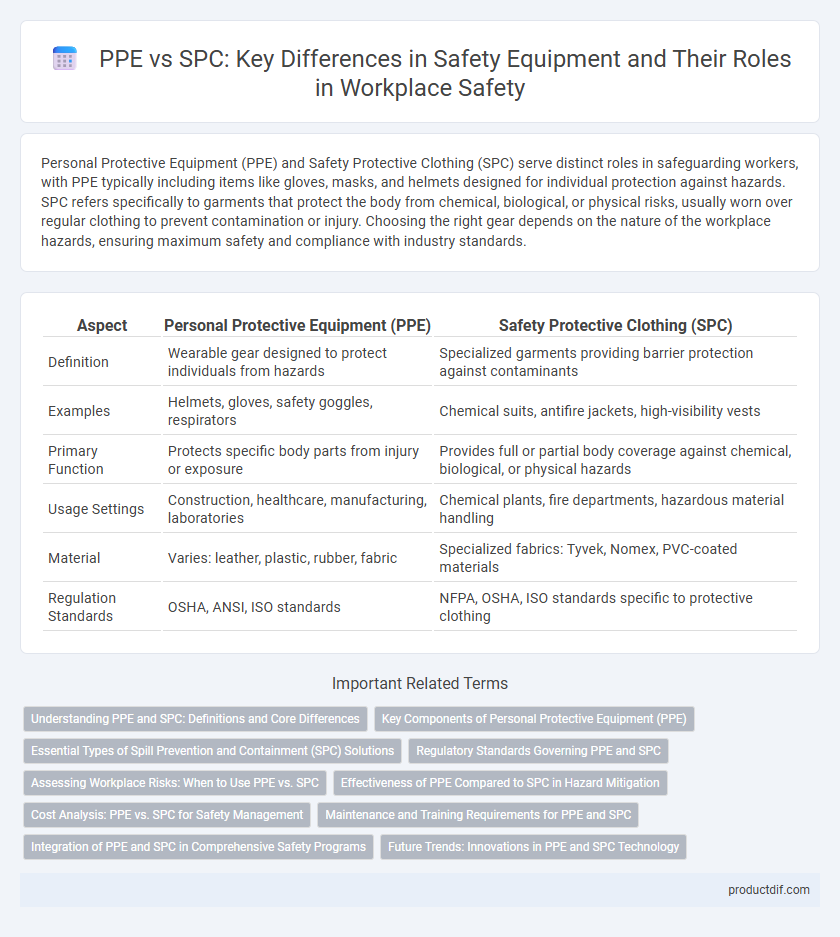
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and Safety Protective Clothing (SPC) serve distinct roles in safeguarding workers, with PPE typically including items like gloves, masks, and helmets designed for individual protection against hazards. SPC refers specifically to garments that protect the body from chemical, biological, or physical risks, usually worn over regular clothing to prevent contamination or injury. Choosing the right gear depends on the nature of the workplace hazards, ensuring maximum safety and compliance with industry standards.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Safety Protective Clothing (SPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wearable gear designed to protect individuals from hazards | Specialized garments providing barrier protection against contaminants |
| Examples | Helmets, gloves, safety goggles, respirators | Chemical suits, antifire jackets, high-visibility vests |
| Primary Function | Protects specific body parts from injury or exposure | Provides full or partial body coverage against chemical, biological, or physical hazards |
| Usage Settings | Construction, healthcare, manufacturing, laboratories | Chemical plants, fire departments, hazardous material handling |
| Material | Varies: leather, plastic, rubber, fabric | Specialized fabrics: Tyvek, Nomex, PVC-coated materials |
| Regulation Standards | OSHA, ANSI, ISO standards | NFPA, OSHA, ISO standards specific to protective clothing |
Understanding PPE and SPC: Definitions and Core Differences
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) refers to wearable gear designed to protect individuals from workplace hazards, including gloves, helmets, and safety goggles. Safety Protective Clothing (SPC) specifically focuses on garments that shield against particular risks such as chemical splashes, heat, or contaminants. Understanding the core difference highlights that PPE encompasses a broader range of equipment, while SPC targets specialized protective clothing for enhanced safety in hazardous environments.
