A safety shield is designed to provide broader protection by covering larger areas of the body, such as the chest and shoulders, making it ideal for preventing injuries from flying debris or chemicals. A face shield specifically protects the face, often featuring a clear visor that allows visibility while guarding against splashes, sparks, or impact. Choosing between a safety shield and a face shield depends on the level of coverage needed and the specific hazards present in the environment.
Table of Comparison
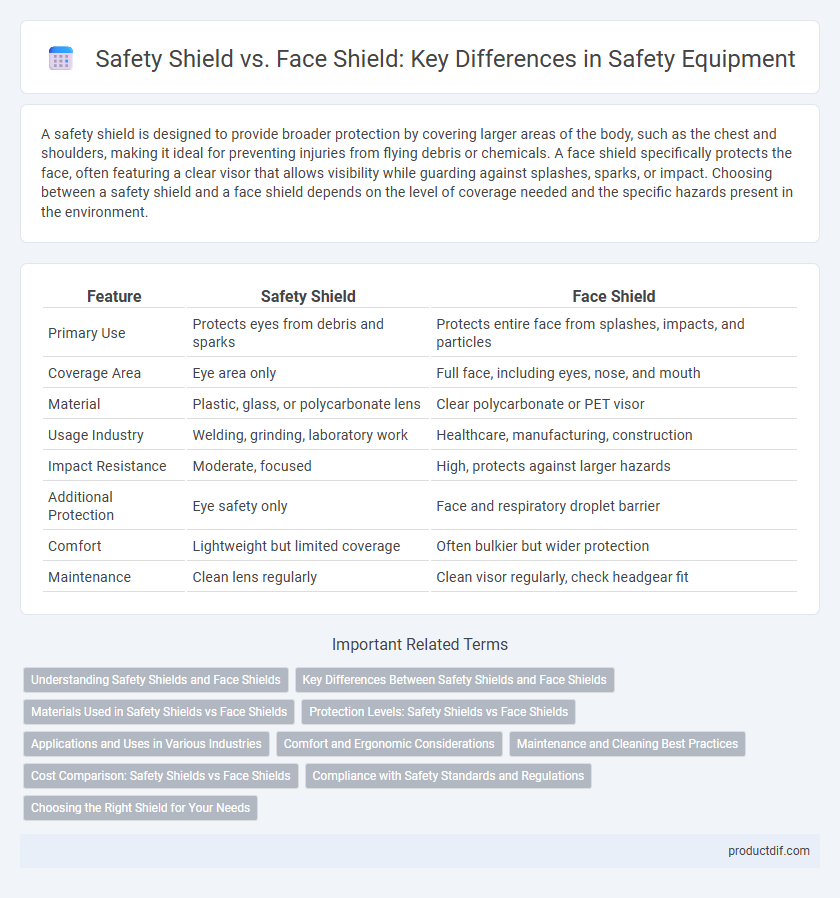
| Feature | Safety Shield | Face Shield |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Protects eyes from debris and sparks | Protects entire face from splashes, impacts, and particles |
| Coverage Area | Eye area only | Full face, including eyes, nose, and mouth |
| Material | Plastic, glass, or polycarbonate lens | Clear polycarbonate or PET visor |
| Usage Industry | Welding, grinding, laboratory work | Healthcare, manufacturing, construction |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, focused | High, protects against larger hazards |
| Additional Protection | Eye safety only | Face and respiratory droplet barrier |
| Comfort | Lightweight but limited coverage | Often bulkier but wider protection |
| Maintenance | Clean lens regularly | Clean visor regularly, check headgear fit |
Understanding Safety Shields and Face Shields
Safety shields and face shields are essential personal protective equipment designed to protect users from hazards such as flying debris, chemical splashes, and infectious fluids. Safety shields typically refer to barriers integrated into machinery or workstations to prevent accidents, while face shields are wearable transparent visors that cover the entire face for direct impact protection. Selecting the appropriate shield depends on the specific environmental risks and the level of protection required for eyes and facial areas.
