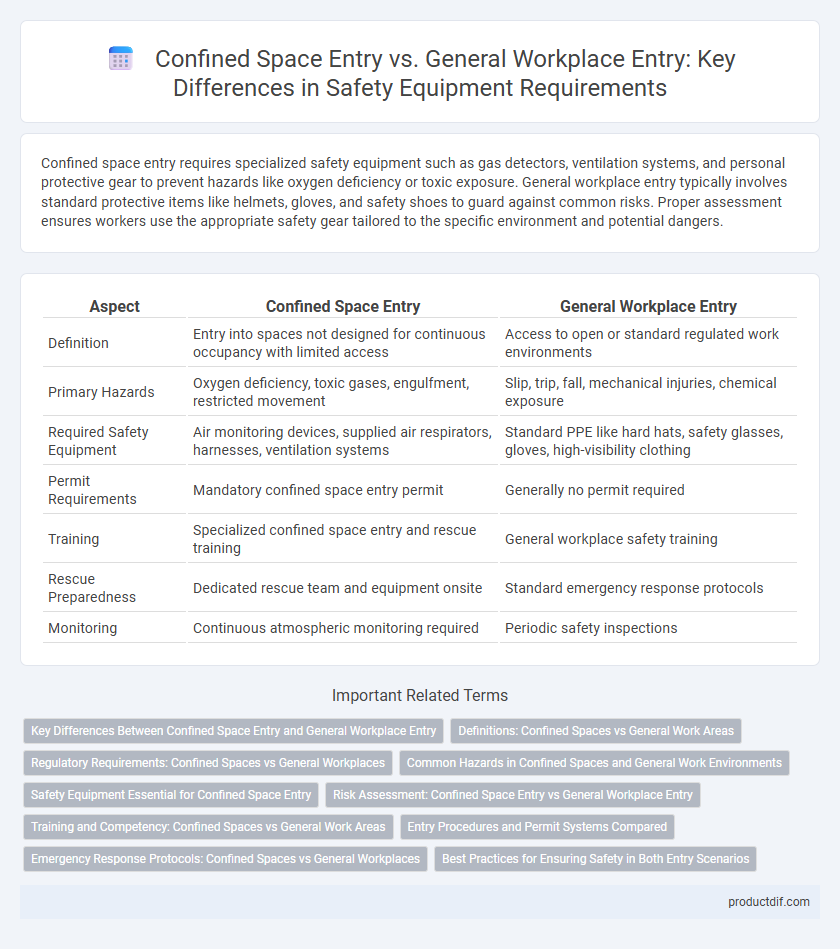
Confined space entry requires specialized safety equipment such as gas detectors, ventilation systems, and personal protective gear to prevent hazards like oxygen deficiency or toxic exposure. General workplace entry typically involves standard protective items like helmets, gloves, and safety shoes to guard against common risks. Proper assessment ensures workers use the appropriate safety gear tailored to the specific environment and potential dangers.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Confined Space Entry | General Workplace Entry |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Entry into spaces not designed for continuous occupancy with limited access | Access to open or standard regulated work environments |
| Primary Hazards | Oxygen deficiency, toxic gases, engulfment, restricted movement | Slip, trip, fall, mechanical injuries, chemical exposure |
| Required Safety Equipment | Air monitoring devices, supplied air respirators, harnesses, ventilation systems | Standard PPE like hard hats, safety glasses, gloves, high-visibility clothing |
| Permit Requirements | Mandatory confined space entry permit | Generally no permit required |
| Training | Specialized confined space entry and rescue training | General workplace safety training |
| Rescue Preparedness | Dedicated rescue team and equipment onsite | Standard emergency response protocols |
| Monitoring | Continuous atmospheric monitoring required | Periodic safety inspections |
Key Differences Between Confined Space Entry and General Workplace Entry
Confined space entry involves accessing areas with limited entry or exit points, such as tanks or silos, where hazardous atmospheres or oxygen deficiency may exist, requiring specialized permits, atmospheric testing, and rescue plans. General workplace entry typically occurs in open areas without these atmospheric hazards and demands standard safety procedures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE) and hazard awareness training. The key difference lies in the level of risk assessment, regulatory requirements under OSHA's Permit-Required Confined Spaces standard, and the complexity of safety controls needed for confined spaces compared to general work environments.
