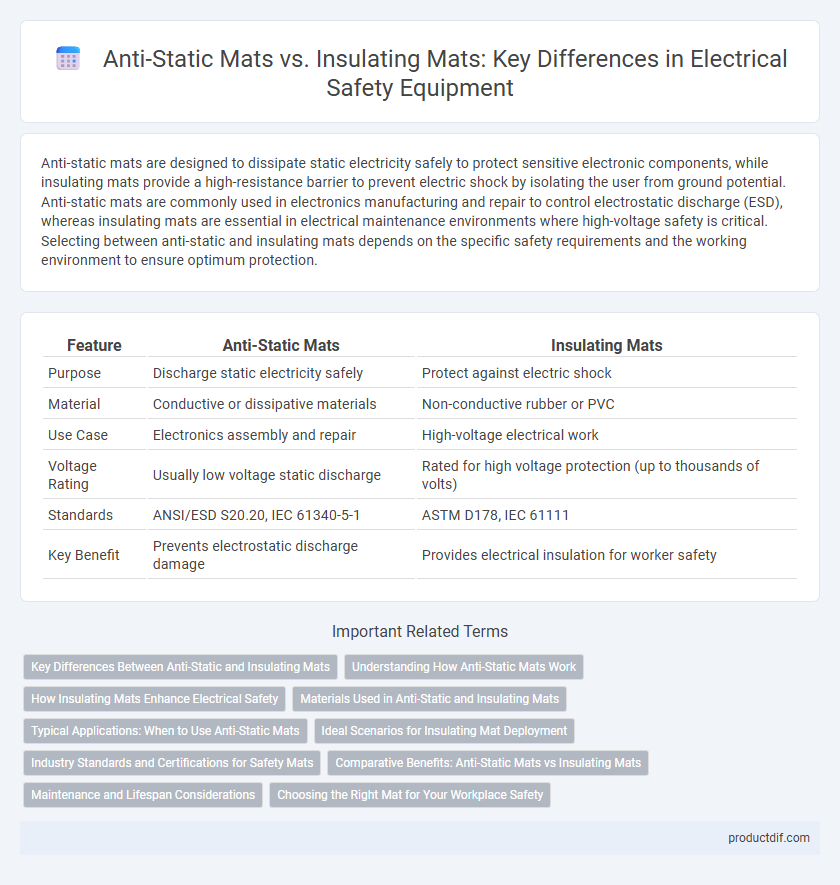
Anti-static mats are designed to dissipate static electricity safely to protect sensitive electronic components, while insulating mats provide a high-resistance barrier to prevent electric shock by isolating the user from ground potential. Anti-static mats are commonly used in electronics manufacturing and repair to control electrostatic discharge (ESD), whereas insulating mats are essential in electrical maintenance environments where high-voltage safety is critical. Selecting between anti-static and insulating mats depends on the specific safety requirements and the working environment to ensure optimum protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Static Mats | Insulating Mats |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Discharge static electricity safely | Protect against electric shock |
| Material | Conductive or dissipative materials | Non-conductive rubber or PVC |
| Use Case | Electronics assembly and repair | High-voltage electrical work |
| Voltage Rating | Usually low voltage static discharge | Rated for high voltage protection (up to thousands of volts) |
| Standards | ANSI/ESD S20.20, IEC 61340-5-1 | ASTM D178, IEC 61111 |
| Key Benefit | Prevents electrostatic discharge damage | Provides electrical insulation for worker safety |
Key Differences Between Anti-Static and Insulating Mats
Anti-static mats are designed to dissipate static electricity safely, preventing electrostatic discharge (ESD) that can damage sensitive electronic components, while insulating mats provide electrical insulation to protect users from electric shock in high-voltage environments. Anti-static mats typically have a surface resistance ranging from 10^5 to 10^8 ohms, allowing controlled discharge of static charges, whereas insulating mats exhibit much higher resistance, often exceeding 10^12 ohms, to block electrical current flow completely. The primary application for anti-static mats is in electronics manufacturing and repair, while insulating mats are essential in electrical maintenance and power line work for worker safety.
