Design Freeze marks the point in medical device development when all design specifications are finalized and no further changes are allowed to ensure consistency in production. Design Lock occurs later, confirming that the design has passed all validations, regulatory reviews, and is approved for manufacturing release. Understanding the distinction between Design Freeze and Design Lock is crucial for efficient project management and compliance in medical device manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
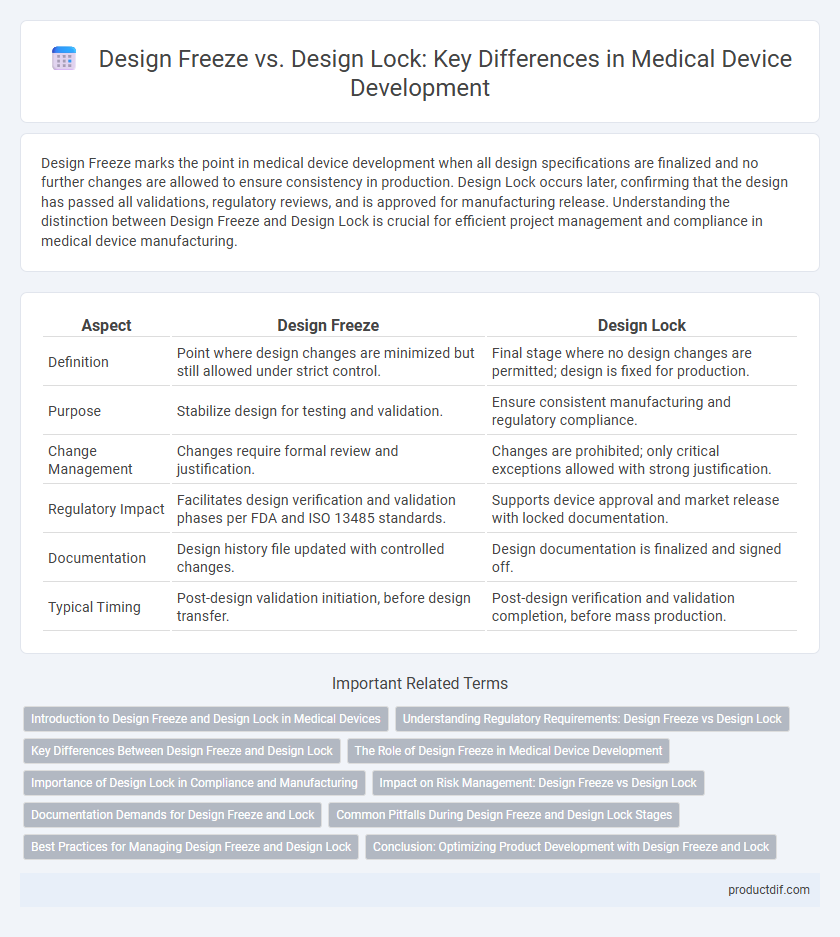
| Aspect | Design Freeze | Design Lock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Point where design changes are minimized but still allowed under strict control. | Final stage where no design changes are permitted; design is fixed for production. |
| Purpose | Stabilize design for testing and validation. | Ensure consistent manufacturing and regulatory compliance. |
| Change Management | Changes require formal review and justification. | Changes are prohibited; only critical exceptions allowed with strong justification. |
| Regulatory Impact | Facilitates design verification and validation phases per FDA and ISO 13485 standards. | Supports device approval and market release with locked documentation. |
| Documentation | Design history file updated with controlled changes. | Design documentation is finalized and signed off. |
| Typical Timing | Post-design validation initiation, before design transfer. | Post-design verification and validation completion, before mass production. |
Introduction to Design Freeze and Design Lock in Medical Devices
Design Freeze in medical device development marks the point at which the device's design specifications are finalized and no further changes are allowed, ensuring consistent documentation and regulatory compliance. Design Lock follows as a state where final design outputs are secured, preventing any alteration during manufacturing and validation phases to maintain product integrity. Both concepts are critical for managing quality, reducing risks, and meeting FDA and ISO regulatory requirements in medical device production.
