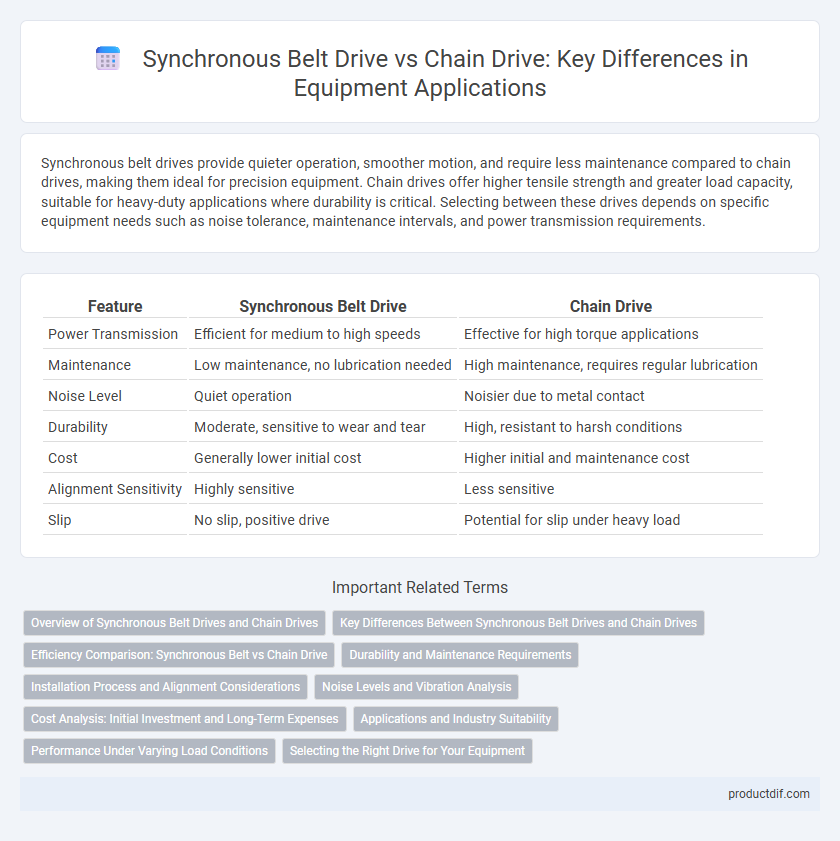
Synchronous belt drives provide quieter operation, smoother motion, and require less maintenance compared to chain drives, making them ideal for precision equipment. Chain drives offer higher tensile strength and greater load capacity, suitable for heavy-duty applications where durability is critical. Selecting between these drives depends on specific equipment needs such as noise tolerance, maintenance intervals, and power transmission requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synchronous Belt Drive | Chain Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Power Transmission | Efficient for medium to high speeds | Effective for high torque applications |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, no lubrication needed | High maintenance, requires regular lubrication |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | Noisier due to metal contact |
| Durability | Moderate, sensitive to wear and tear | High, resistant to harsh conditions |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost |
| Alignment Sensitivity | Highly sensitive | Less sensitive |
| Slip | No slip, positive drive | Potential for slip under heavy load |
Overview of Synchronous Belt Drives and Chain Drives
Synchronous belt drives utilize toothed belts that mesh precisely with pulley grooves, ensuring accurate timing and reduced slippage in power transmission. Chain drives employ interlocking metal links that provide durable and high-torque transfer, suited for heavy-duty applications. Both systems offer efficient mechanical power transfer, with synchronous belts favored for quieter operation and chain drives preferred for rugged environments.
Key Differences Between Synchronous Belt Drives and Chain Drives
Synchronous belt drives use toothed belts made of reinforced rubber or polyurethane, offering quieter operation and lower maintenance compared to chain drives, which utilize metal chains for higher torque transmission and durability in harsh environments. Belt drives provide smoother and more efficient power transfer with less vibration, while chain drives excel in heavy-duty applications requiring increased load capacity and resistance to stretching. Differences in tensile strength, lubrication needs, and design flexibility highlight the distinct advantages and limitations of each system for specific industrial equipment applications.
Efficiency Comparison: Synchronous Belt vs Chain Drive
Synchronous belt drives typically achieve efficiency levels between 95% and 98%, with minimal slip and reduced maintenance requirements compared to chain drives. Chain drives generally operate at efficiencies around 90% to 95%, but their performance can decline due to wear, lubrication issues, and chain elongation. In high-speed or precision applications, synchronous belts offer superior energy transfer efficiency and quieter operation, whereas chain drives are favored for heavy-duty loads despite slightly lower efficiency.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Synchronous belt drives offer superior durability with resistance to corrosion and reduced wear compared to chain drives, which are prone to elongation and rust over time. Maintenance requirements for synchronous belts are lower, as they typically require less frequent tension adjustments and lubrication, unlike chain drives that need regular cleaning, lubrication, and tension checks. This results in decreased downtime and longer service intervals for synchronous belt systems in industrial applications.
Installation Process and Alignment Considerations
Synchronous belt drives require precise tensioning and alignment during installation to prevent belt slippage and excessive wear, often involving adjustable pulleys and tensioners for exact positioning. Chain drives demand careful alignment of sprockets on parallel shafts and proper chain tension to avoid premature chain elongation and sprocket damage. Both systems benefit from regular inspection to maintain alignment and ensure optimal power transmission efficiency.
Noise Levels and Vibration Analysis
Synchronous belt drives produce significantly lower noise levels compared to chain drives due to the absence of metal-to-metal contact, resulting in smoother operation and reduced vibration. Chain drives typically generate higher vibration frequencies and noise because of their impact loading and metal engagement during motion. Vibration analysis confirms that synchronous belts operate with less oscillation, enhancing machine longevity and minimizing maintenance related to noise-induced wear.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Expenses
Synchronous belt drives generally require lower initial investment due to reduced manufacturing complexity and simpler installation compared to chain drives. Long-term expenses for belt drives tend to be lower because they demand less maintenance, produce less noise, and offer longer service life without lubrication. In contrast, chain drives incur higher maintenance costs, including regular lubrication and tension adjustments, which elevate their overall lifecycle cost despite a comparable initial price.
Applications and Industry Suitability
Synchronous belt drives excel in applications requiring precise timing and low noise, making them ideal for automotive engines, robotics, and light industrial machinery. Chain drives offer superior strength and durability, suited for heavy-duty operations in agriculture, construction, and conveyor systems. Selecting between the two depends on factors like load capacity, maintenance requirements, and environmental conditions in the targeted industry.
Performance Under Varying Load Conditions
Synchronous belt drives offer consistent performance under varying load conditions due to their precise tooth engagement, which reduces slippage and maintains accurate speed ratios. Chain drives, while robust and capable of transmitting higher torque, may experience elongation and increased wear under fluctuating loads, impacting efficiency and maintenance intervals. The choice between synchronous belt and chain drives depends on load variability, desired maintenance frequency, and operational precision requirements.
Selecting the Right Drive for Your Equipment
Synchronous belt drives offer quieter operation, lower maintenance, and precise timing ideal for high-speed equipment requiring minimal slippage. Chain drives provide superior strength and durability under heavy loads and high torque, suitable for rugged industrial machinery exposed to harsh environments. Evaluating factors such as load capacity, speed requirements, operational environment, and maintenance intervals is critical when selecting the right drive system for optimal equipment performance.
Synchronous belt drive vs chain drive Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com