Single-phase motors are commonly used in residential and light commercial applications due to their simplicity and lower cost, providing power through a single alternating current phase. Three-phase motors deliver more consistent torque and higher efficiency, making them ideal for industrial and heavy-duty applications with balanced power distribution. Selecting the appropriate motor depends on factors like power requirements, load characteristics, and availability of electrical infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
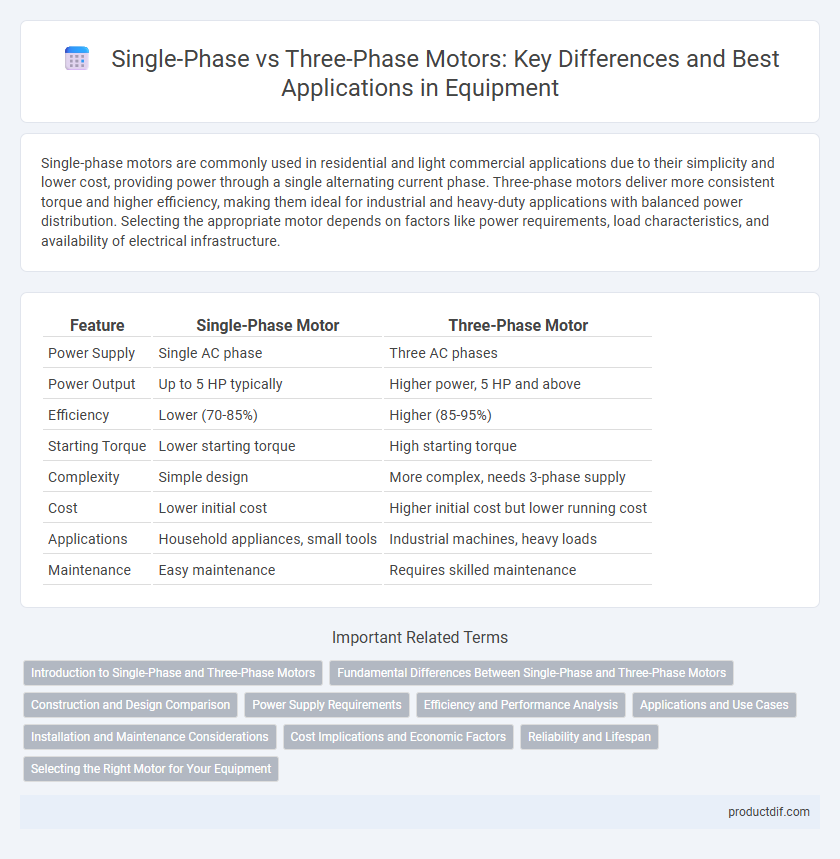
| Feature | Single-Phase Motor | Three-Phase Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Single AC phase | Three AC phases |
| Power Output | Up to 5 HP typically | Higher power, 5 HP and above |
| Efficiency | Lower (70-85%) | Higher (85-95%) |
| Starting Torque | Lower starting torque | High starting torque |
| Complexity | Simple design | More complex, needs 3-phase supply |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but lower running cost |
| Applications | Household appliances, small tools | Industrial machines, heavy loads |
| Maintenance | Easy maintenance | Requires skilled maintenance |
Introduction to Single-Phase and Three-Phase Motors
Single-phase motors operate on a single alternating current (AC) power source, making them suitable for residential and light commercial applications with lower power demands. Three-phase motors run on three separate AC currents, delivering constant power and higher efficiency, which is ideal for industrial and heavy-duty equipment. Understanding the electrical configuration and power requirements is crucial when selecting between single-phase and three-phase motors for specific equipment needs.
Fundamental Differences Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Motors
Single-phase motors operate on a single alternating current (AC) phase, typically used for low-power applications and residential equipment, whereas three-phase motors utilize three AC phases, providing higher power efficiency and smoother operation. The fundamental difference lies in the motor's construction and power supply: single-phase motors require a starting mechanism like a capacitor or auxiliary winding, while three-phase motors produce a rotating magnetic field naturally without extra components. Three-phase motors offer better torque output, improved efficiency, and reduced vibration, making them suitable for industrial machinery and heavy-duty equipment.
Construction and Design Comparison
Single-phase motors typically feature two main windings--start and run--along with a centrifugal switch or capacitor to initiate operation, making their construction simpler and more compact compared to three-phase motors. Three-phase motors consist of three separate windings placed 120 degrees apart on the stator, producing a rotating magnetic field that enables smoother and more efficient operation while also offering greater power density. The robust and balanced design of three-phase motors leads to reduced vibration and improved torque characteristics compared to the relatively unbalanced magnetic fields in single-phase motors.
Power Supply Requirements
Single-phase motors operate on a single alternating current (AC) power source, typically 110-130V or 220-240V, suitable for residential and light commercial applications with lower power demands. Three-phase motors require a three-phase power supply, usually 208V, 380-480V, or higher, providing a more efficient and stable power flow ideal for industrial and heavy-duty machinery. The three-phase system reduces power pulsations and provides consistent torque, making it essential for equipment with high starting torque and continuous operation needs.
Efficiency and Performance Analysis
Single-phase motors typically exhibit lower efficiency and reduced performance compared to three-phase motors due to their simpler winding design and torque production. Three-phase motors provide smoother operation, higher power density, and greater reliability, resulting in improved energy efficiency and consistent performance in industrial applications. Energy consumption analysis shows that three-phase motors can achieve up to 20-30% better efficiency under similar load conditions.
Applications and Use Cases
Single-phase motors are commonly used in residential appliances, small workshops, and light-duty machinery due to their compatibility with standard household electrical supply. Three-phase motors are preferred in industrial settings, heavy machinery, and large HVAC systems because they provide higher efficiency, greater torque, and smoother operation under load. Applications such as conveyor belts, pumps, and compressors benefit from the robust power delivery and reliability of three-phase motors.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Single-phase motors are simpler to install with fewer wiring requirements, making them suitable for residential and small-scale applications, while three-phase motors demand complex wiring but offer higher efficiency and power for industrial settings. Maintenance of single-phase motors often involves checking capacitors and brushes, whereas three-phase motors require regular inspection of windings and rotor balancing to ensure optimal performance. Choosing between the two depends on the application's power needs, installation complexity, and long-term maintenance capacity.
Cost Implications and Economic Factors
Single-phase motors generally have lower upfront costs and simpler installation requirements, making them cost-effective for residential and light commercial use. Three-phase motors offer higher efficiency and lower operational costs over time, which translates into significant energy savings and reduced maintenance expenses in industrial applications. Evaluating total cost of ownership, three-phase motors provide better long-term economic benefits despite a higher initial investment.
Reliability and Lifespan
Single-phase motors typically have a shorter lifespan due to increased heat generation and mechanical stress compared to three-phase motors, which offer enhanced reliability through balanced power delivery and smoother operation. The robust design of three-phase motors reduces vibration and wear, contributing to prolonged service life and lower maintenance requirements. Industries favor three-phase motors for critical applications requiring consistent performance and minimal downtime.
Selecting the Right Motor for Your Equipment
Selecting the right motor for your equipment depends heavily on load requirements and power supply availability; single-phase motors are ideal for low-power applications and residential equipment due to their simpler design and easier installation. Three-phase motors offer superior efficiency, higher power output, and smoother operation, making them essential for industrial machinery and heavy-duty equipment. Evaluating factors like starting torque, energy consumption, and operational costs ensures optimal motor performance and longevity in your specific application.
Single-phase motor vs three-phase motor Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com