Definitions: Confined Spaces vs General Work Areas
Confined spaces are defined as areas not designed for continuous occupancy, with limited means of entry or exit, and potentially hazardous atmospheres requiring specific safety protocols. General work areas encompass open environments designed for regular employee presence, typically with standard safety measures and easier evacuation routes. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for implementing appropriate safety equipment and entry procedures.
Regulatory Requirements: Confined Spaces vs General Workplaces
Confined space entry requires strict adherence to regulatory standards such as OSHA 29 CFR 1910.146, mandating permit systems, atmospheric testing, and continuous monitoring to ensure worker safety. General workplace entry follows broader regulations like OSHA 29 CFR 1910 Subpart D, focusing on hazard identification and control without the intensive monitoring required for confined spaces. Compliance with confined space-specific protocols significantly reduces risks associated with hazardous atmospheres, engulfment, and restricted egress, providing a higher level of worker protection compared to general workplace entry.
Common Hazards in Confined Spaces and General Work Environments
Confined spaces pose unique hazards such as oxygen deficiency, toxic atmospheres, and limited egress, increasing the risk of suffocation, poisoning, and entrapment. General workplace environments typically face hazards including slips, trips, falls, and equipment-related injuries, which are more predictable and easier to mitigate. Understanding these specific dangers is critical for implementing tailored safety protocols and ensuring worker protection across different entry scenarios.
Safety Equipment Essential for Confined Space Entry
Confined space entry demands specialized safety equipment such as gas detectors, ventilation systems, and personal protective gear to monitor and mitigate hazardous atmospheres. Unlike general workplace entry, confined spaces require continuous air quality testing, rescue harnesses, and communication devices to ensure worker safety in restricted environments. Proper training and use of safety equipment reduce risks of oxygen deficiency, toxic exposure, and physical entrapment unique to confined spaces.
Risk Assessment: Confined Space Entry vs General Workplace Entry
Risk assessment for confined space entry involves identifying hazards such as oxygen deficiency, toxic gases, and engulfment risks, requiring specialized monitoring and rescue plans. In contrast, general workplace entry risk assessments focus on common hazards like slips, trips, electrical risks, and ergonomic factors, typically addressed through standard safety protocols. Confined space entries demand a higher level of control measures including continuous atmospheric testing and confined space permits to ensure employee safety.
Training and Competency: Confined Spaces vs General Work Areas
Confined space entry requires specialized training emphasizing hazard recognition, emergency procedures, and use of personal protective equipment, surpassing the scope of general workplace entry training. Workers must demonstrate competency in atmospheric testing, ventilation techniques, and rescue protocols specific to confined spaces. General work area entry training focuses on basic safety practices, hazard communication, and general emergency response, reflecting lower risk complexity.
Entry Procedures and Permit Systems Compared
Confined space entry requires strict adherence to specialized entry procedures and a formal permit system to control hazards like limited ventilation and restricted exits, unlike general workplace entry where standard safety protocols suffice. Entry permits for confined spaces involve detailed hazard assessments, atmospheric testing, and rescue plans, ensuring continuous monitoring and communication. General workplace entries typically follow routine checklists without the need for exhaustive permits, reflecting lower risk levels and simpler access controls.
Emergency Response Protocols: Confined Spaces vs General Workplaces
Emergency response protocols in confined space entry require specialized procedures due to limited access, hazardous atmospheres, and potential engulfment risks, emphasizing continuous monitoring and immediate rescue readiness. General workplace entry protocols focus on standard evacuation routes, accessible first aid, and broader emergency communication systems. Confined spaces demand trained rescue teams equipped with breathing apparatus and retrieval systems to ensure worker safety during emergencies.
Best Practices for Ensuring Safety in Both Entry Scenarios
Confined space entry requires comprehensive hazard assessment, use of specialized personal protective equipment (PPE), and continuous atmospheric monitoring to prevent risks such as asphyxiation, toxic exposure, and engulfment. General workplace entry emphasizes routine safety protocols, hazard communication, and proper use of PPE tailored to common environmental risks, such as slips, trips, and falls. Implementing rigorous training programs, establishing clear entry permits, and enforcing emergency response procedures are best practices that enhance safety in both confined space and general workplace entry scenarios.
Confined space entry vs General workplace entry Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com