Key Components of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) consists of key components such as helmets, gloves, eye protection, and respiratory devices designed to shield workers from hazards. Unlike Standard Personal Clothing (SPC), PPE is specifically engineered to provide barrier protection against chemical, physical, and biological risks. Selecting appropriate PPE based on workplace hazards is critical for ensuring maximum safety and compliance with occupational health regulations.
Essential Types of Spill Prevention and Containment (SPC) Solutions
Essential types of Spill Prevention and Containment (SPC) solutions include spill pallets, containment berms, and absorbent materials designed to manage hazardous liquid leaks effectively. These solutions minimize environmental impact by preventing spills from spreading, while Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) safeguards workers from exposure during cleanup. Integrating SPC products with PPE ensures comprehensive safety in industrial and environmental settings.
Regulatory Standards Governing PPE and SPC
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is regulated by standards such as OSHA 29 CFR 1910.132 in the United States, which mandates employer responsibility for hazard assessment and PPE provision. Safety Protective Clothing (SPC) adheres to specific standards like ANSI/ISEA 107 for high-visibility apparel and NFPA 70E for electrical safety, ensuring compliance with occupational hazard requirements. Regulatory frameworks require regular inspection, certification, and proper use of PPE and SPC to minimize workplace injuries and maintain safety compliance.
Assessing Workplace Risks: When to Use PPE vs. SPC
Assessing workplace risks involves determining the appropriate safety equipment, distinguishing between personal protective equipment (PPE) and standard protective clothing (SPC). PPE is essential for high-risk environments where exposure to hazardous substances or physical dangers is immediate and severe, offering tailored protection such as respirators, gloves, and helmets. SPC is suitable for routine operational tasks with lower risk levels, providing general protection like coveralls and safety shoes to reduce contamination and minor injuries.
Effectiveness of PPE Compared to SPC in Hazard Mitigation
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) provides a physical barrier to protect workers from direct exposure to hazards, including chemical, biological, and physical risks, by minimizing contact and reducing the likelihood of injury or contamination. Safety Protective Clothing (SPC) is designed to shield against specific environmental dangers such as heat, flames, or hazardous substances through enhanced material durability and specialized construction. Comparing effectiveness, PPE offers versatile, general protection suitable for a broad range of hazards, while SPC delivers superior performance in targeted high-risk scenarios, ensuring optimal hazard mitigation when properly selected and maintained.
Cost Analysis: PPE vs. SPC for Safety Management
Cost analysis of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) versus Safety Protective Clothing (SPC) reveals distinct financial implications for safety management. PPE often requires more frequent replacement due to exposure and wear, leading to recurring expenses, whereas SPC typically involves higher initial investment but offers longer durability and enhanced protection. Assessing total costs includes factoring in maintenance, replacement frequency, and potential loss reduction from improved safety performance.
Maintenance and Training Requirements for PPE and SPC
PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) requires regular maintenance such as cleaning, inspection for damage, and timely replacement to ensure effectiveness against workplace hazards. SPC (Safety Protective Clothing) demands designated laundering procedures and storage protocols to maintain material integrity and protective qualities. Both PPE and SPC necessitate comprehensive user training on correct usage, maintenance routines, and emergency response to maximize safety outcomes.
Integration of PPE and SPC in Comprehensive Safety Programs
The integration of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and Safety and Protective Clothing (SPC) enhances worker safety by providing layered protection against workplace hazards. Comprehensive safety programs leverage the strengths of both PPE and SPC to address diverse risks such as chemical exposure, physical injuries, and environmental factors. Implementing coordinated PPE and SPC protocols ensures optimal hazard mitigation and regulatory compliance across industries.
Future Trends: Innovations in PPE and SPC Technology
Advancements in PPE and SPC technology emphasize smart fabrics embedded with sensors that monitor wearer health and environmental hazards in real time. Integration of augmented reality (AR) in helmets and visors enhances situational awareness and hazard detection, improving worker safety outcomes. Future trends also highlight sustainable, lightweight materials that increase comfort while maintaining high protective standards.
PPE vs SPC Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com