Understanding Regulatory Requirements: Design Freeze vs Design Lock
Design Freeze and Design Lock are critical concepts in medical device development, reflecting distinct regulatory milestones that ensure product safety and compliance. Design Freeze marks the point where design outputs are finalized, guaranteeing all specifications meet stringent FDA and ISO 13485 standards before production. Design Lock, often tied to regulatory submission, confirms no further changes are permitted without formal review, ensuring traceability and adherence to Quality System Regulations (QSR) throughout manufacturing and post-market surveillance.
Key Differences Between Design Freeze and Design Lock
Design Freeze in medical device development marks the point where all design specifications are finalized and no further changes are permitted, ensuring regulatory compliance and stability before prototyping. Design Lock, on the other hand, refers to the stage where the design is locked for production, with manufacturing processes and tooling fixed to guarantee consistency and quality control. The key difference lies in Design Freeze focusing on design finalization, while Design Lock emphasizes readiness for mass production and process validation.
The Role of Design Freeze in Medical Device Development
Design Freeze in medical device development serves as a critical milestone that halts further design modifications, ensuring stability and consistency before moving into production and regulatory submission phases. This phase minimizes risks of costly changes and maintains strict compliance with FDA requirements and ISO 13485 standards. Establishing Design Freeze early helps streamline validation, verification, and quality control processes integral to successful device approval and market launch.
Importance of Design Lock in Compliance and Manufacturing
Design Lock is crucial in medical device development because it signifies the finalized state of the design, ensuring all specifications meet regulatory compliance requirements. This stage minimizes risks by preventing further changes that could introduce errors or non-conformities during manufacturing. Securing Design Lock enhances traceability and consistency, which are essential for approval by agencies like the FDA and for maintaining quality control throughout production.
Impact on Risk Management: Design Freeze vs Design Lock
Design Freeze solidifies all design specifications, ensuring comprehensive risk management by facilitating thorough hazard identification and mitigation before production. Design Lock finalizes design elements after validation, emphasizing control of residual risks and supporting compliance with regulatory requirements. Both practices enhance patient safety and device reliability by minimizing design changes that could introduce unforeseen risks.
Documentation Demands for Design Freeze and Lock
Design Freeze requires comprehensive documentation including finalized design specifications, test results, and validation reports to ensure all design aspects are fully defined and approved before proceeding. Design Lock demands stricter documentation control encompassing change control logs, regulatory compliance records, and traceability matrices to maintain design integrity during manufacturing. Both stages emphasize meticulous record-keeping to meet FDA and ISO regulatory standards for medical device development.
Common Pitfalls During Design Freeze and Design Lock Stages
Common pitfalls during the design freeze stage include inadequate verification of design specifications and overlooking regulatory compliance requirements, leading to costly revisions. In the design lock phase, failing to incorporate user feedback and insufficient risk management can result in functionality issues and delayed market approval. Both stages require rigorous documentation and cross-functional collaboration to ensure medical device safety and performance standards are met.
Best Practices for Managing Design Freeze and Design Lock
Effective management of design freeze and design lock in medical device development ensures regulatory compliance and minimizes risk during product finalization. Best practices include thorough verification and validation of design inputs, engaging cross-functional teams for consensus, and maintaining comprehensive documentation to support audit readiness. Implementing controlled change management processes after design freeze or lock preserves product integrity and facilitates smoother FDA submissions.
Conclusion: Optimizing Product Development with Design Freeze and Lock
Design Freeze marks the point where product specifications are finalized to prevent scope changes, ensuring stability in the medical device development process. Design Lock further enhances this by controlling configuration and restricting unauthorized modifications, which supports regulatory compliance and quality assurance. Combining Design Freeze with Design Lock optimizes product development by reducing risks, accelerating time-to-market, and maintaining consistent documentation for audits and approvals.
Design Freeze vs Design Lock Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com