High-capacity pet equipment offers durability and extended use for active or larger pets, ensuring they accommodate greater weight and volume. Low-capacity options are ideal for small or less active pets, providing lightweight and compact solutions tailored to their needs. Choosing the right capacity enhances comfort, safety, and functionality for your pet's specific lifestyle.
Table of Comparison
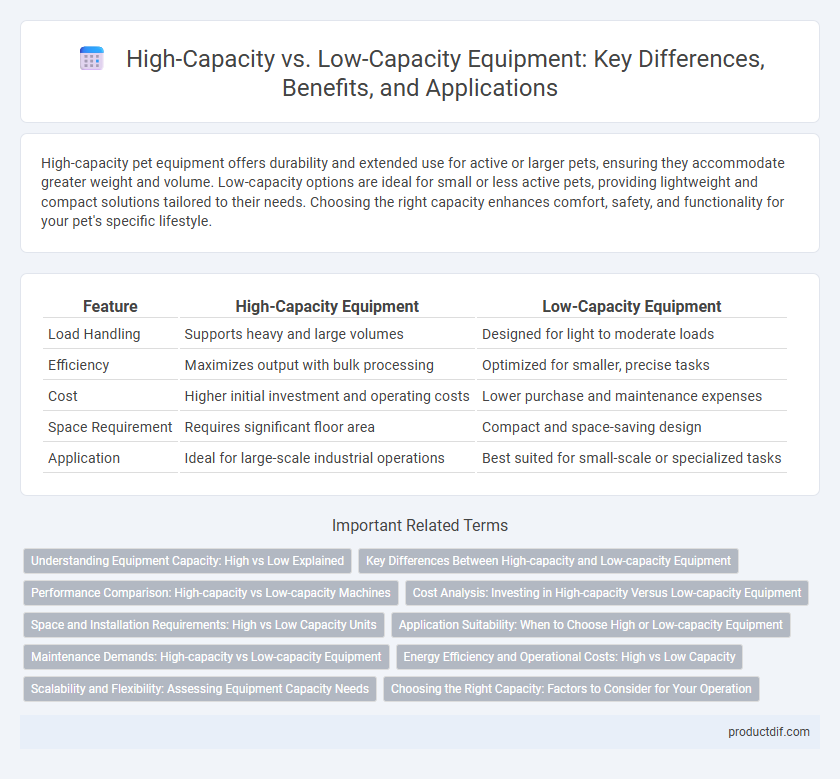
| Feature | High-Capacity Equipment | Low-Capacity Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Load Handling | Supports heavy and large volumes | Designed for light to moderate loads |
| Efficiency | Maximizes output with bulk processing | Optimized for smaller, precise tasks |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and operating costs | Lower purchase and maintenance expenses |
| Space Requirement | Requires significant floor area | Compact and space-saving design |
| Application | Ideal for large-scale industrial operations | Best suited for small-scale or specialized tasks |
Understanding Equipment Capacity: High vs Low Explained
Equipment capacity directly influences operational efficiency and output, with high-capacity machines designed to handle larger volumes and more intensive workloads, suitable for industrial-scale production. Low-capacity equipment offers precision and cost-effectiveness for smaller tasks or limited spaces, ideal for specialized or small-batch operations. Evaluating specific project requirements and resource availability ensures the optimal balance between capacity, performance, and cost-effectiveness in equipment selection.
Key Differences Between High-capacity and Low-capacity Equipment
High-capacity equipment is designed to handle larger volumes or heavier loads, offering greater efficiency and productivity in industrial and commercial applications. Low-capacity equipment, by contrast, is suited for smaller-scale tasks, prioritizing precision and lower energy consumption. The key differences lie in their power output, size, durability, and operational cost, impacting suitability depending on the scope and scale of the project.
Performance Comparison: High-capacity vs Low-capacity Machines
High-capacity machines deliver superior performance by handling larger workloads and maintaining consistent operational speeds, resulting in increased productivity and reduced downtime. Low-capacity machines, though less efficient for extensive tasks, offer greater flexibility and lower energy consumption, ideal for smaller-scale operations. Evaluating machine capacity against specific production demands ensures optimal equipment utilization and cost-effectiveness.
Cost Analysis: Investing in High-capacity Versus Low-capacity Equipment
High-capacity equipment requires a larger initial investment but offers lower operational costs per unit, making it cost-effective for high-volume production. Low-capacity equipment has a lower upfront cost but can lead to higher expenses over time due to increased maintenance and inefficiency. A detailed cost analysis must consider factors like production scale, maintenance schedules, and energy consumption to determine the optimal equipment choice.
Space and Installation Requirements: High vs Low Capacity Units
High-capacity equipment demands significantly more space due to larger dimensions and heavier weight, requiring reinforced flooring and expanded clearance for maintenance access. In contrast, low-capacity units occupy minimal space and offer flexible installation options, often fitting into compact or confined areas without structural modifications. Proper assessment of installation requirements ensures optimized workflow and prevents costly retrofits during system upgrades.
Application Suitability: When to Choose High or Low-capacity Equipment
High-capacity equipment is ideal for large-scale industrial operations requiring continuous, heavy-duty performance, such as manufacturing plants and mining sites where high throughput and efficiency are critical. Low-capacity equipment suits smaller-scale applications like boutique workshops or short-duration projects, offering greater flexibility and lower operational costs. Selecting the appropriate capacity depends on factors such as production volume, project duration, space constraints, and budget considerations.
Maintenance Demands: High-capacity vs Low-capacity Equipment
High-capacity equipment requires more frequent and intensive maintenance due to increased wear and tear from handling larger workloads and extended operational hours. Low-capacity equipment generally demands less frequent servicing, resulting in lower maintenance costs and downtime. Proper predictive maintenance strategies can optimize the performance and longevity of both high-capacity and low-capacity machinery.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Costs: High vs Low Capacity
High-capacity equipment generally offers increased energy efficiency by operating at optimal load levels, reducing wasted power compared to low-capacity units frequently running at maximum capacity. However, high-capacity machines often require higher upfront investment and maintenance expenses, influencing overall operational costs. Low-capacity equipment might have lower initial costs but usually leads to higher energy consumption and increased expenses over time due to less efficient performance under heavy workloads.
Scalability and Flexibility: Assessing Equipment Capacity Needs
High-capacity equipment offers superior scalability to support growing operational demands, ensuring seamless integration with expanding workflows. Low-capacity equipment provides greater flexibility for smaller-scale or variable tasks, optimizing cost-efficiency without compromising performance. Evaluating equipment capacity needs requires balancing forecasted growth with current operational requirements to maximize productivity and investment returns.
Choosing the Right Capacity: Factors to Consider for Your Operation
Selecting the appropriate equipment capacity depends on operational demand, budget constraints, and space availability. High-capacity machines increase productivity and reduce downtime but require higher initial investment and maintenance costs. Low-capacity options are cost-effective for smaller scale tasks, offering flexibility and lower energy consumption, making them ideal for limited or variable workloads.
High-capacity vs Low-capacity Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com