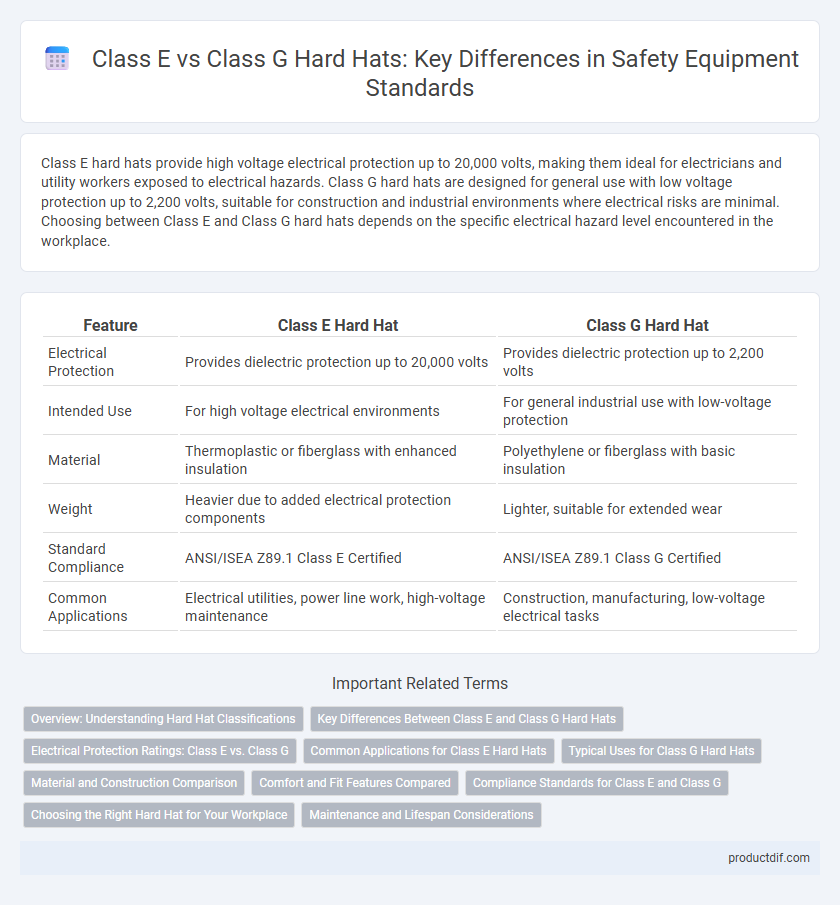
Class E hard hats provide high voltage electrical protection up to 20,000 volts, making them ideal for electricians and utility workers exposed to electrical hazards. Class G hard hats are designed for general use with low voltage protection up to 2,200 volts, suitable for construction and industrial environments where electrical risks are minimal. Choosing between Class E and Class G hard hats depends on the specific electrical hazard level encountered in the workplace.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Class E Hard Hat | Class G Hard Hat |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Protection | Provides dielectric protection up to 20,000 volts | Provides dielectric protection up to 2,200 volts |
| Intended Use | For high voltage electrical environments | For general industrial use with low-voltage protection |
| Material | Thermoplastic or fiberglass with enhanced insulation | Polyethylene or fiberglass with basic insulation |
| Weight | Heavier due to added electrical protection components | Lighter, suitable for extended wear |
| Standard Compliance | ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 Class E Certified | ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 Class G Certified |
| Common Applications | Electrical utilities, power line work, high-voltage maintenance | Construction, manufacturing, low-voltage electrical tasks |
Overview: Understanding Hard Hat Classifications
Class E hard hats offer protection against high-voltage electrical hazards up to 20,000 volts, making them essential for electricians and utility workers. Class G hard hats provide impact protection and limited electrical protection up to 2,200 volts, suitable for general construction and manufacturing environments. Understanding these classifications helps ensure proper safety equipment selection based on workplace electrical risk levels.
