Heavy-duty equipment is designed for rigorous tasks and prolonged use, featuring robust construction and enhanced durability to withstand harsh environments. Light-duty equipment caters to less intensive operations, offering greater portability and ease of use but with limited power and load capacity. Choosing between heavy-duty and light-duty depends on the specific operational demands, budget, and frequency of use.
Table of Comparison
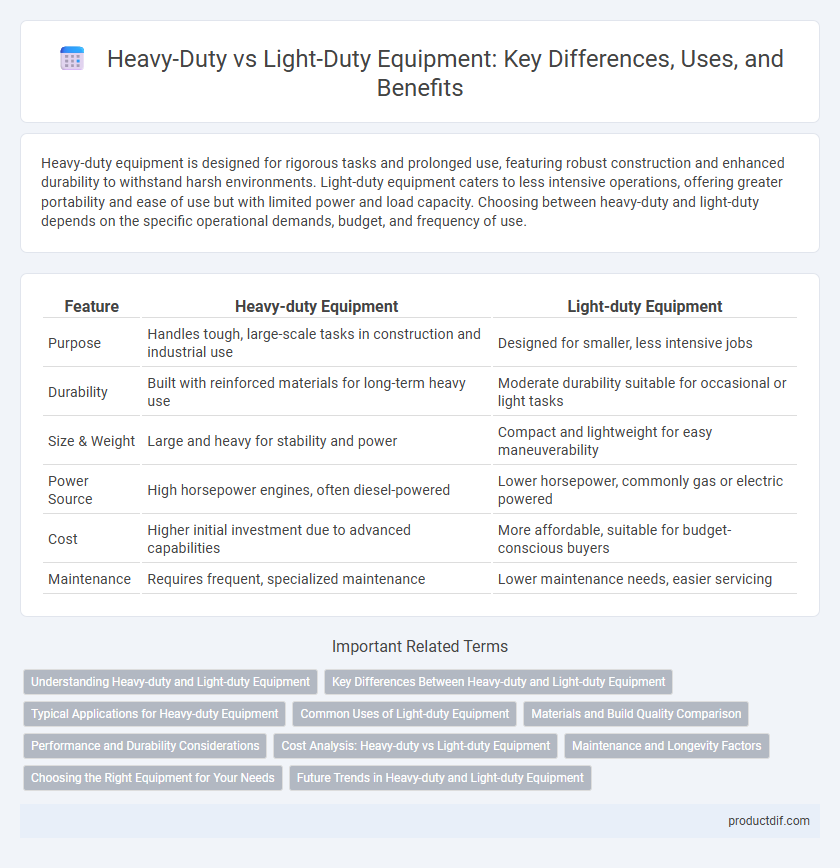
| Feature | Heavy-duty Equipment | Light-duty Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Handles tough, large-scale tasks in construction and industrial use | Designed for smaller, less intensive jobs |
| Durability | Built with reinforced materials for long-term heavy use | Moderate durability suitable for occasional or light tasks |
| Size & Weight | Large and heavy for stability and power | Compact and lightweight for easy maneuverability |
| Power Source | High horsepower engines, often diesel-powered | Lower horsepower, commonly gas or electric powered |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to advanced capabilities | More affordable, suitable for budget-conscious buyers |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent, specialized maintenance | Lower maintenance needs, easier servicing |
Understanding Heavy-duty and Light-duty Equipment
Heavy-duty equipment is designed for rigorous, continuous use in demanding industrial environments, featuring enhanced durability, higher load capacities, and robust components built to withstand extreme conditions. Light-duty equipment, in contrast, suits smaller scale tasks with lower weight and intensity, offering greater maneuverability and cost-efficiency for maintenance, landscaping, and residential projects. Choosing between heavy-duty and light-duty machinery depends on operational requirements, workload demands, and long-term performance expectations.
Key Differences Between Heavy-duty and Light-duty Equipment
Heavy-duty equipment is designed for high-capacity tasks, featuring robust construction, increased horsepower, and enhanced durability to handle intensive industrial or construction work. Light-duty equipment is intended for smaller-scale operations, offering greater maneuverability, lower weight, and reduced power consumption suitable for residential or light commercial use. Key differences include load capacity, engine power, durability, and typical applications, with heavy-duty equipment excelling in demanding environments and light-duty models optimized for efficiency and ease of use.
Typical Applications for Heavy-duty Equipment
Heavy-duty equipment is designed for intensive tasks such as construction, mining, and agriculture, where durability and power are critical. Examples include bulldozers, excavators, and large cranes used for earthmoving, material handling, and heavy lifting. These machines excel in demanding environments requiring high load capacity and continuous operation.
Common Uses of Light-duty Equipment
Light-duty equipment is commonly used for residential landscaping, small-scale construction projects, and routine maintenance tasks due to its ease of operation and portability. Tasks such as lawn mowing, garden tilling, and light material handling benefit from the maneuverability and lower power requirements of light-duty machinery. These tools are ideal for environments where precision and minimal surface impact are crucial, making them suitable for home use and light commercial applications.
Materials and Build Quality Comparison
Heavy-duty equipment typically features high-grade steel and reinforced components designed for maximum durability and resistance to wear in extreme conditions. Light-duty equipment uses lighter materials such as aluminum alloys or engineered plastics, prioritizing portability and ease of handling over ultimate strength. The build quality of heavy-duty tools ensures superior longevity and performance under intense stress, while light-duty counterparts are optimized for moderate tasks with less structural reinforcement.
Performance and Durability Considerations
Heavy-duty equipment delivers superior performance and durability, designed to handle intense workloads and harsh operating conditions with robust materials and reinforced components. Light-duty equipment suits smaller tasks, offering ease of maneuverability and energy efficiency but lacks the resilience needed for continuous heavy use, leading to faster wear and increased maintenance. Choosing between heavy-duty and light-duty relies on balancing performance demands with durability requirements to optimize operational efficiency and lifespan.
Cost Analysis: Heavy-duty vs Light-duty Equipment
Heavy-duty equipment demands higher initial investment but offers durability and longer service life, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs. Light-duty equipment entails lower upfront expenses and easier maneuverability, ideal for short-term projects or lower workload intensity. Cost analysis should evaluate project scale, frequency, and long-term return on investment to determine the most economical choice.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Heavy-duty equipment requires robust maintenance schedules due to its intensive operational demands, including frequent inspections and specialized parts replacement to ensure durability. Light-duty machinery benefits from simpler upkeep routines, often involving routine checks and basic servicing, contributing to extended service life under less strenuous conditions. Proper maintenance tailored to each type significantly influences longevity, with heavy-duty equipment designed for prolonged use in harsh environments and light-duty equipment optimized for efficiency in lighter tasks.
Choosing the Right Equipment for Your Needs
Heavy-duty equipment is designed for intense, continuous use in demanding environments, offering higher durability and greater power for construction, mining, or industrial tasks. Light-duty equipment suits smaller-scale projects with less frequent use, providing ease of maneuverability, lower operational costs, and sufficient performance for residential or maintenance work. Selecting the right equipment depends on assessing workload intensity, project complexity, budget constraints, and required operational efficiency to maximize productivity and equipment lifespan.
Future Trends in Heavy-duty and Light-duty Equipment
Future trends in heavy-duty equipment emphasize electrification and autonomous technology to enhance efficiency and reduce emissions in construction and mining industries. Light-duty equipment development focuses on compact, battery-powered models with smart connectivity for urban and residential tasks. Both sectors are increasingly integrating IoT and AI-driven maintenance systems to improve operational uptime and reduce lifecycle costs.
Heavy-duty vs Light-duty Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com