Understanding How Anti-Static Mats Work
Anti-static mats function by dissipating static electricity through a controlled resistance, preventing electrostatic discharge that can damage sensitive electronic components. These mats are typically made from materials like rubber or vinyl infused with carbon, which allows them to conduct static charges safely to the ground. Unlike insulating mats that block electrical current, anti-static mats provide a path for the charge to flow away, enhancing workplace safety in electronics manufacturing and repair environments.
How Insulating Mats Enhance Electrical Safety
Insulating mats significantly enhance electrical safety by providing a non-conductive barrier between workers and energized equipment, effectively reducing the risk of electric shock and electrocution. These mats are made from materials with high dielectric strength, allowing them to withstand and isolate electrical currents, which is crucial in high-voltage environments. Unlike anti-static mats, which dissipate static electricity, insulating mats focus on preventing the flow of current, making them essential for personnel working directly with live electrical circuits.
Materials Used in Anti-Static and Insulating Mats
Anti-static mats are typically made from conductive or dissipative materials such as carbon-filled rubber, vinyl, or polyurethane that safely discharge static electricity to ground. Insulating mats are constructed from non-conductive materials like natural rubber, neoprene, or silicone, designed to prevent electric current flow and protect users from electrical shock. The choice of materials directly influences the mat's ability to either dissipate static charges or provide electrical insulation in safety environments.
Typical Applications: When to Use Anti-Static Mats
Anti-static mats are essential in environments where sensitive electronic components are handled, such as electronics manufacturing, repair stations, and cleanrooms, to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage. These mats are typically used on workbenches and floors to safely dissipate static electricity and protect devices and personnel. In contrast, insulating mats are primarily employed in electrical maintenance and high-voltage environments to provide protection against electric shocks rather than controlling static electricity.
Ideal Scenarios for Insulating Mat Deployment
Insulating mats are ideal for environments where workers handle live electrical equipment or perform high-voltage testing, providing essential protection against electrical shock by limiting current flow. These mats are commonly deployed in electrical substations, control rooms, and maintenance areas for electrical wiring and apparatus. Their insulating properties ensure safety by creating a barrier between the worker and grounded surfaces, reducing the risk of electric accidents.
Industry Standards and Certifications for Safety Mats
Anti-static mats comply with industry standards like ANSI/ESD S20.20 and IEC 61340-5-1, ensuring effective static discharge control critical in electronics manufacturing environments. Insulating mats meet ASTM D178 standards and OSHA requirements, providing protection against electrical shock in high-voltage settings. Certification from UL and CSA further validates the performance and safety of both anti-static and insulating mats for workplace hazard mitigation.
Comparative Benefits: Anti-Static Mats vs Insulating Mats
Anti-static mats effectively dissipate static electricity, preventing electrostatic discharge (ESD) that can damage sensitive electronic components, while insulating mats provide a high-resistance barrier that protects workers from electrical shock by blocking current flow. Anti-static mats are ideal in electronics manufacturing and repair environments, whereas insulating mats are crucial in high-voltage electrical work to ensure personnel safety. Choosing between anti-static and insulating mats depends on specific workplace risks, with anti-static mats prioritizing ESD control and insulating mats focusing on electrical shock protection.
Maintenance and Lifespan Considerations
Anti-static mats require regular cleaning with specific anti-static solutions to maintain their conductivity properties and extend their functional lifespan, typically lasting 3 to 5 years with proper care. Insulating mats demand routine inspection for physical wear and contamination, as their effectiveness depends on preserving dielectric strength, often lasting 5 to 10 years depending on environmental conditions. Both mat types benefit from avoiding exposure to harsh chemicals and excessive moisture to prevent degradation and ensure safety compliance over time.
Choosing the Right Mat for Your Workplace Safety
Choosing the right mat for workplace safety depends on the specific hazards and electrical requirements of the environment. Anti-static mats are designed to dissipate static electricity, preventing electrostatic discharge in sensitive electronic areas, while insulating mats provide electrical insulation to protect workers from electrical shock by inhibiting current flow. Understanding the voltage levels and electrostatic risks in your workspace ensures selecting either anti-static or insulating mats effectively enhances safety compliance and minimizes injury risks.
Anti-static mats vs Insulating mats Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com