Fixed automation offers high production speed and efficiency for large-scale manufacturing with repetitive tasks, using dedicated equipment configured for specific operations. Flexible automation provides adaptability to different products and processes through programmable machines, enabling quick changeovers and customization. Choosing between fixed and flexible automation depends on production volume, product variety, and cost considerations.
Table of Comparison
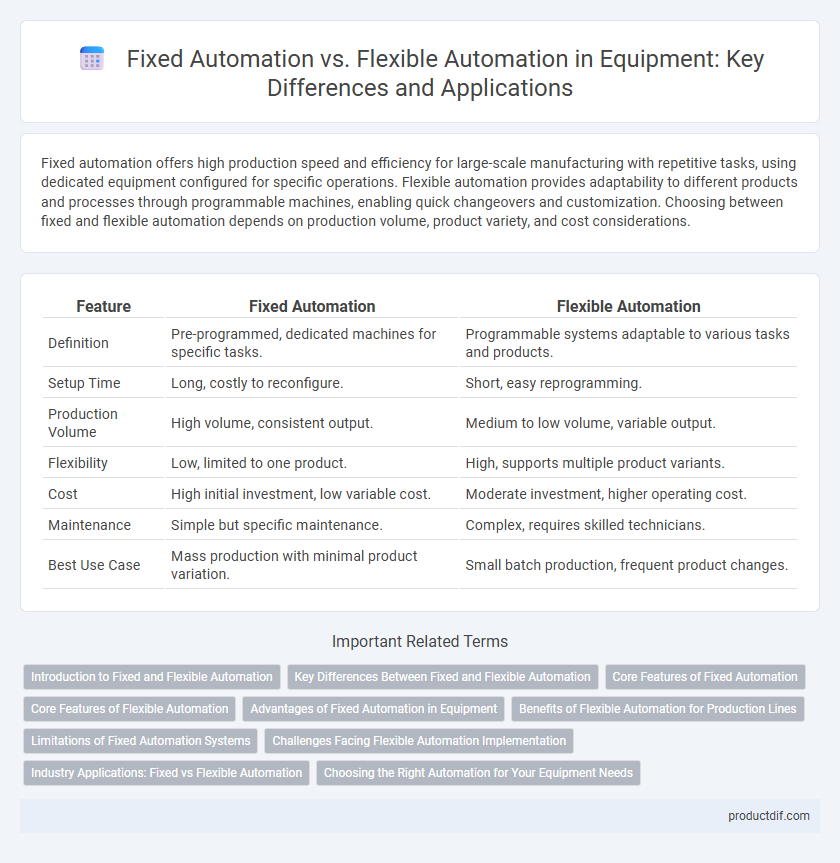
| Feature | Fixed Automation | Flexible Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-programmed, dedicated machines for specific tasks. | Programmable systems adaptable to various tasks and products. |
| Setup Time | Long, costly to reconfigure. | Short, easy reprogramming. |
| Production Volume | High volume, consistent output. | Medium to low volume, variable output. |
| Flexibility | Low, limited to one product. | High, supports multiple product variants. |
| Cost | High initial investment, low variable cost. | Moderate investment, higher operating cost. |
| Maintenance | Simple but specific maintenance. | Complex, requires skilled technicians. |
| Best Use Case | Mass production with minimal product variation. | Small batch production, frequent product changes. |
Introduction to Fixed and Flexible Automation
Fixed automation involves the use of specialized equipment designed for high-volume production with minimal variation in product design, ensuring high efficiency and low unit costs. Flexible automation utilizes programmable machines capable of performing multiple tasks, allowing manufacturers to rapidly switch between product types and respond to changing demands. Both automation types enhance productivity but differ significantly in adaptability and investment costs.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Flexible Automation
Fixed automation features specialized equipment designed for high-volume production with minimal variation, resulting in high efficiency but limited adaptability. Flexible automation employs programmable machines capable of handling diverse tasks, allowing quick changes in production processes to accommodate different products. The key differences lie in their scalability, with fixed automation excelling in consistency and speed, while flexible automation prioritizes versatility and responsiveness to market demands.
Core Features of Fixed Automation
Fixed automation is characterized by its high production rate and dedicated equipment designed for a specific set of tasks, commonly used in mass production environments. Core features include rigid machinery with a fixed sequence of operations, limited product variation, and minimal human intervention. This type of automation offers exceptional efficiency and consistency but lacks the adaptability to handle frequent changes in product design or production volume.
Core Features of Flexible Automation
Flexible automation features programmable machines and robots capable of processing multiple tasks without manual intervention, enhancing adaptability in production lines. It integrates computer control systems that allow quick reconfiguration for different product types, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency. This system supports real-time monitoring and data collection, enabling responsive adjustments and improved precision in manufacturing processes.
Advantages of Fixed Automation in Equipment
Fixed automation offers high production rates and excellent repeatability, making it ideal for mass-producing identical products with minimal variation. Equipment designed for fixed automation typically requires lower per-unit costs due to the efficient use of dedicated machinery and reduced cycle times. This method ensures consistent product quality and minimizes human intervention, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced labor costs.
Benefits of Flexible Automation for Production Lines
Flexible automation enhances production lines by allowing rapid adaptation to varying product designs and volumes without extensive downtime. It reduces labor costs through automated programming and reconfiguration, improving efficiency and minimizing human error. The scalability of flexible automation supports just-in-time manufacturing, increasing overall productivity and responsiveness to market demands.
Limitations of Fixed Automation Systems
Fixed automation systems are limited by their inability to adapt to product variations, making them unsuitable for low-volume or customizable manufacturing. High initial setup costs and inflexible machinery restrict responsiveness to market changes and product updates. Maintenance and reconfiguration require significant downtime, reducing overall operational efficiency in dynamic production environments.
Challenges Facing Flexible Automation Implementation
Flexible automation faces significant challenges such as high initial investment costs, complex system integration, and the need for advanced programming skills. Adapting to changing production requirements demands continuous updates and maintenance, increasing operational complexity. Limited standardization and the requirement for specialized technical expertise hinder widespread adoption in dynamic manufacturing environments.
Industry Applications: Fixed vs Flexible Automation
Fixed automation excels in high-volume manufacturing industries such as automotive and consumer electronics, where repetitive tasks and consistent product design demand high-speed and precise operations. Flexible automation is ideal for industries like aerospace and custom machinery manufacturing, enabling rapid changeover and adaptability to varying product specifications without extensive reconfiguration. The choice between fixed and flexible automation depends on production volume, product variety, and the need for operational agility in dynamic industrial environments.
Choosing the Right Automation for Your Equipment Needs
Fixed automation offers high production rates for large volume manufacturing with minimal flexibility, ideal for equipment designed for repetitive, standardized tasks. Flexible automation provides versatility to handle various products and rapid changeovers, making it suitable for equipment requiring adaptability and customization. Evaluating production volume, product variety, and changeover frequency is crucial to select the appropriate automation system that balances efficiency and investment cost.
Fixed automation vs Flexible automation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com