Prototyping tools are designed for flexibility and quick iteration, allowing engineers to test concepts and refine designs rapidly. Production tools prioritize durability and efficiency, enabling high-volume manufacturing with consistent quality and minimal downtime. Choosing between these tools depends on project stage and scalability requirements.
Table of Comparison
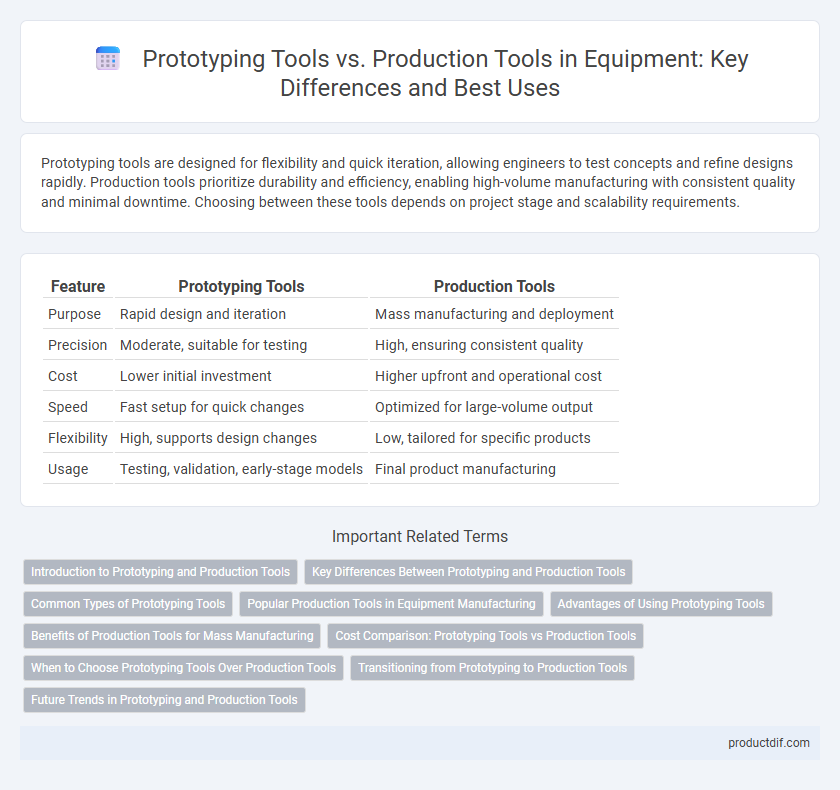
| Feature | Prototyping Tools | Production Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Rapid design and iteration | Mass manufacturing and deployment |
| Precision | Moderate, suitable for testing | High, ensuring consistent quality |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher upfront and operational cost |
| Speed | Fast setup for quick changes | Optimized for large-volume output |
| Flexibility | High, supports design changes | Low, tailored for specific products |
| Usage | Testing, validation, early-stage models | Final product manufacturing |
Introduction to Prototyping and Production Tools
Prototyping tools enable rapid design iterations and functional testing, facilitating early-stage development and concept validation. Production tools are engineered for large-scale manufacturing, ensuring precision, consistency, and durability in final product output. Selecting the appropriate tooling directly impacts efficiency, cost, and quality throughout the product lifecycle.
Key Differences Between Prototyping and Production Tools
Prototyping tools are designed for flexibility and rapid iteration, enabling quick testing and modification of designs, often supporting 3D printing, CNC machining, or low-volume assembly. Production tools prioritize durability, efficiency, and consistency, optimized for high-volume manufacturing processes with features like automation, precision, and longevity. Key differences include cost-effectiveness at scale, speed of operation, material compatibility, and tool customization tailored to either experimental development or mass production.
Common Types of Prototyping Tools
Common types of prototyping tools include 3D printers, CNC machines, laser cutters, and CAD software, which facilitate rapid design iterations and functional testing. These tools allow engineers to create physical models quickly, enabling early detection of design flaws and performance issues before moving to production. Unlike production tools, prototyping equipment emphasizes flexibility and speed over high-volume manufacturing efficiency.
Popular Production Tools in Equipment Manufacturing
Popular production tools in equipment manufacturing include CNC machines, injection molding equipment, and automated assembly lines, which ensure high precision and scalability for mass production. These tools outperform prototyping tools in durability and speed, facilitating consistent quality in large volumes of parts and assemblies. Investing in advanced production tools reduces lead times and lowers per-unit costs, critical factors in competitive manufacturing environments.
Advantages of Using Prototyping Tools
Prototyping tools accelerate design validation by enabling rapid iterations and early detection of flaws, significantly reducing development time compared to production tools. They facilitate cost efficiency by allowing multiple design modifications without the expense associated with manufacturing final parts. Enhanced collaboration is achieved through interactive models that improve communication among engineers, designers, and stakeholders during the product development lifecycle.
Benefits of Production Tools for Mass Manufacturing
Production tools significantly enhance efficiency in mass manufacturing by enabling high-speed, consistent, and precise output, drastically reducing per-unit costs. These tools are designed for durability and repeatability, minimizing downtime and maintenance expenses compared to prototyping tools. Their integration into automated assembly lines supports large-scale production demands while maintaining stringent quality standards.
Cost Comparison: Prototyping Tools vs Production Tools
Prototyping tools typically incur lower initial costs due to their flexibility and suitability for small-scale or iterative design processes, making them ideal for early-stage development. Production tools require substantial upfront investment as they are designed for mass manufacturing with high precision and durability, which reduces per-unit cost over large volumes. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that while prototyping tools minimize early expenses, production tools offer cost-efficiency in long-term, high-volume manufacturing scenarios.
When to Choose Prototyping Tools Over Production Tools
Prototyping tools are ideal during the early stages of product development when rapid iteration and design validation are crucial, enabling teams to test concepts and identify issues before full-scale manufacturing. These tools offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness for small batches or customized components, making them suitable for exploratory projects or proof-of-concept models. Production tools, by contrast, are best reserved for mass production due to their durability, precision, and efficiency in creating large volumes of identical parts.
Transitioning from Prototyping to Production Tools
Transitioning from prototyping tools to production tools involves scaling capabilities to ensure reliability, efficiency, and repeatability in manufacturing processes. Prototyping tools prioritize flexibility and rapid iteration, while production tools emphasize robust automation, quality control, and high throughput. Selecting appropriate equipment that supports seamless integration between stages is crucial for optimizing product development cycles and minimizing time-to-market.
Future Trends in Prototyping and Production Tools
Future trends in prototyping tools emphasize increased integration of AI-driven design automation and advanced materials for rapid iteration, enhancing accuracy and reducing development time. Production tools are evolving toward smart manufacturing systems incorporating IoT sensors and predictive maintenance to optimize efficiency and minimize downtime. The convergence of digital twins and augmented reality in both prototyping and production tools is set to transform equipment validation and operator training processes.
Prototyping tools vs Production tools Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com