Electrostatic discharge protection safeguards sensitive electronic components from sudden static electricity spikes by dissipating built-up charges before they can cause damage. Surge protection defends equipment against voltage spikes, often resulting from lightning strikes or power fluctuations, by diverting excess current away from the device. Both protections are essential for maintaining the integrity and longevity of electronic equipment but target different types of electrical threats.
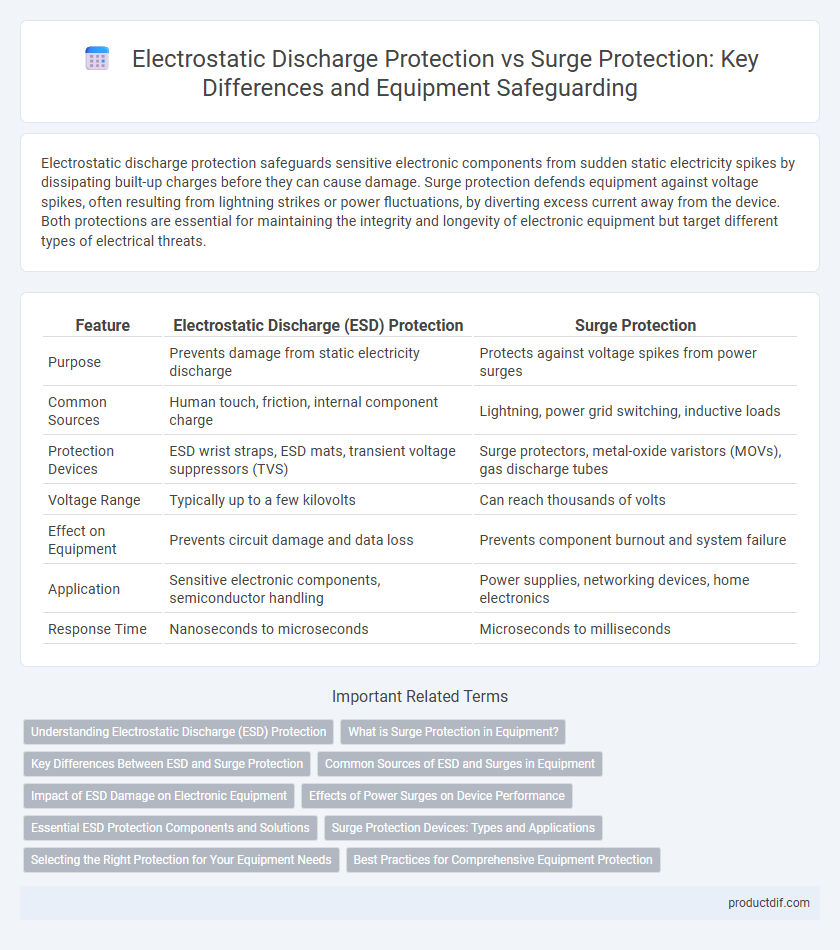
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection | Surge Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents damage from static electricity discharge | Protects against voltage spikes from power surges |
| Common Sources | Human touch, friction, internal component charge | Lightning, power grid switching, inductive loads |
| Protection Devices | ESD wrist straps, ESD mats, transient voltage suppressors (TVS) | Surge protectors, metal-oxide varistors (MOVs), gas discharge tubes |
| Voltage Range | Typically up to a few kilovolts | Can reach thousands of volts |
| Effect on Equipment | Prevents circuit damage and data loss | Prevents component burnout and system failure |
| Application | Sensitive electronic components, semiconductor handling | Power supplies, networking devices, home electronics |
| Response Time | Nanoseconds to microseconds | Microseconds to milliseconds |
Understanding Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection safeguards sensitive electronic equipment from sudden, high-voltage static electricity bursts by diverting or neutralizing the charge before it damages components. ESD protection typically involves grounding straps, conductive mats, and specialized coatings that prevent static buildup and ensure device integrity. Understanding ESD protection is critical for maintaining the reliability and longevity of semiconductor devices, printed circuit boards, and integrated circuits in various industrial applications.
What is Surge Protection in Equipment?