Key Differences Between Safety Shields and Face Shields
Safety shields are typically fixed barriers used to protect operators from sparks, debris, or chemical splashes in industrial environments, whereas face shields are wearable personal protective equipment designed to safeguard the entire face from impact, splashes, and hazardous materials. Safety shields often provide localized protection at a specific workstation, while face shields offer mobility and full facial coverage for workers performing dynamic tasks. Material composition varies; safety shields usually feature durable, transparent materials like polycarbonate or acrylic panels, whereas face shields incorporate flexible headbands and adjustable straps for comfort and secure fit.
Materials Used in Safety Shields vs Face Shields
Safety shields commonly utilize rigid materials such as polycarbonate and acrylic, providing impact resistance and durability against flying debris. Face shields often incorporate flexible materials like PET or acetate, offering lightweight comfort with chemical splash protection. Both shields prioritize transparency and optical clarity, but safety shields emphasize toughness while face shields focus on comfort and chemical resistance.
Protection Levels: Safety Shields vs Face Shields
Safety shields provide basic protection by deflecting debris and splashes away from the eyes and upper face, suitable for low-risk environments. Face shields offer comprehensive coverage, including the entire face, protecting against chemical splashes, flying particles, and infectious materials in high-risk settings. Choosing between safety shields and face shields depends on the specific hazard exposure, with face shields delivering higher protection levels for intense or full-face hazards.
Applications and Uses in Various Industries
Safety shields provide robust protection against flying debris and chemical splashes, making them ideal for manufacturing, construction, and laboratory settings. Face shields offer clear visibility and full-face coverage, commonly used in healthcare, automotive repair, and welding industries. Both are essential PPE, selected based on specific hazards and industry requirements to enhance worker safety.
Comfort and Ergonomic Considerations
Safety shields offer superior comfort with their lightweight design and adjustable features, reducing strain during prolonged use in industrial environments. Face shields provide broader facial protection but can cause discomfort due to heat buildup and limited ventilation, impacting ergonomic efficiency. Selecting safety equipment prioritizing ergonomic fit enhances wearer compliance and reduces fatigue-related risks.
Maintenance and Cleaning Best Practices
Safety shield and face shield maintenance require regular cleaning with mild soap and water to prevent damage to the transparent visor and ensure clear visibility. Avoid using abrasive materials or harsh chemicals that can scratch or degrade the polycarbonate or acetate components. Proper drying and storage in a dust-free environment preserve the shield's protective qualities and extend its service life.
Cost Comparison: Safety Shields vs Face Shields
Safety shields generally offer a more affordable option compared to face shields, with prices ranging from $5 to $15, while face shields typically cost between $10 and $30 due to their larger size and enhanced protection features. The cost difference reflects variations in materials, durability, and design complexity, where safety shields often use simpler components like plastic panels, and face shields incorporate adjustable headgear and anti-fog coatings. Organizations prioritizing budget constraints may prefer safety shields for basic protection, whereas face shields justify higher costs by providing comprehensive coverage suitable for medical or industrial environments.
Compliance with Safety Standards and Regulations
Safety shields and face shields must comply with specific safety standards such as ANSI/ISEA Z87.1 in the United States and EN 166 in Europe to ensure adequate protection against impact, chemical splashes, and other workplace hazards. Face shields typically offer full-face coverage and meet stricter criteria for impact resistance and optical clarity, whereas safety shields provide localized protection and may be suited for lower-risk environments. Proper compliance with these regulations guarantees that the equipment effectively reduces injury risks and meets industry safety requirements.
Choosing the Right Shield for Your Needs
Selecting the right safety shield depends on the specific hazards you face, such as flying debris, chemical splashes, or heat exposure. Safety shields typically offer rigid protection against impact, while face shields provide full-face coverage with greater flexibility and comfort for prolonged use. Prioritize shields with ANSI/ISEA Z87.1 certification to ensure reliable impact resistance and optical clarity for optimal protection in industrial or laboratory environments.
Safety shield vs Face shield Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com