A Bill of Materials (BOM) lists all components and raw materials required to manufacture a product, detailing quantities and specifications. The Bill of Process (BOP) outlines the step-by-step manufacturing procedures, including machine settings, labor, and sequence of operations. While BOM defines what is needed, BOP explains how to assemble or produce the equipment efficiently.
Table of Comparison
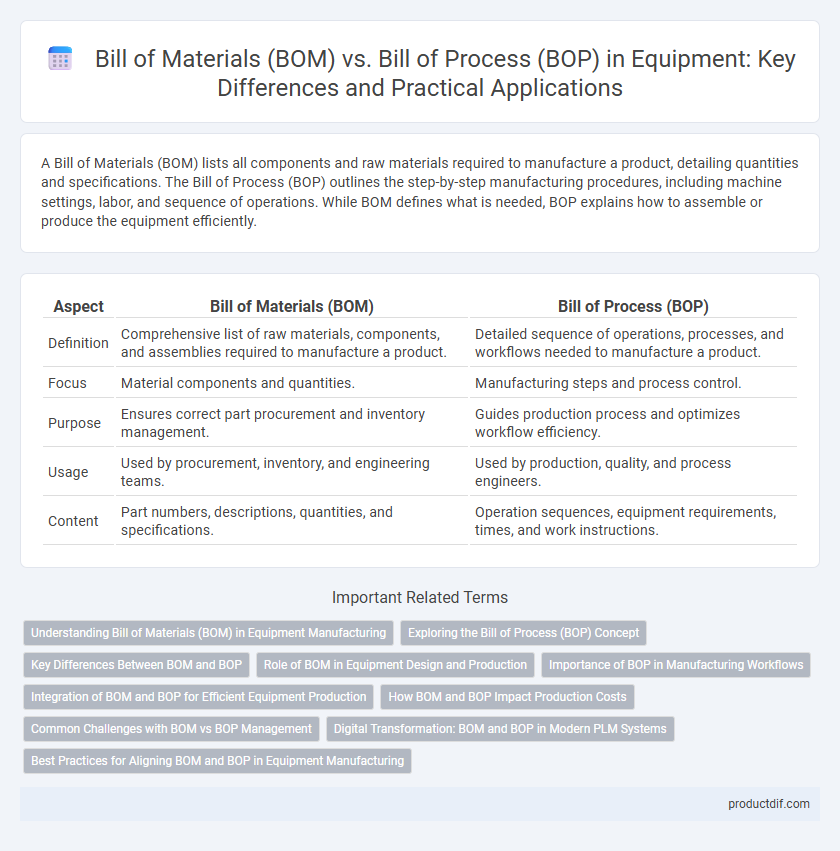
| Aspect | Bill of Materials (BOM) | Bill of Process (BOP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive list of raw materials, components, and assemblies required to manufacture a product. | Detailed sequence of operations, processes, and workflows needed to manufacture a product. |
| Focus | Material components and quantities. | Manufacturing steps and process control. |
| Purpose | Ensures correct part procurement and inventory management. | Guides production process and optimizes workflow efficiency. |
| Usage | Used by procurement, inventory, and engineering teams. | Used by production, quality, and process engineers. |
| Content | Part numbers, descriptions, quantities, and specifications. | Operation sequences, equipment requirements, times, and work instructions. |
Understanding Bill of Materials (BOM) in Equipment Manufacturing
A Bill of Materials (BOM) in equipment manufacturing is a detailed list of raw materials, components, and assemblies required to construct a piece of equipment, serving as a crucial reference for procurement and production planning. It includes itemized quantities, part numbers, and specifications that ensure accuracy in sourcing and inventory management, directly impacting cost control and manufacturing efficiency. Unlike the Bill of Process (BOP), which outlines the sequence of manufacturing steps, the BOM focuses exclusively on the tangible physical inputs essential for equipment assembly.