Key Differences Between Class E and Class G Hard Hats
Class E hard hats provide electrical protection up to 20,000 volts, making them suitable for high-voltage environments, whereas Class G hard hats offer protection up to 2,200 volts, ideal for general construction and light electrical tasks. Both types meet ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 standards but differ significantly in voltage resistance and weight, with Class E typically being heavier due to added insulation. The choice between Class E and Class G hard hats hinges on the specific electrical hazard levels workers face on-site.
Electrical Protection Ratings: Class E vs. Class G
Class E hard hats provide electrical protection up to 20,000 volts, making them suitable for high-voltage environments and electrical work. Class G hard hats offer protection up to 2,200 volts, designed for general construction and industrial applications with lower electrical hazards. Selecting the appropriate class depends on the specific voltage risks present on the job site to ensure maximum safety compliance.
Common Applications for Class E Hard Hats
Class E hard hats are commonly used in environments with high electrical hazards, such as electrical power generation, transmission, and distribution industries. These hats provide dielectric protection up to 20,000 volts, making them essential for electricians, linemen, and utility workers. Their robust construction also suits construction sites where electrical safety is a primary concern.
Typical Uses for Class G Hard Hats
Class G hard hats are typically used in electrical and construction environments where low-voltage protection is essential, providing dielectric protection up to 2,200 volts. These helmets are common among electricians, utility workers, and general laborers working near energized equipment or power lines. Their lightweight design and impact resistance make them suitable for various industrial safety applications requiring moderate electrical hazard protection.
Material and Construction Comparison
Class E hard hats are constructed using high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or fiberglass reinforced composite materials designed to provide dielectric protection up to 20,000 volts, making them suitable for electrical work environments. Class G hard hats are made from similar materials such as HDPE but offer dielectric protection up to 2,200 volts and are generally lighter due to less rigorous electrical insulation requirements. Both classes feature a suspension system for impact absorption, but Class E hard hats incorporate additional layers or coatings to enhance electrical resistance and durability under high-voltage conditions.
Comfort and Fit Features Compared
Class E hard hats are designed with heavier insulation for electrical protection, which can impact overall comfort but often include adjustable suspension systems for a secure fit. Class G hard hats, while providing lower voltage protection, typically feature lighter materials and enhanced ventilation, improving comfort during extended use. Both classes offer customizable fit options such as ratchet suspension and padded sweatbands to enhance wearer comfort in various work environments.
Compliance Standards for Class E and Class G
Class E hard hats comply with ANSI/ISEA Z89.1-2014 standards, providing electrical insulation up to 20,000 volts, making them suitable for high-voltage environments. Class G hard hats meet the same ANSI standard but offer protection against low-voltage electrical hazards up to 2,200 volts. Both classes ensure impact resistance and penetration protection, with their compliance tailored to distinct electrical safety requirements on job sites.
Choosing the Right Hard Hat for Your Workplace
Choosing the right hard hat for your workplace depends on the specific electrical hazard protection required; Class E hard hats offer high-voltage protection up to 20,000 volts, making them ideal for electricians and utility workers. Class G hard hats provide general protection against low-voltage hazards up to 2,200 volts and are suitable for construction and general labor environments. Understanding the voltage levels and safety standards in your workplace ensures optimal head protection and compliance with OSHA regulations.
Maintenance and Lifespan Considerations
Class E hard hats, designed for electrical protection up to 20,000 volts, require regular inspection for cracks, dents, and electrical degradation to maintain their safety standards, with a recommended replacement every 5 years or sooner if damaged. Class G hard hats, offering lower voltage protection up to 2,200 volts, have a similar maintenance routine but generally feature a slightly longer lifespan of up to 5 years, provided they remain free from impact damage and exposure to harsh chemicals. Both types must be stored away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures to prevent material weakening and ensure optimal performance throughout their service life.
Class E hard hat vs Class G hard hat Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com