Cut-resistant gloves provide essential protection against sharp objects, reducing the risk of cuts and lacerations during handling tasks, while heat-resistant gloves are designed to shield hands from high temperatures and burns. Choosing the right safety equipment depends on the specific hazards encountered, with cut-resistant gloves ideal for tasks involving knives or sharp tools, and heat-resistant gloves necessary for handling hot surfaces or materials. Both types of gloves enhance workplace safety but serve distinct protective purposes requiring careful selection based on the nature of the potential harm.
Table of Comparison
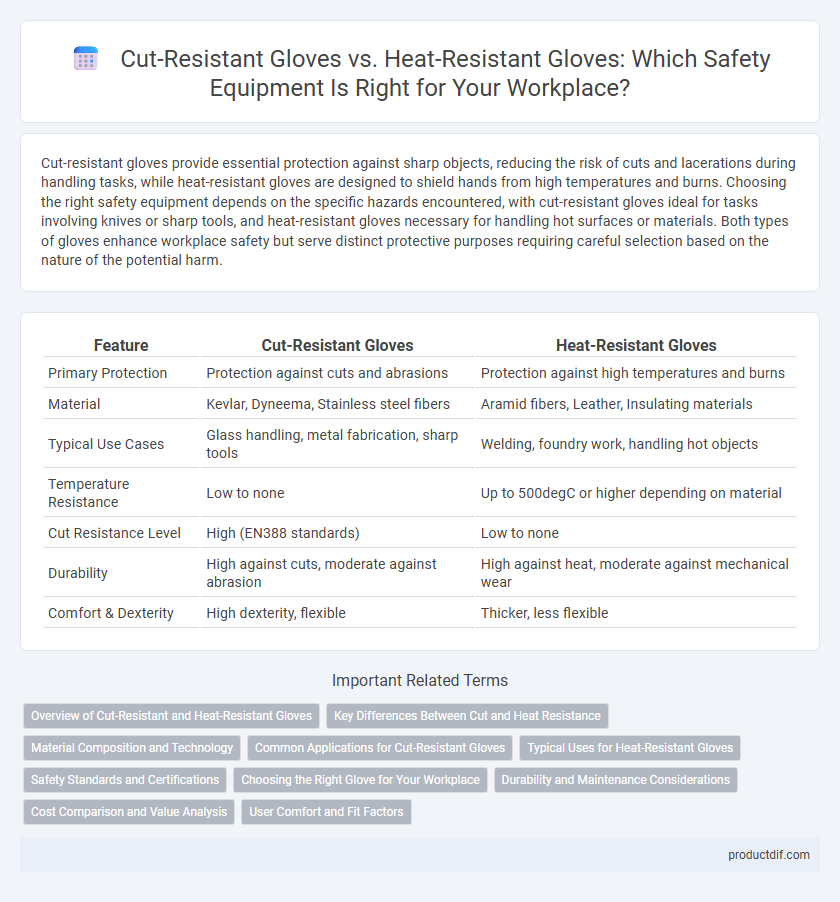
| Feature | Cut-Resistant Gloves | Heat-Resistant Gloves |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Protection | Protection against cuts and abrasions | Protection against high temperatures and burns |
| Material | Kevlar, Dyneema, Stainless steel fibers | Aramid fibers, Leather, Insulating materials |
| Typical Use Cases | Glass handling, metal fabrication, sharp tools | Welding, foundry work, handling hot objects |
| Temperature Resistance | Low to none | Up to 500degC or higher depending on material |
| Cut Resistance Level | High (EN388 standards) | Low to none |
| Durability | High against cuts, moderate against abrasion | High against heat, moderate against mechanical wear |
| Comfort & Dexterity | High dexterity, flexible | Thicker, less flexible |
Overview of Cut-Resistant and Heat-Resistant Gloves
Cut-resistant gloves are designed with advanced fibers like Kevlar, Dyneema, or steel to protect hands from sharp objects and reduce the risk of lacerations in industries such as manufacturing and construction. Heat-resistant gloves incorporate materials like Aramid fibers and aluminized coatings to shield hands from high temperatures, making them essential for welding, foundry work, and handling hot equipment. Both glove types are critical in workplace safety, offering specialized protection tailored to specific hazards encountered in industrial environments.
