Energy-efficient equipment reduces energy consumption and lowers utility costs compared to conventional equipment, offering long-term savings and environmental benefits. These advanced systems utilize innovative technologies to maximize performance while minimizing waste. Choosing energy-efficient options supports sustainable practices without sacrificing functionality or reliability.
Table of Comparison
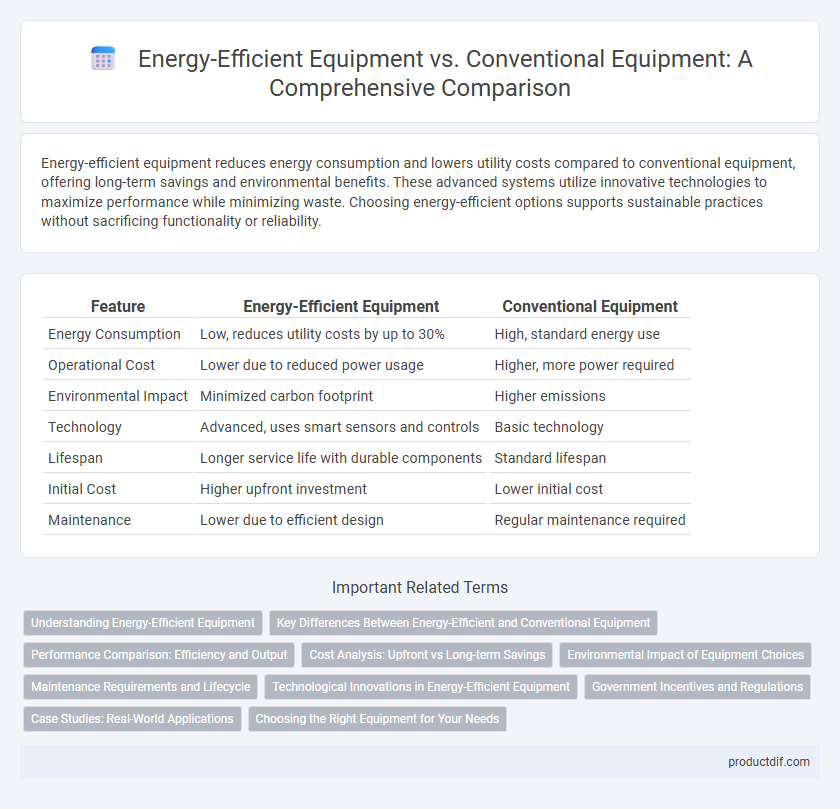
| Feature | Energy-Efficient Equipment | Conventional Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Low, reduces utility costs by up to 30% | High, standard energy use |
| Operational Cost | Lower due to reduced power usage | Higher, more power required |
| Environmental Impact | Minimized carbon footprint | Higher emissions |
| Technology | Advanced, uses smart sensors and controls | Basic technology |
| Lifespan | Longer service life with durable components | Standard lifespan |
| Initial Cost | Higher upfront investment | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Lower due to efficient design | Regular maintenance required |
Understanding Energy-Efficient Equipment
Energy-efficient equipment utilizes advanced technologies such as variable speed drives, improved insulation, and smart sensors to reduce energy consumption significantly compared to conventional equipment. These systems optimize operational performance by minimizing waste, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and reducing utility costs. Understanding the specific energy ratings, such as ENERGY STAR certification, and examining lifecycle costs are crucial for evaluating the true benefits of energy-efficient equipment over traditional alternatives.
Key Differences Between Energy-Efficient and Conventional Equipment
Energy-efficient equipment operates using advanced technology designed to reduce energy consumption while maintaining performance levels similar to conventional equipment. Key differences include lower operational costs, reduced environmental impact due to decreased greenhouse gas emissions, and often longer lifespan resulting from enhanced materials and designs. Conventional equipment typically relies on older, less efficient technology with higher energy use and increased maintenance requirements.
Performance Comparison: Efficiency and Output
Energy-efficient equipment delivers higher performance by converting more input energy into useful output, reducing waste compared to conventional equipment. Studies show energy-efficient models typically achieve 20-30% greater efficiency while maintaining or enhancing output levels. This results in lower operational costs and a smaller environmental footprint without compromising productivity.
Cost Analysis: Upfront vs Long-term Savings
Energy-efficient equipment typically requires a higher upfront investment compared to conventional equipment but delivers significant long-term savings through reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs. Over the equipment's lifecycle, these savings often offset the initial expense, resulting in a more cost-effective solution for businesses and consumers. Detailed cost analysis reveals that energy-efficient models provide enhanced return on investment by minimizing utility bills and maintenance expenses.
Environmental Impact of Equipment Choices
Energy-efficient equipment significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions by consuming less power compared to conventional equipment, contributing to lower carbon footprints in industrial and residential settings. The adoption of energy-efficient technology decreases reliance on fossil fuels, leading to improved air quality and conservation of natural resources. Lifecycle assessments consistently show that energy-efficient equipment offers substantial environmental benefits through reduced operational energy demand and minimized waste production.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifecycle
Energy-efficient equipment typically requires less frequent maintenance due to advanced technologies that enhance durability and reduce wear. The lifecycle of energy-efficient equipment often exceeds that of conventional models, resulting in lower total cost of ownership and extended operational performance. Reduced maintenance demands and longer service life contribute significantly to sustainable asset management and cost savings.
Technological Innovations in Energy-Efficient Equipment
Technological innovations in energy-efficient equipment include advanced sensors, smart controls, and IoT integration that optimize power consumption and reduce waste. These developments enable real-time monitoring and adaptive performance adjustments, significantly improving operational efficiency compared to conventional equipment. Enhanced materials and design improvements also contribute to lowered energy usage and extended equipment lifespan.
Government Incentives and Regulations
Government incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and grants significantly enhance the adoption of energy-efficient equipment by reducing upfront costs and improving return on investment. Regulatory frameworks, including mandatory efficiency standards and emissions limits, compel manufacturers and businesses to prioritize advanced energy-saving technologies over conventional equipment. These policies accelerate market transformation towards sustainability while driving innovation and compliance across industries.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case studies demonstrate significant energy savings when upgrading from conventional equipment to energy-efficient models, with industrial plants reducing power consumption by up to 30%. For instance, a manufacturing facility implementing high-efficiency motors and LED lighting achieved a 25% decrease in operational costs annually. These real-world applications highlight the long-term financial benefits and reduced environmental impact of adopting energy-efficient equipment in various sectors.
Choosing the Right Equipment for Your Needs
Energy-efficient equipment reduces operational costs by consuming less power while maintaining high performance, making it ideal for long-term savings and sustainability. Conventional equipment may have lower upfront costs but often results in higher energy bills and maintenance expenses over time. Assessing factors such as energy consumption rates, return on investment, and environmental impact ensures the right equipment aligns with both budget and operational goals.
Energy-efficient equipment vs conventional equipment Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com