Surge protection in equipment involves safeguarding electrical devices from voltage spikes caused by transient surges or lightning strikes, which can damage sensitive components. Surge protectors divert excess voltage to the ground, ensuring the stable operation of equipment and preventing costly failures. Effective surge protection extends the lifespan of electronics by maintaining voltage within safe limits during unexpected power fluctuations.
Key Differences Between ESD and Surge Protection
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection primarily shields sensitive electronic components from sudden, high-voltage static discharges caused by human contact or nearby charged objects, focusing on low-energy, fast pulses. Surge protection, on the other hand, safeguards equipment from high-energy voltage spikes generated by external sources such as lightning strikes or power grid fluctuations, addressing longer-duration, larger current surges. Key differences include the magnitude and origin of the electrical disturbance, with ESD protection targeting low-current, short-duration discharges and surge protection designed for high-current, extended-duration overvoltages.
Common Sources of ESD and Surges in Equipment
Common sources of electrostatic discharge (ESD) in equipment include human handling, friction between materials, and dielectric breakdown. Surge protection is primarily challenged by lightning strikes, power grid switching, and switching inductive loads within electrical circuits. Understanding these sources helps in implementing effective protective measures to prevent damage and ensure equipment reliability.
Impact of ESD Damage on Electronic Equipment
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection is critical for safeguarding sensitive electronic components from sudden high-voltage electrostatic events that can cause immediate or latent damage, leading to component failure or degraded performance. Unlike surge protection, which guards against voltage spikes from external power fluctuations, ESD protection targets localized, fast transient discharges often originating from human contact or triboelectric effects. Effective ESD mitigation minimizes costly equipment downtime and enhances device reliability by preventing microchip corrosion, gate oxide breakdown, and circuit malfunction.
Effects of Power Surges on Device Performance
Power surges can cause immediate or latent damage to electronic equipment by overwhelming sensitive components, leading to performance degradation, data corruption, or complete failure. Electrostatic discharge protection primarily guards against sudden, short bursts of static electricity, preventing damage to microchips and circuit paths. Surge protection devices mitigate the effects of voltage spikes from power surges, preserving device functionality and extending equipment lifespan by absorbing or redirecting excessive electrical energy.
Essential ESD Protection Components and Solutions
Essential ESD protection components include wrist straps, grounding mats, and ionizers that prevent harmful static discharge by safely dissipating electric charges. Surge protection solutions involve devices like transient voltage suppressors (TVS), metal-oxide varistors (MOVs), and gas discharge tubes (GDTs) designed to shield equipment from sudden voltage spikes. Integrating both ESD and surge protection elements ensures comprehensive safeguarding of sensitive electronic equipment against static electricity damage and power surges.
Surge Protection Devices: Types and Applications
Surge Protection Devices (SPDs) are essential for safeguarding electrical equipment from voltage spikes caused by lightning strikes, switching operations, or transient surges in power lines. Common types of SPDs include Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs), Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs), and Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) diodes, each suited to specific applications based on response time and energy absorption capacity. MOVs are widely used in residential and industrial settings for general surge absorption, GDTs provide high-energy surge mitigation in telecommunications, and TVS diodes offer fast response protection in sensitive electronic circuits.
Selecting the Right Protection for Your Equipment Needs
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection is essential for sensitive electronic components vulnerable to sudden static electricity bursts, while surge protection guards against voltage spikes caused by lightning or power grid fluctuations. Selecting the right protection involves assessing your equipment's susceptibility to ESD events and electrical surges, ensuring compatibility with device specifications and operating environments. Implementing tailored ESD mats, wrist straps, or transient voltage surge suppressors (TVSS) optimizes equipment lifespan and maintains operational integrity.
Best Practices for Comprehensive Equipment Protection
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection and surge protection serve distinct but complementary roles in safeguarding sensitive equipment from electrical damage. Implementing high-quality ESD wrist straps, mats, and ionizers prevents static buildup, while surge protectors and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) shield devices from voltage spikes caused by lightning or switching events. Combining these solutions with proper grounding, regular maintenance, and adherence to industry standards ensures comprehensive protection against both ESD and power surges.
Electrostatic discharge protection vs surge protection Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com