Key Differences Between Cut and Heat Resistance
Cut-resistant gloves are engineered with high-performance fibers such as Kevlar, Dyneema, or stainless steel to provide superior protection against sharp objects and blade cuts, ensuring durability and safety in handling glass, metal, or knives. Heat-resistant gloves utilize materials like aluminized fabrics, leather, or silicone to withstand high temperatures and prevent burns during welding, foundry work, or hot surface handling. The primary distinction lies in the types of hazards they mitigate--cut-resistant gloves focus on sharp object penetration prevention, while heat-resistant gloves protect against thermal injuries.
Material Composition and Technology
Cut-resistant gloves are typically made from high-performance fibers such as Kevlar, Dyneema, or stainless steel mesh, utilizing advanced weaving techniques to provide superior protection against sharp objects. Heat-resistant gloves often incorporate materials like aluminized fabric, Kevlar blends, or silicone coatings, designed to reflect radiant heat and offer insulation against extreme temperatures. Both types employ specialized technologies like fiber reinforcement and thermal barriers to enhance durability and performance in hazardous environments.
Common Applications for Cut-Resistant Gloves
Cut-resistant gloves are commonly used in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and food processing, where workers handle sharp tools or materials to prevent lacerations and injuries. These gloves provide essential protection for tasks involving glass handling, metal fabrication, and assembly lines with cutting equipment. Their design emphasizes durability and dexterity, enabling safe manipulation of sharp objects while maintaining comfort and grip.
Typical Uses for Heat-Resistant Gloves
Heat-resistant gloves are typically used in industries involving high-temperature environments, such as metal forging, glass handling, and welding operations. These gloves provide essential protection against burns and heat exposure, enabling workers to safely handle hot tools, machinery, and materials. They are also common in food processing and industrial kitchens where workers deal with ovens, grills, and hot surfaces.
Safety Standards and Certifications
Cut-resistant gloves must comply with ANSI/ISEA 105 or EN 388 standards, ensuring protection against mechanical risks such as cuts and abrasions. Heat-resistant gloves are certified under standards like EN 407 or ASTM F1060, which assess resistance to thermal hazards including high temperatures and flames. Selecting gloves with relevant safety certifications guarantees compliance and optimal protection tailored to specific industrial hazards.
Choosing the Right Glove for Your Workplace
Cut-resistant gloves provide protection against sharp objects such as knives and metal shards, using materials like Kevlar, Dyneema, or steel fibers to ensure durability in high-risk environments. Heat-resistant gloves, made from materials like silicone, aluminized fabric, or leather, are designed to shield hands from burns, hot surfaces, and flames commonly encountered in welding, foundries, and kitchens. Selecting the right glove depends on the specific hazards present, prioritizing cut resistance for sharp-edge tasks and heat resistance for thermal protection to optimize workplace safety and compliance.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Cut-resistant gloves typically offer superior durability against sharp objects, maintaining integrity through repeated abrasion and cutting tasks, while heat-resistant gloves focus on withstanding high temperatures and may degrade faster with continuous exposure to intense heat. Maintenance of cut-resistant gloves often involves removing debris and inspecting for cuts or tears, whereas heat-resistant gloves require careful cleaning to avoid compromising thermal insulation and frequent checks for burns or heat damage. Selecting gloves based on the specific industrial environment ensures optimal longevity and protection, balancing durability demands with proper maintenance routines.
Cost Comparison and Value Analysis
Cut-resistant gloves generally offer a cost-effective solution for protection against sharp objects, with prices ranging from $10 to $30 per pair, while heat-resistant gloves, designed for high-temperature environments, typically cost between $20 and $60 per pair due to specialized materials like Kevlar and aluminized fabrics. Evaluating the value involves considering the specific workplace hazards; cut-resistant gloves maximize safety and durability in handling sharp tools, whereas heat-resistant gloves provide essential protection in foundries or welding operations, justifying their higher price points. Investing in gloves tailored to the primary risk ensures optimal safety performance and cost efficiency, reducing injury-related expenses and downtime.
User Comfort and Fit Factors
Cut-resistant gloves typically offer a snug fit with flexibility, allowing enhanced dexterity and tactile sensitivity, critical for precise tasks. Heat-resistant gloves prioritize insulation and often have a thicker design, which can reduce comfort and limit hand movement during extended use. Selecting gloves requires balancing protection level with ergonomic fit to ensure user comfort and effective performance in specific hazardous environments.
Cut-resistant gloves vs Heat-resistant gloves Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com