and high-capacity output, while tooling provides enhanced customization and adaptability for specialized tasks. Consider factors like maintenance costs, compatibility with existing systems, and durability to optimize operational efficiency and product quality.
Innovations in Machinery and Tooling Technology
Innovations in machinery and tooling technology have accelerated manufacturing efficiency by integrating advanced automation, precision control, and smart sensor systems. Modern machinery now incorporates AI-driven diagnostics and adaptive tooling to optimize production processes and reduce downtime. These advancements enable higher accuracy, faster cycle times, and enhanced flexibility across diverse industrial applications.
Future Trends in Industrial Equipment: Machinery vs Tooling
Future trends in industrial equipment reveal a convergence of smart machinery and advanced tooling designed to enhance automation and precision in manufacturing. Machinery increasingly integrates IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time performance optimization. Tooling innovations focus on adaptive materials and modular designs that support rapid customization and scalability in production lines.
Machinery vs Tooling Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com