Exploring the Bill of Process (BOP) Concept
The Bill of Process (BOP) outlines the detailed sequence of manufacturing steps required to transform raw materials into a finished product, emphasizing workflow efficiency and quality control. Unlike the Bill of Materials (BOM), which lists all components and materials, the BOP specifies operations, machine settings, labor instructions, and inspection criteria. Integrating BOP into production planning enhances traceability, reduces errors, and optimizes resource allocation in complex equipment manufacturing.
Key Differences Between BOM and BOP
Bill of Materials (BOM) lists the raw materials, components, and assemblies required to manufacture a product, focusing on the physical parts and quantities. Bill of Process (BOP) outlines the sequential manufacturing steps, including operations, machine settings, and labor requirements to assemble the product. The key difference lies in BOM detailing "what" is needed, while BOP specifies "how" it is produced.
Role of BOM in Equipment Design and Production
The Bill of Materials (BOM) serves as a comprehensive inventory detailing all components, parts, and raw materials required for equipment design and production. It ensures accurate procurement, cost estimation, and assembly by listing quantities, specifications, and part numbers essential for manufacturing. The BOM facilitates efficient inventory management and acts as the foundational document guiding the entire equipment production process.
Importance of BOP in Manufacturing Workflows
The Bill of Process (BOP) outlines the detailed sequence of manufacturing operations essential for transforming raw materials into finished products, ensuring consistency and efficiency in workflows. Unlike the Bill of Materials (BOM), which lists the components and materials required, the BOP focuses on operational steps, work centers, and quality control measures to optimize production. Utilizing a well-defined BOP enhances traceability, reduces errors, and supports lean manufacturing principles by streamlining process management.
Integration of BOM and BOP for Efficient Equipment Production
Integrating the Bill of Materials (BOM) and Bill of Process (BOP) streamlines equipment production by aligning material requirements with manufacturing sequences, reducing errors and delays. This integration enhances real-time visibility into component usage and process workflows, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing downtime. Companies leveraging combined BOM and BOP data achieve higher production efficiency, improved quality control, and faster time-to-market for complex equipment assemblies.
How BOM and BOP Impact Production Costs
Bill of Materials (BOM) directly impacts production costs by detailing all raw materials and components required for manufacturing, enabling accurate cost estimation and inventory control. Bill of Process (BOP) influences costs through the specification of operational steps, labor requirements, and equipment usage, optimizing workflow efficiency and minimizing waste. Together, BOM and BOP provide a comprehensive framework that enhances cost management and streamlines production in manufacturing environments.
Common Challenges with BOM vs BOP Management
Managing Bill of Materials (BOM) and Bill of Process (BOP) presents challenges such as data inconsistency, where BOM focuses on product components and BOP details manufacturing steps, causing misalignment. Integration difficulties arise from disparate systems managing BOM and BOP data separately, leading to delays in production planning and errors. Ensuring accurate version control and synchronization between BOM and BOP is critical to prevent costly manufacturing defects and maintain efficient equipment utilization.
Digital Transformation: BOM and BOP in Modern PLM Systems
Bill of Materials (BOM) in modern PLM systems provides a detailed inventory of components required for equipment manufacturing, enabling precise cost estimation and inventory control. In contrast, Bill of Process (BOP) outlines the sequence of operations and workflows, ensuring efficient production planning and quality management. Digital transformation integrates BOM and BOP within PLM platforms, enhancing real-time collaboration, reducing cycle times, and enabling adaptive process adjustments for advanced equipment manufacturing.
Best Practices for Aligning BOM and BOP in Equipment Manufacturing
Aligning the Bill of Materials (BOM) with the Bill of Process (BOP) in equipment manufacturing enhances production accuracy by ensuring component lists correspond directly to manufacturing steps. Best practices include synchronizing revision controls between BOM and BOP, integrating cross-functional teams for concurrent updates, and utilizing digital manufacturing platforms to maintain real-time visibility and consistency. This alignment reduces errors, minimizes lead times, and improves overall equipment quality and traceability.
Bill of Materials (BOM) vs Bill of Process (BOP) Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com